生产者消费者模式是一个典型的并发编程需要考虑的问题, 通过一个中间容器来解决生产者和消费者的强耦合特性。 生产者和消费者彼此之间不直接通讯,而通过阻塞队列来进行通讯,所以生产者生产完数据之后不用等待消费者处理,直接扔给阻塞队列,消费者不找生产者要数据,而是直接从阻塞队列里取,阻塞队列就相当于一个缓冲区,平衡了生产者和消费者的处理能力
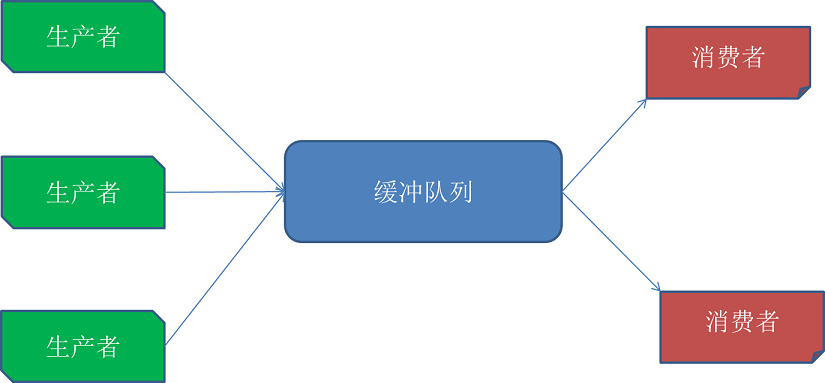
其特点大致如下:
- 一组生产者生产数据到缓冲区中,另外一组消费者从缓冲区中取数据
- 如果缓冲区已经满了,则生产者线程阻塞,等待队列有空间存放数据
- 如果缓冲区为空,那么消费者线程阻塞,等待队列有数据进来
- 生产者往缓冲去写入数据的同时,消费者可以同时拿取数据
- 缓冲区数据先入先出
码农的世界里面向来是Talk is cheap, show me the code.
笔者写了一个小demo,缓冲区用的是BlockingQueue 接口的实现类,java.util.concurrent包下具有ArrayBlockingQueue, DelayQueue, LinkedBlockingQueue, PriorityBlockingQueue, SynchronousQueue.
示例中使用的是ArrayBlockingQueue, 一个数组实现的有界阻塞队列。有界也就意味着,它不能够存储无限多数量的元素。它有一个同一时间能够存储元素数量的上限。你可以在对其初始化的时候设定这个上限,但之后就无法对这个上限进行修改了。一旦初始化,大小就无法修改。

package demo; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; public class Producer implements Runnable { private ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> myQueue; private Random random = new Random(); public ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> getMyQueue() { return myQueue; } public void setMyQueue(ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> myQueue) { this.myQueue = myQueue; } @Override public void run() { int tmp =-1; try { while (true) { long millis = (long) (Math.random() * 6000); // 模拟耗时计算 Thread.sleep(millis); int element = random.nextInt(2000); myQueue.put(element); tmp = myQueue.size(); String msg = Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is producing data : " + element; msg += " "; msg += "Current queue size : " + tmp; System.out.println(msg); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }

package demo; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; public class Consumer implements Runnable { private ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> myQueue; public ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> getMyQueue() { return myQueue; } public void setMyQueue(ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> myQueue) { this.myQueue = myQueue; } @Override public void run() { int element = -1; int tmp = -1; try { while (true) { long millis = (long) (Math.random() * 5000); // 模拟复杂计算 Thread.sleep(millis); element = myQueue.take(); tmp = myQueue.size(); // 延迟一毫秒写日志 Thread.sleep(1); String msg = Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is consuming data : " + element; msg += " "; msg += "Current queue size : " + tmp; System.out.println(msg); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }

package demo; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Main { private static final int SIZE = 10; private static ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(SIZE); public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub ExecutorService producerPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); ExecutorService consumerPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); Producer p1 = new Producer(); p1.setMyQueue(queue); Producer p2 = new Producer(); p2.setMyQueue(queue); Producer p3 = new Producer(); p3.setMyQueue(queue); producerPool.execute(p1); producerPool.execute(p2); producerPool.execute(p3); Consumer c1 = new Consumer(); c1.setMyQueue(queue); Consumer c2 = new Consumer(); c2.setMyQueue(queue); consumerPool.execute(c1); consumerPool.execute(c2); //consumerPool.shutdown(); //producerPool.shutdown(); } }
