1、什么是VUEX
Vuex是管理vue的组件状态的工具。
个人理解:vuex是管理组件之间通信的一个插件。
2、为什么要用VUEX
我们知道组件之间是独立的,组件之间想要实现通信,我目前知道的就只有props选项,但这也仅限于父组件和子组件之间的通信。如果兄弟组件之间想要实现通信呢?嗯..,方法应该有。抛开怎么实现的问题,试想一下,当做中大型项目时,面对一大堆组件之间的通信,还有一大堆的逻辑代码,会不会很抓狂??那为何不把组件之间共享的数据给“拎”出来,在一定的规则下管理这些数据呢? 这就是Vuex的基本思想了。
3、VUEX核心
他有4个核心选项:state mutations getters actions

3.1. State
用来存放组件之间共享的数据。他跟组件的data选项类似,只不过data选项是用来存放组件的私有数据。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<script src="./js/vuex.js"></script>
<script src="./js/vue2.0.js"></script>
<body>
<div id="app">
<hello></hello>
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.use(Vuex);
var myStore = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
//存放组件之间共享的数据
name:"jjk"
},
mutations:{
//显式的更改state里的数据
},
getters:{
//过滤state数据
},
actions:{
//
}
});
Vue.component('hello',{
template:"<p>{{name}}</p>",
computed: {
name:function(){
return this.$store.state.name
}
},
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
}
})
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
name:"dk"
},
store:myStore,
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
}
})
</script>
</html>

3.2. mutations
前面讲到的都是如何获取state的数据,那如何把数据存储到state中呢?在 Vuex store 中,实际改变 状态(state) 的唯一方式是通过 提交(commit) 一个 mutation。 mutations下的函数接收state作为参数,接收一个叫做payload(载荷)的东东作为第二个参数,这个东东是用来记录开发者使用该函数的一些信息,比如说提交了什么,提交的东西是用来干什么的,包含多个字段,所以载荷一般是对象(其实这个东西跟git的commit很类似)还有一点需要注意:mutations方法必须是同步方法!
具体看实例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<script src="./js/vuex.js"></script>
<script src="./js/vue2.0.js"></script>
<body>
<div id="app">
<hello></hello>
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.use(Vuex);
var myStore = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
//存放组件之间共享的数据
name:"jjk",
age:18,
num:1
},
mutations:{
//显式的更改state里的数据
change:function(state,a){
// state.num++;
console.log(state.num += a);
}
},
getters:{
getAge:function(state){
return state.age;
}
},
actions:{
//
}
});
Vue.component('hello',{
template:"<p @click='changeNum'>姓名:{{name}} 年龄:{{age}} 次数:{{num}}</p>",
computed: {
name:function(){
return this.$store.state.name
},
age:function(){
return this.$store.getters.getAge
},
num:function(){
return this.$store.state.num
}
},
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
},
methods: {
changeNum: function(){
//在组件里提交
// this.num++;
this.$store.commit('change',10)
}
},
data:function(){
return {
// num:5
}
}
})
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
name:"dk"
},
store:myStore,
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
}
})
</script>
</html>
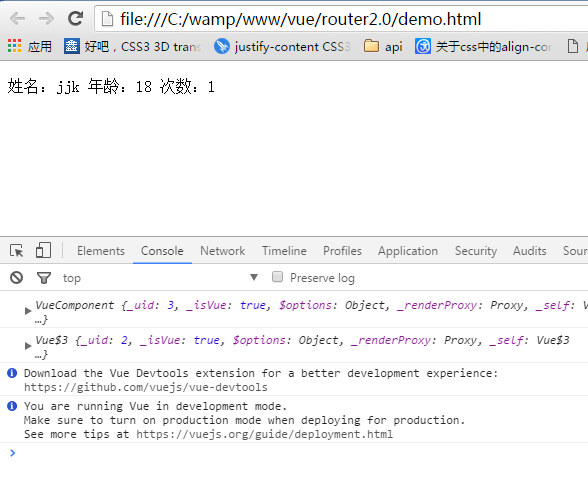
当点击p标签前,chrome中显示:
点击p标签后:
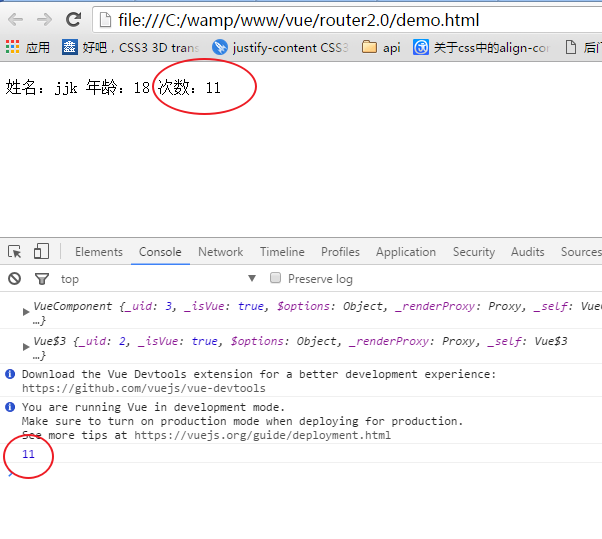
可以看出:更改state的数据并显示在组件中,有几个步骤:1. 在mutations选项里,注册函数 函数里面装逻辑代码。2.在组件里,this.$store.commit('change',payload) 注意:提交的函数名要一一对应 3.触发函数,state就会相应更改 4.在组件的计算属性里 this.$store.state 获取你想要得到的数据
3.3. getters
有时候,我们需要对state的数据进行筛选,过滤。这些操作都是在组件的计算属性进行的。如果多个组件需要用到筛选后的数据,那我们就必须到处重复写该计算属性函数;或者将其提取到一个公共的工具函数中,并将公共函数多处导入 - 两者都不太理想。如果把数据筛选完在传到计算属性里就不用那么麻烦了,getters就是干这个的,你可以把getters看成是store的计算属性。getters下的函数接收接收state作为第一个参数。那么,组件是如何获取经过getters过滤的数据呢? 过滤的数据会存放到$store.getters对象中。具体看一个例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<script src="./js/vuex.js"></script>
<script src="./js/vue2.0.js"></script>
<body>
<div id="app">
<hello></hello>
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.use(Vuex);
var myStore = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
//存放组件之间共享的数据
name:"jjk",
age:18
},
mutations:{
//显式的更改state里的数据
},
getters:{
getAge:function(state){
return state.age;
}
},
actions:{
//
}
});
Vue.component('hello',{
template:"<p>姓名:{{name}} 年龄:{{age}}</p>",
computed: {
name:function(){
return this.$store.state.name
},
age:function(){
return this.$store.getters.getAge
}
},
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
}
})
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
name:"dk"
},
store:myStore,
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
}
})
</script>
</html>

3.4. actions
既然mutations只能处理同步函数,我大js全靠‘异步回调’吃饭,怎么能没有异步,于是actions出现了...
actions和mutations的区别
1.Actions 提交的是 mutations,而不是直接变更状态。也就是说,actions会通过mutations,让mutations帮他提交数据的变更。
2.Action 可以包含任意异步操作。ajax、setTimeout、setInterval不在话下
再来看一下实例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<script src="./js/vuex.js"></script>
<script src="./js/vue2.0.js"></script>
<body>
<div id="app">
<hello></hello>
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.use(Vuex);
var myStore = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
//存放组件之间共享的数据
name:"jjk",
age:18,
num:1
},
mutations:{
//显式的更改state里的数据
change:function(state,a){
// state.num++;
console.log(state.num += a);
},
changeAsync:function(state,a){
console.log(state.num +=a);
}
},
getters:{
getAge:function(state){
return state.age;
}
},
actions:{
//设置延时
add:function(context,value){
setTimeout(function(){
//提交事件
context.commit('changeAsync',value);
},1000)
}
}
});
Vue.component('hello',{
template:`
<div>
<p @click='changeNum'>姓名:{{name}} 年龄:{{age}} 次数:{{num}}</p>
<button @click='changeNumAnsyc'>change</button>
</div>`,
computed: {
name:function(){
return this.$store.state.name
},
age:function(){
return this.$store.getters.getAge
},
num:function(){
return this.$store.state.num
}
},
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
},
methods: {
changeNum: function(){
//在组件里提交
// this.num++;
this.$store.commit('change',10)
},
//在组件里派发事件 当点击按钮时,changeNumAnsyc触发-->actions里的add函数被触发-->mutations里的changeAsync函数触发
changeNumAnsyc:function(){
this.$store.dispatch('add', 5);
}
},
data:function(){
return {
// num:5
}
}
})
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
name:"dk"
},
store:myStore,
mounted:function(){
console.log(this)
}
})
</script>
</html>
点击按钮一秒后,chrome中显示:
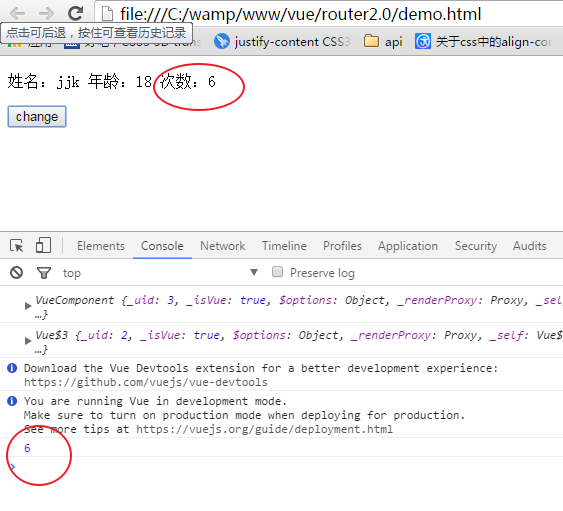
先整明白 context dispatch是什么东西:
context:context是与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的对象。可以通过context.state和context.getters来获取 state 和 getters。
dispatch:翻译为‘派发、派遣’的意思,触发事件时,dispatch就会通知actions(跟commit一样一样的)参数跟commit也是一样的。
action的大体流程:
- 在actions选项里添加函数(异步)并提交到对应的函数(在mutation选项里)中 context.commit('changeAsync',value);
actions:{
add:function(context,value){
setTimeout(function(){
context.commit('changeAsync',value);
},1000)
}
}
2. 在组件里: changeNumAnsyc:function(){this.$store.dispatch('add', 5);} 将dispatch“指向”actions选项里的函数
3、在mutations选项里,要有对应的函数 changeAsync:function(state,a){console.log(state.num +=a);}
3.5. 总结
各个类型的 API各司其职,mutation 只管存,你给我(dispatch)我就存;action只管中间处理,处理完我就给你,你怎么存我不管;Getter 我只管取,我不改的。 action放在了 methods 里面,说明我们应该把它当成函数来用(讲道理,钩子函数也应该可以的) mutation是写在store里面的,这说明,它就是个半成品,中间量,我们不应该在外面去操作它。getter写在了 computed 里面,这说明虽然 getter我们写的是函数,但是我们应该把它当成计算属性来用。
4、如何使用VUEX
3.1. 安装vuex
Npm install vuex -- save
3.2. 创建store
1、创建文件夹store,用来管理文件,具体路径无所谓,建议放到src目录下
2、文件夹store文件夹内创建index.js文件,这个文件我们用来组装模块并导出 store 的文件
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' // 告诉 vue “使用” vuex Vue.use(Vuex) // 创建一个对象来保存应用启动时的初始状态 // 需要维护的状态 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { // 放置初始状态 app启动的时候的全局的初始值 bankInf: {"name":"我是vuex的第一个数据","id":100,"bankName":"中国银行"} } }) // 整合初始状态和变更函数,我们就得到了我们所需的 store // 至此,这个 store 就可以连接到我们的应用中 export default store

3.3. Main.js文件中注册store
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import router from './router' import store from './../store/index' /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', router, store, template: '<App/>', components: { App } })
3.4. 使用store之获取
任意组件中使用store中的数据,就是使用计算属性返回store中的数据到一个新属性上
<div class="bank">
<list-header :headerData="bankName"></list-header>
04银行详情页面
<input name="" v-model="textValue">
<button type="button" name="获取数据" @click="newBankName"></button>
</div>
3.5. 使用store之修改
使用命令:this.$store.commit
export default { ... computed: { bankName() { return this.$store.state.bankInf.bankName; } }, methods: { newBankName: function() { this.$store.commit('newBankName', this.textValue) } } ... }
在store中的index.js中添加mutations:
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { // 放置初始状态 app启动的时候的全局的初始值 bankInf: {"name":"我是vuex的第一个数据","id":100,"bankName":"中国银行"}, count:0 }, mutations: { newBankName(state,msg) { state.bankInf.bankName = msg; } } })
5、常见错误
如果在使用中发现报错this.$store.commit is not a function ,请打开你项目的配置文件package.json,查看你正在使用的vuex的版本,我正在使用的是vuex2.0,
如果想删除旧版本的vuex并安装新版本的vuex请使用
npm rm vuex --save
然后安装最新的vuex
npm install vuex --save
即可解决这个错误,或者是查看vuex官网api修改提交mutation的语句