1、线性表基础
1.1. 概念
是最基本,最简单和最常用的数据结构(线性表,栈,队列,串和数组都是线性结构),同时也是其他数据结构的基础。。
线性表中各数据元素之间的关系是一对一,即除了第一个和最后一个数据元素之外,其它数据元素都是首尾相接的。
是由n(n要大于等于0)个数据元素(结点)组成的有限序列。
形如:A1、A2、A3….An这样含有有限的数据序列,我们就称之为线性表。
1.2. 特点
(1)有且仅有一个开始结点
(2)有且仅有一个终结结点
(3)内部结点都有且仅有一个直接前驱结点和一个直接后继结点
1.3. 常见操作
定义线性表的接口,要实现这些功能:
判断是否为空
线性表长度
GET和SET方法
ADD方法
REMOVE方法
Clear方法

2、线性表的两种实现方式
2.1. 顺序方式
概念:用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的数据元素,这种存储结构的线性表称为顺序表。
特点:逻辑上相邻的数据元素,物理次序也是相邻的。
他的优点是存储密度大,因为存储顺序是连续的,几乎不浪费空间
他的缺点是插入删除等运算不方便,如在中间插入一个数据元素,那么这个数据元素之后的所有数据元素都要后移一个位置,才能重新生成一个完整的线性表。
顺序表的程序实现
interface IMyLinearList { bool IsEmpty(); bool Add(int index,Object item); void Clear(); object Remove(int index); Object Get(int index); Object Set(int index, object item); int Size(); } class MySequenceList : IMyLinearList { private object[] sList = null; private int size = 0; private int defaultCapacity = 10; public MySequenceList(int capacity) { if (capacity > 0) { sList = new object[capacity]; } else { sList = new object[defaultCapacity]; } size = 0; } bool IMyLinearList.Add(int index, object item) { /* * 新增思路:首先将index位置后的所有元素都后移一个位置,空出index的位置 */ if (index < 0 || index > size) { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("索引越界"); } if (sList.Length == size) { //重新给顺序表分配内存空间 object[] temp = sList; sList = new object[sList.Length * 2]; for (int i = 0; i < temp.Length; i++) { sList[i] = temp[i]; } } //将索引位置为index后面的所有元素都后移一位,目的是给新插入的值留位置 for (int j = size - 1; j >= index; j--) { sList[j + 1] = sList[j]; } //后移完毕,添加新的值 sList[index] = item; size++; return true; } void IMyLinearList.Clear() { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { sList[i] = null; } size = 0; } object IMyLinearList.Get(int index) { RangeCheck(index); return sList[index]; } object IMyLinearList.Set(int index, object item) { RangeCheck(index); object oldValue = sList[index]; sList[index] = item; return oldValue; } bool IMyLinearList.IsEmpty() { return size == 0; } object IMyLinearList.Remove(int index) { //删除数据,后面的数据元素前移一位 RangeCheck(index); object oldValue = sList[index]; for (int i = index; i < size - 1; i++) { sList[i] = sList[i + 1]; } sList[size - 1] = null; size--; return oldValue; } int IMyLinearList.Size() { return size; } private void RangeCheck(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("索引越界"); } } }
运行:
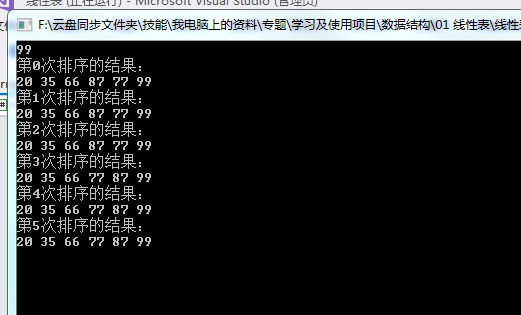
IMyLinearList lineList = new MySequenceList(20); //lineList.Add(-1,90); //抛出异常,索引越界 lineList.Add(0,35); lineList.Add(1, 20); lineList.Add(2, 66); lineList.Add(3, 87); lineList.Add(4, 77); lineList.Add(5, 99); Console.WriteLine(lineList.Get(5));
顺序表的选择排序:

class ArraySort { /// <summary> /// 一轮选择排序算法 /// 原理:遍历之后剩余的元素,谁小就放到前头 /// </summary> /// <param name="iList">要排序的线性表</param> /// <param name="placeNum">要排序的位置</param> /// <returns>排序一轮后的结果</returns> public static IMyLinearList Sort(IMyLinearList iList, int placeNum) { if (placeNum < 0 || placeNum >= iList.Size()) { return iList; } int elment = (int)iList.Get(placeNum);//要排序的元素值 int j = elment;//一轮排序中找到的最小元素值 int elementIndex = placeNum;//记录将要排序的元素最终放置的位置 for (int i = placeNum; i < iList.Size(); i++) //排序是从要排序的位置开始一直到线性表的结尾 { if (j > (int)iList.Get(i)) {//如果找到了 比 要排序的元素值还小的值,就需要把这个值付给j j = (int)iList.Get(i); elementIndex = i;//记录下位置 } } //循环完毕后,替换位置 if (elementIndex != placeNum) { iList.Set(placeNum, j);//要排序的位置 赋值值 iList.Set(elementIndex, elment);//要替换的位置 赋新值 } return iList; } }
IMyLinearList lineList = new MySequenceList(20); //lineList.Add(-1,90); //抛出异常,索引越界 lineList.Add(0,35); lineList.Add(1, 20); lineList.Add(2, 66); lineList.Add(3, 87); lineList.Add(4, 77); lineList.Add(5, 99); Console.WriteLine(lineList.Get(5)); //选择排序 for (int i = 0; i < lineList.Size(); i++) { ArraySort.Sort(lineList, i); Console.WriteLine("第"+i.ToString()+"次排序的结果:"); for (int j = 0; j < lineList.Size(); j++) { Console.Write(lineList.Get(j)+" "); } Console.WriteLine(); } Console.ReadKey();
2.2. 链式方式
概念:用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素(这组存储单元可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的),包括数据域和指针域,数据域存数据,指针域指示其后继的信息。
存储单元的地址是分散的,但逻辑关系是连续的。
为了表示这些数据元素是一个数据表,而且表示出数据元素之间的先后关系,因此需要在每个结点上需要一个附加信息即指针。他指向这个数据元素的后继结点的地址。
有三种方式:单链表、循环链表和双链表。
2.2.1. 单链表
也叫线性链表,是由一个个结点链接而成。单链表的结点只有一个存放数据的数据域和一个称为next的指向后继结点的指针域。
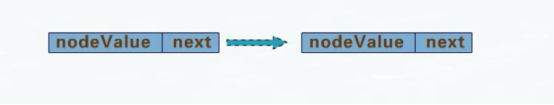
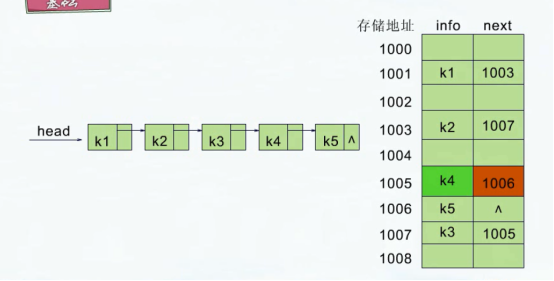
如图所示,k1的next指针域存储的地址是1003(1003是一个内存存储地址),根据1003就可以找到k2结点,以此类推。。。
单链表的程序实现:
public interface IMyLinearList { bool IsEmpty(); bool Add(int index,Object item); void Clear(); object Remove(int index); Object Get(int index); Object Set(int index, object item); int Size(); } /// <summary> /// 结点类 /// </summary> class Node { /// <summary> /// 结点值 /// </summary> public object nodeValue; /// <summary> /// 指向下一个结点的指针 /// </summary> public Node next; public Node() { nodeValue = null; next = null; } public Node(object initValue) { this.nodeValue = initValue; this.next = null; } public Node(object initValue, Node next) { this.nodeValue = initValue; this.next = next; } } /// <summary> /// 单链表 /// </summary> class SingleLinkedList : IMyLinearList { public Node Head { get; set; } public SingleLinkedList() { } public SingleLinkedList(Node head) { this.Head = head; } bool IMyLinearList.IsEmpty() { return Head == null; } bool IMyLinearList.Add(int index, object item) { IMyLinearList list = this; if (index < 0 || index > list.Size()) { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("索引越界"); } if (Head == null) { Head = new Node(item); } else { Node p = Head; for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) { p = p.next; } p.next = new Node(item, p.next); } return true; } void IMyLinearList.Clear() { Head = null; } object IMyLinearList.Remove(int index) { object oldValue = null; if (index >= 0 && Head != null) { if (index == 0) {//删除头结点 oldValue = Head.nodeValue; Head = Head.next; } else {//删除非头结点 Node p = Head; for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) { if (p.next != null) { p = p.next; } } if (p.next != null) { oldValue = p.next.nodeValue; p.next = p.next.next; } } } return oldValue; } object IMyLinearList.Get(int index) { RangeCheck(index); Node p = Head; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { p = p.next; } return p.nodeValue; } object IMyLinearList.Set(int index, object item) { RangeCheck(index); Node p = Head; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { p = p.next; } object oldValue = p.nodeValue; p.nodeValue = item; return oldValue; } int IMyLinearList.Size() { int size = 0; Node p = this.Head; while (p != null) { size++; p = p.next; } return size; } private void RangeCheck(int index) { IMyLinearList list = this; if (index < 0 || index > list.Size() - 1) { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("索引越界"); } } }
调用:
IMyLinearList list = new SingleLinkedList(); list.Add(0, 10); //list.Add(10,33); //索引越界 Console.WriteLine(list.Get(0)); Console.Read();
2.2.2. 循环链表
他在单链表的基础上,将表尾结点的指针指向了表头结点,形成了环状结构。

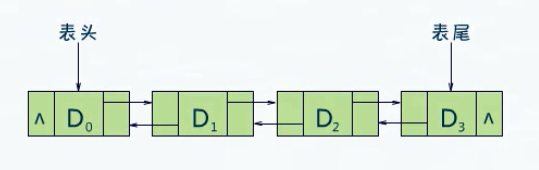
2.2.3. 双链表
双链表是可以同时在向前和向后两个方向上查找数据元素的单链表。她的结点除了数据域之外,还有previous和next两个指针域,分别指向直接前趋结点和直接后继结点。