原文参考(有删改):https://www.jianshu.com/p/6dba42c022a9
问题描述
开机时间相对参考机过慢,大约慢15s左右。Android 系统7.0。
问题分析
开机问题涉及的层次较多,很多进程都在设备启动期间启动,但只有关键路径 (bootloader --> kernel --> init --> file system mount --> zygote --> system server-->PMS-->AMS-->Launcher) 中的组件才会直接影响启动时间。
可以借助bootchart来分析,也可以直接通过log分析。不幸的是本项目机器因未知原因导致无法抓取到bootchart。
幸好在我浏览源码时发现了一个神器perfboot工具。具体在system/core/init/perfboot.py。
运行该命令需要在源码编译环境下。详细请参考源码文件,此处不做过多介绍。
使用命令:
./perfboot.py --iterations=5 --interval=30 -v --output=J5D_UE.tsv
获取问题机与参考机的开机数据。生成下图
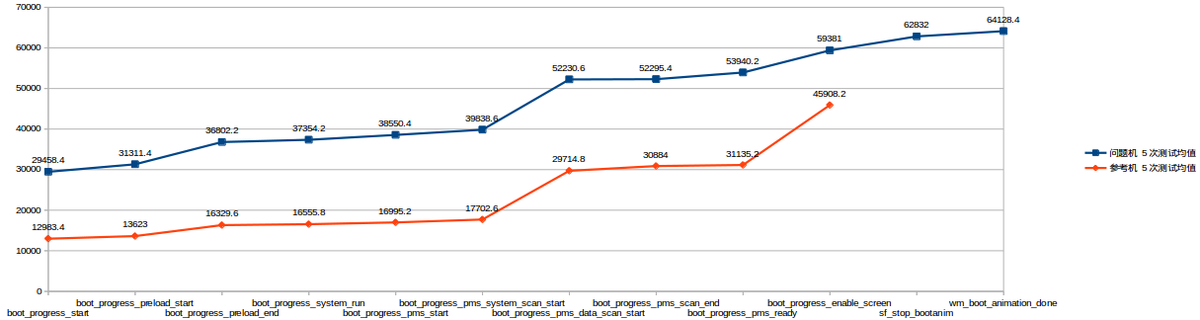
参考机vs问题机
上图X轴是开机启动过程中的一些重要节点。Y轴是开机时间。
详细说明下X轴上各个节点表征的含义。
|boot_progress_start|系统进入用户空间,标志着kernel启动完成,本例中可以看出kernel启动耗时30s左右
|:---
|boot_progress_preload_start|Zygote启动
|boot_progress_preload_end|Zygote结束
|boot_progress_system_run|SystemServer ready,开始启动Android系统服务,如PMS,APMS等
|boot_progress_pms_start|PMS开始扫描安装的应用
|boot_progress_pms_system_scan_start|PMS先行扫描/system目录下的安装包
|boot_progress_pms_data_scan_start|PMS扫描/data目录下的安装包
|boot_progress_pms_scan_end|PMS扫描结束
|boot_progress_pms_ready|PMS就绪
|boot_progress_ams_ready|AMS就绪
|boot_progress_enable_screen|AMS启动完成后开始激活屏幕,从此以后屏幕才能响应用户的触摸,它在WindowManagerService发出退出开机动画的时间节点之前,而真正退出开机动画还会花费少许时间,具体依赖animation zip 包中的desc.txt。wm_boot_animation_done才是用户感知到的动画结束时间节点
|sf_stop_bootanim|SF设置service.bootanim.exit属性值为1,标志系统要结束开机动画了,可以用来跟踪开机动画结尾部分消耗的时间
|wm_boot_animation_done|开机动画结束,这一步用户能直观感受到开机结束
通过上图可以直观的看到问题机在进入boot_progress_start节点之前相对参考机耗时较多。而这之前主要涉及bootloader和kernel。
bootloader 优化
这一块没有接触过,交给底层同事优化。大概说下抓取log的方式.
adb shell cat /proc/bootmsg > bootmsg.txt.
从log里底层同事发现是bootimg签名有问题,更详细的分析,自己对这块真心不懂,总结不出帮助性的意见。
kernel层优化
kernel的优化先check一遍config的配置,kernel中config的配置种类繁多,就算是工作几年的kernel工程师也不一定能清楚每一个config值的作用。Android提供了一个基础配置表。
可以用脚本:kernel/scripts/kconfig/merge_config.sh来生成一份config文件。具体用法戳这
拿生成的config文件和当前项目中的config做对比,同时也对比参考机的config文件。
对比的时候可以用一个现成的工具kernel/scripts/diffconfig来比较。
综合比较后的结果,本地一点点调试,查找资料。最终去掉了如下config:
CONFIG_MTD_TESTS=m ----> m改为n
CONFIG_SERIAL_MSM_HSL=y ----> y改为n
CONFIG_SERIAL_MSM_HSL_CONSOLE=y ----> y改为n
CONFIG_MMC_BLOCK_TEST=m ---->注释掉
CONFIG_MMC_TEST=m ---->注释掉
CONFIG_SERIAL_MSM_HSL=y ----> y改为n
CONFIG_SERIAL_MSM_HSL_CONSOLE=y ----> y改为n
CONFIG_MSM_SMD_DEBUG=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_CGROUP_DEBUG=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_RELAY=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_RMNET_DATA_DEBUG_PKT=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_DEBUG_GPIO=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_CORESIGHT=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_CORESIGHT_EVENT=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_CORESIGHT_FUSE=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_CORESIGHT_CTI=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_CORESIGHT_TMC=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_CORESIGHT_TPIU=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_CORESIGHT_FUNNEL=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_CORESIGHT_REPLICATOR=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_CORESIGHT_STM=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_CORESIGHT_HWEVENT=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_DEBUG_MEMORY_INIT=y ---->注释掉
CONFIG_DYNAMIC_DEBUG=y ---->注释掉
//以下也全部注释掉
CONFIG_SCHED_DEBUG
CONFIG_DEBUG_KMEMLEAK
CONFIG_DEBUG_KMEMLEAK_EARLY_LOG_SIZE=400
CONFIG_DEBUG_KMEMLEAK_DEFAULT_OFF
CONFIG_DEBUG_SPINLOCK
CONFIG_DEBUG_MUTEXES
CONFIG_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SLEEP
CONFIG_DEBUG_STACK_USAGE
CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST
CONFIG_FAULT_INJECTION_DEBUG_FS
CONFIG_LOCKUP_DETECTOR
CONFIG_DEBUG_PAGEALLOC
CONFIG_PAGE_POISONING
CONFIG_RMNET_DATA_DEBUG_PKT
CONFIG_MMC_PERF_PROFILING
CONFIG_DEBUG_BUS_VOTER
CONFIG_SLUB_DEBUG
CONFIG_DEBUG_BUGVERBOSE
CONFIG_ALLOC_BUFFERS_IN_4K_CHUNK
CONFIG_SERIAL_CORE
CONFIG_SERIAL_CORE_CONSOLE
CONFIG_SERIAL_MSM_HSL
CONFIG_SERIAL_MSM_HSL_CONSOLE
CONFIG_MSM_TZ_LOG
CONFIG_DYNAMIC_DEBUG
config的配置有
y,n,m:m表示编译成模块,不编译进内核。不配置的话相当于n。
CONFIG_DEBUG_INFO 不能去掉, 会引起CTS不过。由于config的的各项值可能散落在kernel的不同文件中,我们可以单独编译下kernel,然后去out目录下查看obj/KERNEL_OBJ/.config 文件,这里面的配置项是完全的。
kernel关闭掉一些debug开关后。在新版本上复测结果如下:
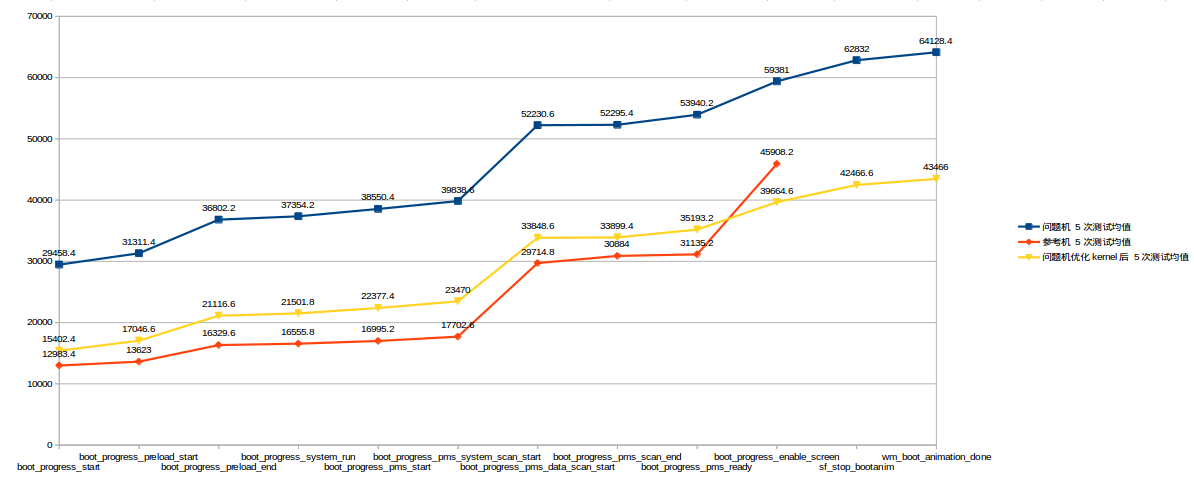
优化lk和kernel后
这里提下如何看kernel的log,
开机后用命令:adb shell dmesg > dmesg.txt抓取Log
log里面搜关键字"Bootloader start count"-->LK 启动
“Bootloader end count”-->LK 结束
"Kernel MPM timestamp"-->bootloader运行完成
通过对bootloader和kernel的优化,直接减少了14s左右的开机时间,可以看到优化的效果还是比较明显的。
frameworks层优化
用命令: adb logcat -b events|grep boot我们过滤出启动阶段的主要事件。
01-01 13:38:52.139 391 391 I boot_progress_start: 15452
01-01 13:38:53.329 391 391 I boot_progress_preload_start: 16641
01-01 13:38:56.675 391 391 I boot_progress_preload_end: 19989
01-01 13:38:57.020 1729 1729 I boot_progress_system_run: 20333
01-01 13:38:57.824 1729 1729 I boot_progress_pms_start: 21137
01-01 13:38:58.865 1729 1729 I boot_progress_pms_system_scan_start: 22179
01-01 13:39:08.852 1729 1729 I boot_progress_pms_data_scan_start: 32166
01-01 13:39:08.907 1729 1729 I boot_progress_pms_scan_end: 32221
01-01 13:39:10.109 1729 1729 I boot_progress_pms_ready: 33422
01-01 13:39:12.557 1729 1729 I boot_progress_ams_ready: 35871
01-01 13:39:15.189 1729 1782 I boot_progress_enable_screen: 38503
01-01 13:39:17.973 290 321 I sf_stop_bootanim: 41287
01-01 13:39:18.887 1729 1961 I wm_boot_animation_done: 42201
结合对比图看,boot_progress_enable_screen之前问题机跟对比机各个节点耗时相差不大。
在这里说明下,Android M上启动阶段到boot_progress_enable_screen就结束了,而Android N上还多了sf_stop_bootanim和wm_boot_animation_done两个事件。
这也就是图-优化kernel后棕红色的线条到boot_progress_enable_screen就没有延生的原因,因为它表示的参考机,而参考机正好是Android M系统。
从log的时间戳可以看出:
boot_progress_enable_screen--->花费2s左右的时间到达sf_stop_bootanim--->花费1s多时间到达wm_boot_animation_done。多出来的两个过程总共多花接近4s的时间。
我们要重点看下这个过程发生了什么,为什么会多出来这近4s时间。
1.先看下boot_progress_enable_screen出现的位置。
它在frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
void enableScreenAfterBoot() {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_ENABLE_SCREEN,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
mWindowManager.enableScreenAfterBoot();
synchronized (this) {
updateEventDispatchingLocked();
}
}
2.sf_stop_bootanim出现的位置。
它在frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger_hwc1.cpp。
这里特别说明下SurfaceFlinger_hwc1.cpp是SurfaceFlinger.cpp的升级版,它支持HWC 2.0,使用的是SurfaceFlinger.cpp还是SurfaceFlinger_hwc1.cpp跟平台选择相关。
void SurfaceFlinger::bootFinished()
{
...
// stop boot animation
// formerly we would just kill the process, but we now ask it to exit so it
// can choose where to stop the animation.
property_set("service.bootanim.exit", "1");
const int LOGTAG_SF_STOP_BOOTANIM = 60110;
LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOGTAG_SF_STOP_BOOTANIM,
ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
}
3.wm_boot_animation_done出现的位置。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
public void performEnableScreen() {
...
// Don't enable the screen until all existing windows have been drawn.
if (!mForceDisplayEnabled && checkWaitingForWindowsLocked()) {
return;
}
if (!mBootAnimationStopped) {
// Do this one time.
Trace.asyncTraceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "Stop bootanim", 0);
try {
IBinder surfaceFlinger = ServiceManager.getService("SurfaceFlinger");
if (surfaceFlinger != null) {
//Slog.i(TAG_WM, "******* TELLING SURFACE FLINGER WE ARE BOOTED!");
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken("android.ui.ISurfaceComposer");
surfaceFlinger.transact(IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION, // BOOT_FINISHED
data, null, 0);
data.recycle();
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
Slog.e(TAG_WM, "Boot completed: SurfaceFlinger is dead!");
}
mBootAnimationStopped = true;
}
if (!mForceDisplayEnabled && !checkBootAnimationCompleteLocked()) {
if (DEBUG_BOOT) Slog.i(TAG_WM, "performEnableScreen: Waiting for anim complete");
return;
}
...
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.WM_BOOT_ANIMATION_DONE, SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
...
}
找到了3个节点出现的位置,现在再来分析如何将这3个节点串联起来。
1-->2过程: AMS的enableScreenAfterBoot调用WMS的enableScreenAfterBoot方法,在WMS中的enableScreenAfterBoot会继续调用内部方法performEnableScreen,该方法内部判断开机动画如果没有停止,就调用SurfaceFlinger去停止开机动画
surfaceFlinger.transact(IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION, // BOOT_FINISHED
data, null, 0);
这里的FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION实际上就是BOOT_FINISHED。
frameworks/native/include/gui/ISurfaceComposer.h
class BnSurfaceComposer: public BnInterface<ISurfaceComposer> {
public:
enum {
// Note: BOOT_FINISHED must remain this value, it is called from
// Java by ActivityManagerService.
BOOT_FINISHED = IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION,
surfaceFlinger.transact发出的调用请求会被ISurfaceComposer处理。
frameworks/native/libs/gui/ISurfaceComposer.cpp
status_t BnSurfaceComposer::onTransact(
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
{
...
switch(code) {
case BOOT_FINISHED: {
CHECK_INTERFACE(ISurfaceComposer, data, reply);
bootFinished();
return NO_ERROR;
}
}
...
}
这里的bootFinished就是SurfaceFlinger_hwc1.cpp定义的bootFinished()方法,最终来到了第2个节点sf_stop_bootanim。
为了验证上述调用过程,我们添加上打印调用栈的log看看输出。
void SurfaceFlinger::bootFinished()
{
const nsecs_t now = systemTime();
const nsecs_t duration = now - mBootTime;
ALOGI("Boot is finished (%ld ms)", long(ns2ms(duration)) );
mBootFinished = true;
android::CallStack stack;
stack.update();
stack.log("azhengye", ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, " ");
String8 strtemp = stack.toString("");
ALOGD("Sunny %s", strtemp.string());
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
04-28 12:41:15.978 308 2956 D azhengye: #00 pc 0002b761 /system/lib/libsurfaceflinger.so
04-28 12:41:15.978 308 2956 D azhengye: #01 pc 00045c9f /system/lib/libgui.so
04-28 12:41:15.978 308 2956 D azhengye: #02 pc 000310cf /system/lib/libsurfaceflinger.so
04-28 12:41:15.978 308 2956 D azhengye: #03 pc 000359b3 /system/lib/libbinder.so
04-28 12:41:15.979 308 2956 D azhengye: #04 pc 0003d159 /system/lib/libbinder.so
04-28 12:41:15.979 308 2956 D azhengye: #05 pc 0003cdb7 /system/lib/libbinder.so
04-28 12:41:15.979 308 2956 D azhengye: #06 pc 0003d2bb /system/lib/libbinder.so
04-28 12:41:15.979 308 2956 D azhengye: #07 pc 0004f5f5 /system/lib/libbinder.so
04-28 12:41:15.979 308 2956 D azhengye: #08 pc 0000e349 /system/lib/libutils.so
04-28 12:41:15.979 308 2956 D azhengye: #09 pc 000473d3 /system/lib/libc.so
04-28 12:41:15.979 308 2956 D azhengye: #10 pc 0001a0c9 /system/lib/libc.so
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SurfaceFlinger_hwc1.cpp:312 android::SurfaceFlinger::bootFinished()
ISurfaceComposer.cpp:371 android::BnSurfaceComposer::onTransact(unsigned int, android::Parcel const&, android::Parcel*, unsigned int)
SurfaceFlinger_hwc1.cpp:3103 android::SurfaceFlinger::onTransact(unsigned int, android::Parcel const&, android::Parcel*, unsigned int)
Binder.cpp:126 android::BBinder::transact(unsigned int, android::Parcel const&, android::Parcel*, unsigned int)
IPCThreadState.cpp:1111 android::IPCThreadState::executeCommand(int)
IPCThreadState.cpp:445 android::IPCThreadState::getAndExecuteCommand()
IPCThreadState.cpp:513 android::IPCThreadState::joinThreadPool(bool)
ProcessState.cpp:63 (discriminator 1)android::PoolThread::threadLoop()
Threads.cpp:751 android::Thread::_threadLoop(void*)
pthread_create.cpp:198 (discriminator 1)__pthread_start(void*)
clone.cpp:41 (discriminator 1)__start_thread
上述log也印证了之前的分析,至此1-->2的过程算是通了。在来看2-->3过程,在3节点出现之前还有一次判断:
if (!mForceDisplayEnabled && !checkBootAnimationCompleteLocked()) {
if (DEBUG_BOOT) Slog.i(TAG_WM, "performEnableScreen: Waiting for anim complete");
return;
}
这里系统需要去检测开机动画是否还在播放,
private boolean checkBootAnimationCompleteLocked() {
if (SystemService.isRunning(BOOT_ANIMATION_SERVICE)) {
mH.removeMessages(H.CHECK_IF_BOOT_ANIMATION_FINISHED);
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.CHECK_IF_BOOT_ANIMATION_FINISHED,
BOOT_ANIMATION_POLL_INTERVAL);
return false;
}
return true;
}
BOOT_ANIMATION_SERVICE是在初始化SurfaceFlinger时启动的。
frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger_hwc1.cpp
void SurfaceFlinger::init() {
...
// start boot animation
startBootAnim();
}
顺藤摸瓜来到了BootAnimation,前面分析过在SurfaceFlinger的bootFinished方法中将"service.bootanim.exit"置为了1,这个设置在BootAnimation就被读取了。
frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation/BootAnimation.cpp
...
#define EXIT_PROP_NAME "service.bootanim.exit"
...
void BootAnimation::checkExit() {
// Allow surface flinger to gracefully request shutdown
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get(EXIT_PROP_NAME, value, "0");
int exitnow = atoi(value);
if (exitnow) {
requestExit();
if (mAudioPlayer != NULL) {
mAudioPlayer->requestExit();
}
}
}
跟踪到这2-->3过程也就通畅了。在理清了该过程的调用逻辑后,问题也浮出了水面。原来之前的同事在解决一个开机进桌面出现黑屏问题时,在checkExit内部人为delay了几秒的时间...
在排查log时还发现下面的错误:
01-01 15:55:23.506 1865 1865 E BitmapFactory: Unable to decode stream: java.io.FileNotFoundException: /data/system/users/0/wallpaper_orig (No such file or directory)
adb shell 进入手机发现确实没有/data/system/users/0/wallpaper_orig文件。
会不会是是wallpaper异常导致消耗时间多余呢?
为了清晰debug在过滤下log
adb logcat -b all|grep -E "Wallpaper may change|haveWall|sf_stop_bootanim|boot_progress_enable_screen"
输出如下log:
01-02 12:13:03.814 1851 2082 V WindowManager: Wallpaper may change! Adjusting
01-02 12:13:04.865 1851 2082 V WindowManager: Wallpaper may change! Adjusting
01-02 12:13:06.986 1851 2006 I boot_progress_enable_screen: 40388
01-02 12:13:06.988 1851 2082 V WindowManager: Wallpaper may change! Adjusting
01-02 12:13:07.052 1851 2006 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=false wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:07.056 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=false wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:07.184 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=false wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:08.049 1851 2082 V WindowManager: Wallpaper may change! Adjusting
01-02 12:13:08.066 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=false wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:08.067 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=false wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:08.071 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=false wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:08.072 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=false wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:08.076 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=false wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:09.894 1851 2082 V WindowManager: Wallpaper may change! Adjusting
01-02 12:13:09.908 1851 3413 V WindowManager: Wallpaper may change! Adjusting
01-02 12:13:10.178 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=true wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:10.186 292 3736 I sf_stop_bootanim: 43587
01-02 12:13:10.191 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=true wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:10.196 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=true wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:10.397 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=true wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
然后在做实验push一个wallpaper_orig到指定目录,BitmapFactory的错误虽然不见了。然而对于缩短时间并没有什么卵用。
看来不是这个异常没有拖慢开机速度。但我注意到
01-02 12:13:10.178 1851 2082 I WindowManager: ******** booted=true msg=false haveBoot=false haveApp=false haveWall=true wallEnabled=true haveKeyguard=true
01-02 12:13:10.186 292 3736 I sf_stop_bootanim: 43587
这段log中haveWall=true之前一直都是haveWall=false,haveWall表示系统Window已经成功加载好了Wallpaper。Log中不断的输出
WindowManager: Wallpaper may change! Adjusting
这里究竟为什么Wallpaper会不断的Adjusting呢?看起来一旦Wallpaper调整好就会将haveWall置true。
追踪了下该句log在代码中的位置:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
private boolean checkWaitingForWindowsLocked() {
//省略无关代码
if (DEBUG_SCREEN_ON || DEBUG_BOOT) {
Slog.i(TAG_WM, "******** booted=" + mSystemBooted + " msg=" + mShowingBootMessages
+ " haveBoot=" + haveBootMsg + " haveApp=" + haveApp
+ " haveWall=" + haveWallpaper + " wallEnabled=" + wallpaperEnabled
+ " haveKeyguard=" + haveKeyguard);
}
// If we are turning on the screen to show the boot message,
// don't do it until the boot message is actually displayed.
if (!mSystemBooted && !haveBootMsg) {
return true;
}
// If we are turning on the screen after the boot is completed
// normally, don't do so until we have the application and
// wallpaper.
if (mSystemBooted && ((!haveApp && !haveKeyguard) ||
(wallpaperEnabled && !haveWallpaper))) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
这个checkWaitingForWindowsLocked表示是否需要等待系统Windows就绪。被同在WindowManagerService类中的performEnableScreen方法调用
public void performEnableScreen() {
// Don't enable the screen until all existing windows have been drawn.
if (!mForceDisplayEnabled && checkWaitingForWindowsLocked()) {
return;
}
}
从注释看performEnableScreen执行的是激活屏幕动作,然而在此之前需要等待系统必要的windows已经被画好了,也就是说我屏幕一旦激活了,绘制好的windows就能马上显示出来。否则performEnableScreen直接就退出了。
而performEnableScreen又是被同在WindowManagerService类中enableScreenAfterBoot方法调用。大致的调用过程如下:
AMS打印出boot_progress_enable_screen---->调用WMS的enableScreenAfterBoot--->调用WMS的performEnableScreen--->调用WMS的checkWaitingForWindowsLocked检查是否可以Enable Screen,因为Wallpaper没有准备好,因此checkWaitingForWindowsLocked返回了true,进而导致performEnableScreen直接返回,没有去执行本来要做的Enable Screen动作。
WindowManager: Wallpaper may change! Adjusting
是在下面的code打印出来的。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowSurfacePlacer.java
// "Something has changed! Let's make it correct now."
private void performSurfacePlacementInner(boolean recoveringMemory) {
//省略无关代码
if (mWallpaperMayChange) {
if (DEBUG_WALLPAPER_LIGHT)
Slog.v(TAG, "Wallpaper may change! Adjusting");
defaultDisplay.pendingLayoutChanges |= FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_WALLPAPER;
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT_REPEATS) debugLayoutRepeats("WallpaperMayChange",
defaultDisplay.pendingLayoutChanges);
}
//省略无关代码
}
debug调用栈如下:
1-01 21:18:30.572 2912 2962 W System.err: java.lang.Exception: print stack
01-01 21:18:30.573 2912 2962 W System.err: at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.checkWaitingForWindowsLocked(WindowManagerService.java:5841)
01-01 21:18:30.574 2912 2962 W System.err: at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.performEnableScreen(WindowManagerService.java:5905)
01-01 21:18:30.575 2912 2962 W System.err: at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService$H.handleMessage(WindowManagerService.java:8390)
01-01 21:18:30.576 2912 2962 W System.err: at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
01-01 21:18:30.577 2912 2962 W System.err: at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:154)
01-01 21:18:30.578 2912 2962 W System.err: at android.os.HandlerThread.run(HandlerThread.java:61)
01-01 21:18:30.578 2912 2962 W System.err: at com.android.server.ServiceThread.run(ServiceThread.java:46)
这块没有检查出多余的操作,没继续check了。
经过以上分析后修改代码,最终问题机的开机速度达到了参考机的标准。性能问题是一个持续挖掘改善的过程,开机过程中还能优化的地方肯定还有。
debug 技术说明
汇总下分析该问题时,汇集的一些debug技术。
- java代码中打印堆栈 Slog.d("azhengye", "Stack=="+new RuntimeException("azhengye debug").fillInStackTrace());
或者new Exception("print stack").printStackTrace(); 然后log中搜索"System.err:" - c++ debug: 为了在native查看函数调用栈可以在需要的地方添加如下代码。
#include <utils/CallStack.h>
android::CallStack stack;
stack.update();
String8 strtemp = stack.toString("");
ALOGD(" %s", strtemp.string());
过滤出的log还需要用arm-linux-androideabi-addr2line转行下,好在有现成的脚本帮我们做这件事,这里一并贴出来。
#!/usr/bin/python
# stack symbol parser
import os
import string
import sys
ANDROID_TARGET_OUT = os.getcwd()+"/"
# addr2line tool path and symbol path
addr2line_tool = 'arm-linux-androideabi-addr2line'
symbol_dir = ANDROID_TARGET_OUT + '/symbols'
symbol_bin = symbol_dir + '/system/bin/'
symbol_lib = symbol_dir + '/system/lib/'
class ReadLog:
def __init__(self,filename):
self.logname = filename
def parse(self):
f = file(self.logname,'r')
lines = f.readlines()
if lines != []:
print 'read file ok'
else:
print 'read file failed'
result =[]
for line in lines:
if line.find('stack') != -1:
print 'stop search'
break
elif line.find('system') != -1:
#print 'find one item' + line
result.append(line)
return result
class ParseContent:
def __init__(self,addr,lib):
self.address = addr # pc address
self.exename = lib # executable or shared library
def addr2line(self):
cmd = addr2line_tool + " -C -f -s -e " + symbol_dir + self.exename + " " + self.address
#print cmd
stream = os.popen(cmd)
lines = stream.readlines();
list = map(string.strip,lines)
return list
inputarg = sys.argv
if len(inputarg) < 2:
print 'Please input panic log'
exit()
filename = inputarg[1]
readlog = ReadLog(filename)
inputlist = readlog.parse()
for item in inputlist:
itemsplit = item.split()
test = ParseContent(itemsplit[-2],itemsplit[-1])
list = test.addr2line()
print "%-30s%s" % (list[1],list[0])
在源码编译的imge文件夹下执行上面的脚本,调试 SF 的bootFinished就用的该脚本,下面是个输出例子。
01-02 01:38:13.305 477 3072 D azhengye : #00 pc 000059b9 /system/bin/bootanimation
01-02 01:38:13.305 477 3072 D azhengye : #01 pc 00006515 /system/bin/bootanimation
01-02 01:38:13.305 477 3072 D azhengye : #02 pc 0000591f /system/bin/bootanimation
01-02 01:38:13.305 477 3072 D azhengye : #03 pc 000054f1 /system/bin/bootanimation
01-02 01:38:13.305 477 3072 D azhengye : #04 pc 0000e349 /system/lib/libutils.so
01-02 01:38:13.305 477 3072 D azhengye : #05 pc 000473d3 /system/lib/libc.so
01-02 01:38:13.305 477 3072 D azhengye : #06 pc 0001a0c9 /system/lib/libc.so
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
python panic.py /data/My_Doc/Performance/boot_c_log
read file ok
BootAnimation.cpp:534 android::BootAnimation::checkExit()
BootAnimation.cpp:972 android::BootAnimation::playAnimation(android::BootAnimation::Animation const&)
BootAnimation.cpp:870 android::BootAnimation::movie()
BootAnimation.cpp:452 android::BootAnimation::threadLoop()
Threads.cpp:751 android::Thread::_threadLoop(void*)
pthread_create.cpp:198 (discriminator 1)__pthread_start(void*)
clone.cpp:41 (discriminator 1)__start_thread
-
堆栈dump
adb shell kill -3
输出的trace会保存在 /data/anr/traces.txt文件中。这个需要注意,如果没有 /data/anr/这个目录 或/data/anr/traces.txt这个文件,需要手工创建一下,并设置好读写权限。如果是native thread的堆栈打印,可能需要修改dalvik/vm/Thread.cpp的dumpNativeThread方法。
- debuggerd coredump 这个是开始分析问题查资料找到的debug方法,不过自己没有实践,仅作记录参考。
debuggerd是android的一个daemon进程,负责在进程异常出错时,将进程的运行时信息dump出来供分析。debuggerd生成的coredump数据是以文本形式呈现,被保存在 /data/tombstone/ 目录下,它可以在不中断进程执行的情况下打印当前进程的native堆栈。使用方法是:
debuggerd -b
这可以协助我们分析进程执行行为,也可以用来定位native进程中锁死或错误逻辑引起的死循环的代码位置。
总结
各家厂商都会定制不同的开机行为,因此没有一个固定的方法能fix所有的开机问题,但通过本文我们总结分析该类问题的套路,那就是关注boot阶段的各个event事件,先量化出开机慢在哪里,然后在去针对性的优化。
源码真的是个宝库,多读吧。