由于时间的缘故,创建存储过程、自定义函数、聚集、触发器等内容转自别人的文章。
文章来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/doc/archive/2009/02/11/1388513.html
SQLCLR(一)存储过程
存储过程方法上方标注[Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlProcedure]存储过程:
 using System;
using System; using System.Data;
using System.Data; using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Data.SqlClient; using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Data.SqlTypes; using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server;
using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server;

 public partial class StoredProcedures
public partial class StoredProcedures {
{ //这里是告诉sqlserver,这个方法要注册成存储过程
//这里是告诉sqlserver,这个方法要注册成存储过程 //我感觉[Attribute]这个东西翻译成标签更形像:)
//我感觉[Attribute]这个东西翻译成标签更形像:) [Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlProcedure]
[Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlProcedure] public static void TestStoredProcedure(string name, ref string outstr)
public static void TestStoredProcedure(string name, ref string outstr) {
{ // 在此处放置代码
// 在此处放置代码 outstr = "hello," + name;
outstr = "hello," + name;
 using (SqlConnection cn = new SqlConnection())
using (SqlConnection cn = new SqlConnection()) {
{ //使用上下文链接也就是当前数据库链接
//使用上下文链接也就是当前数据库链接 cn.ConnectionString = "context connection=true";
cn.ConnectionString = "context connection=true"; using (SqlCommand cmd = cn.CreateCommand())
using (SqlCommand cmd = cn.CreateCommand()) {
{ cmd.CommandText = "Select * from userinfo";
cmd.CommandText = "Select * from userinfo"; cn.Open();
cn.Open(); //SqlContext.Pipe.Send这个方法输出结果集
//SqlContext.Pipe.Send这个方法输出结果集 //接受SqlDataReader,SqlDataRecord和string
//接受SqlDataReader,SqlDataRecord和string SqlContext.Pipe.Send(cmd.ExecuteReader());
SqlContext.Pipe.Send(cmd.ExecuteReader()); //你也可以用下边这样
//你也可以用下边这样 //SqlContext.Pipe.ExecuteAndSend(cmd);
//SqlContext.Pipe.ExecuteAndSend(cmd); }
} }
} }
} };
};
 DECLARE @name nvarchar(4000)
DECLARE @name nvarchar(4000) DECLARE @outstr nvarchar(4000)
DECLARE @outstr nvarchar(4000) set @name='david fan'
set @name='david fan' -- TODO: 在此处设置参数值。
-- TODO: 在此处设置参数值。 EXECUTE [TestProject].[dbo].[TestStoredProcedure]
EXECUTE [TestProject].[dbo].[TestStoredProcedure]  @name
@name ,@outstr OUTPUT
,@outstr OUTPUT print @outstr
print @outstr结果如下:
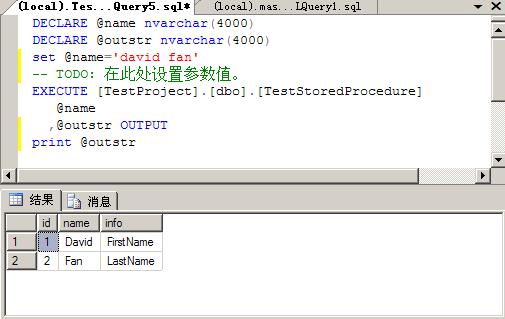
输出参数返回值:

SQLCLR(二)自定义函数
自定义函数方法上方标注[Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlFunction]。自定义函数又分TVF函数和Scalar两种,最大区别在于TVF返回表,后者返回Scalar(标量)
示例函数的作用是搜索目录下的某一类型的文件
 using System;
using System; using System.Data;
using System.Data; using System.Data.Sql;
using System.Data.Sql; using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Data.SqlTypes; using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server;
using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server; using System.Collections;
using System.Collections; using System.IO;
using System.IO; using System.Security.Principal;
using System.Security.Principal;
 public partial class UserDefinedFunctions
public partial class UserDefinedFunctions {
{ //需要返回一个表时用TVF(streaming table-valued function)
//需要返回一个表时用TVF(streaming table-valued function) //可以用select from 语句查询这个方法的返回
//可以用select from 语句查询这个方法的返回 //TVF需要返回Ienumerable接口,例如:Array,这里返回一个数组
//TVF需要返回Ienumerable接口,例如:Array,这里返回一个数组
 //FillRowMethodName为填充表行的方法
//FillRowMethodName为填充表行的方法 //TableDefinition为表结构,对应FillRowMethodName方法的参数
//TableDefinition为表结构,对应FillRowMethodName方法的参数 [Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlFunction(FillRowMethodName = "BuildRow",
[Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlFunction(FillRowMethodName = "BuildRow", TableDefinition = "Name nvarchar(32), Length bigint, Modified DateTime")]
TableDefinition = "Name nvarchar(32), Length bigint, Modified DateTime")] public static IEnumerable FileListCs(string directoryName, string pattern)
public static IEnumerable FileListCs(string directoryName, string pattern) {
{ FileInfo[] files;
FileInfo[] files; //模拟当前SQL安全上下文
//模拟当前SQL安全上下文 WindowsImpersonationContext OriginalContext= SqlContext.WindowsIdentity.Impersonate();
WindowsImpersonationContext OriginalContext= SqlContext.WindowsIdentity.Impersonate(); try
try {
{ DirectoryInfo di = new DirectoryInfo(directoryName);
DirectoryInfo di = new DirectoryInfo(directoryName); files = di.GetFiles(pattern);
files = di.GetFiles(pattern); }
} finally
finally {
{ if (OriginalContext != null)
if (OriginalContext != null) {
{ OriginalContext.Undo();
OriginalContext.Undo(); }
} }
} return files;
return files; }
}
 public static void BuildRow(object Obj,
public static void BuildRow(object Obj, ref SqlString fileName,
ref SqlString fileName, ref SqlInt64 fileLength,
ref SqlInt64 fileLength, ref SqlDateTime fileModified)
ref SqlDateTime fileModified) {
{ if (Obj != null)
if (Obj != null) {
{ FileInfo file = (FileInfo)Obj;
FileInfo file = (FileInfo)Obj; fileName = file.Name;
fileName = file.Name; fileLength = file.Length;
fileLength = file.Length; fileModified = file.LastWriteTime;
fileModified = file.LastWriteTime; }
} else
else {
{ fileName = SqlString.Null;
fileName = SqlString.Null; fileLength = SqlInt64.Null;
fileLength = SqlInt64.Null; fileModified = SqlDateTime.Null;
fileModified = SqlDateTime.Null; }
} }
} }
}
打开sqlserver2005查询分析器执行下边语句 TestProject 为我的数据库名,你的如果不是,当然需要修改了。
 ALTER DATABASE TestProject SET TRUSTWORTHY ON;
ALTER DATABASE TestProject SET TRUSTWORTHY ON;查询分析器中执行
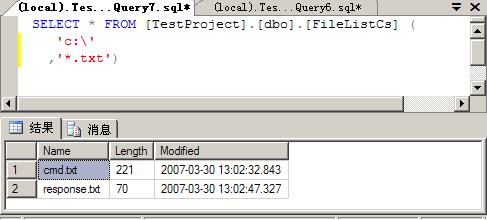
 SELECT * FROM [TestProject].[dbo].[FileListCs] (
SELECT * FROM [TestProject].[dbo].[FileListCs] ( 'c:\'
'c:\' ,'*.txt')
,'*.txt')结果如下:
二) Scalar 函数
这类函数返回类型如图,像SqlString这类sqlserver的scalar类型
下面就是这类函数的一个小例子。
 using System;
using System; using System.Data;
using System.Data; using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Data.SqlClient; using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Data.SqlTypes; using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server;
using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server;
 public partial class UserDefinedFunctions
public partial class UserDefinedFunctions {
{ [Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlFunction]
[Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlFunction] public static SqlString ScalarFunction()
public static SqlString ScalarFunction() {
{ // 在此处放置代码
// 在此处放置代码 return new SqlString("Hello");
return new SqlString("Hello"); }
} };
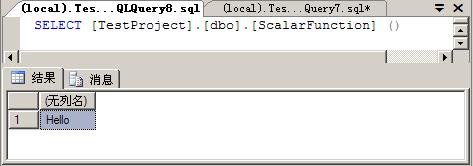
};sqlserver查询查询分析器中运行如下语句
 SELECT [TestProject].[dbo].[ScalarFunction] ()
SELECT [TestProject].[dbo].[ScalarFunction] ()结果如下:
SQLCLR(三)触发器
这一节比较简单了,主要是讲如何在SQLCLR下设计触发器。在SQLServer2005里分两种触发 器,DDL和DML两种触发器。DDL触发器是响应CREATE、ALTER 和 DROP 开头的语句。我们常用的是DML触发器,这一类触发器响应当数据库中发生数据操作包括表或视图中修改数据的 INSERT 、UPDATE 或 DELETE 。对于.net来讲触发器也是方法,在上方标注[Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlTrigger]标签(只我这样翻译)。
我们看一个小例子
 using System;
using System; using System.Data;
using System.Data; using System.Data.Sql;
using System.Data.Sql; using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server;
using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server; using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
 public partial class Triggers
public partial class Triggers {
{ //Name触发器的名字
//Name触发器的名字 //Target触发器对应表
//Target触发器对应表 //Event可以是{ FOR | AFTER | INSTEAD OF } { [ INSERT ] [ , ] [ UPDATE ] [ , ] [ DELETE ] }
//Event可以是{ FOR | AFTER | INSTEAD OF } { [ INSERT ] [ , ] [ UPDATE ] [ , ] [ DELETE ] } [Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlTrigger(Name = "NameInfoTrigger", Target = "NameInfo", Event = "FOR UPDATE")]
[Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlTrigger(Name = "NameInfoTrigger", Target = "NameInfo", Event = "FOR UPDATE")] public static void GetChange()
public static void GetChange() {
{ using (SqlConnection cn = new SqlConnection())
using (SqlConnection cn = new SqlConnection()) {
{ cn.ConnectionString = "context connection=true";
cn.ConnectionString = "context connection=true"; cn.Open();
cn.Open(); using (SqlCommand cmd = cn.CreateCommand())
using (SqlCommand cmd = cn.CreateCommand()) {
{ cmd.CommandText = "insert into ChangeHistory select b.name + '->' + a.name,getdate() from INSERTED a JOIN DELETED b ON a.id = b.id";
cmd.CommandText = "insert into ChangeHistory select b.name + '->' + a.name,getdate() from INSERTED a JOIN DELETED b ON a.id = b.id"; SqlContext.Pipe.ExecuteAndSend(cmd);
SqlContext.Pipe.ExecuteAndSend(cmd); }
} }
} }
} }
}
右键部署。
数据库里的两张表
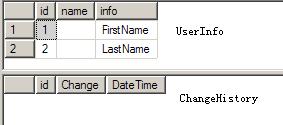
我执行两条UPDATE语句
 update [NameInfo] set [name]='David' where id=1
update [NameInfo] set [name]='David' where id=1 update [nameinfo] set [name]='Fan' where id=2
update [nameinfo] set [name]='Fan' where id=2结果:
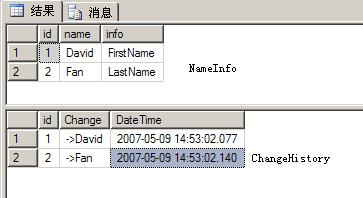
再执行两条
 update [NameInfo] set [name]='*David*' where id=1
update [NameInfo] set [name]='*David*' where id=1 update [nameinfo] set [name]='*Fan*' where id=2
update [nameinfo] set [name]='*Fan*' where id=2再看结果:

SQLCLR(四)用户定义类型UDT
用户自定义类型是SQL Server 2005的新特性。和前几篇文章介绍的SQLCLR相比,UDT相对有此复杂。UDT也有许多限制和必须遵守UDT规范。UDT的二进制不能超过8000 个字节,必须包含一个null值表示,因为SQLServer的数据类型是允许null值的。
UDT可以是结构或类。如果是类的话需加[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
标签(属性),这是保证序列化时不改变属性的次序。
现在看一段代码
 using System;
using System; using System.IO;
using System.IO; using System.Data;
using System.Data; using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Data.SqlClient; using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Data.SqlTypes; using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server;
using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server;
 [Serializable]
[Serializable] [Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlUserDefinedType(Format.UserDefined, MaxByteSize = 1024)]
[Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SqlUserDefinedType(Format.UserDefined, MaxByteSize = 1024)] public struct Person : INullable, IBinarySerialize
public struct Person : INullable, IBinarySerialize {
{ public override string ToString()
public override string ToString() {
{ // 用您的代码替换下列代码
// 用您的代码替换下列代码 return FormatU();
return FormatU(); }
}
 public bool IsNull
public bool IsNull {
{ get
get {
{ // 在此处放置代码
// 在此处放置代码 return m_Null;
return m_Null; }
} }
}
 public static Person Null
public static Person Null {
{ get
get {
{ Person h = new Person();
Person h = new Person(); h.m_Null = true;
h.m_Null = true; return h;
return h; }
} }
}
 public static Person Parse(SqlString s)
public static Person Parse(SqlString s) {
{ if (s.IsNull)
if (s.IsNull) return Null;
return Null;
 Person u = new Person();
Person u = new Person(); string value = s.Value;
string value = s.Value; if (value == "null") return Null;
if (value == "null") return Null;
 string[] parts = value.Split(',');
string[] parts = value.Split(','); u.name = parts[0];
u.name = parts[0]; u.age = ParseAge(parts[1]);
u.age = ParseAge(parts[1]); u.sex = parts[2];
u.sex = parts[2]; return u;
return u; }
}
 // 这是占位符方法
// 这是占位符方法 public string FormatU()
public string FormatU() {
{ //在此处插入方法代码
//在此处插入方法代码 return string.Format("名称:{0},年龄:{1},性别:{2}", name, age, sex);
return string.Format("名称:{0},年龄:{1},性别:{2}", name, age, sex); }
}
 // 这是占位符静态方法
// 这是占位符静态方法 public static int ParseAge(string str)
public static int ParseAge(string str) {
{ //在此处插入方法代码
//在此处插入方法代码 return int.Parse(str.Substring(0, str.LastIndexOf("岁")));
return int.Parse(str.Substring(0, str.LastIndexOf("岁"))); }
}
 // 这是占位符字段成员
// 这是占位符字段成员 private int age;
private int age; public int Age
public int Age {
{ get { return age; }
get { return age; } set { age = value; }
set { age = value; } }
}
 private string name;
private string name; public string Name
public string Name {
{ get { return name; }
get { return name; } set { name = value; }
set { name = value; } }
}
 private string sex;
private string sex; public string Sex
public string Sex {
{ get { return sex; }
get { return sex; } set { sex = value; }
set { sex = value; } }
}
 // 私有成员
// 私有成员 private bool m_Null;
private bool m_Null; public byte[] b;
public byte[] b;
 public void Read(BinaryReader r)
public void Read(BinaryReader r) {
{ name = r.ReadString();
name = r.ReadString(); sex = r.ReadString();
sex = r.ReadString(); age = r.ReadInt32();
age = r.ReadInt32(); m_Null = r.ReadBoolean();
m_Null = r.ReadBoolean(); }
} public void Write(BinaryWriter w)
public void Write(BinaryWriter w) {
{ w.Write(name);
w.Write(name); w.Write(sex);
w.Write(sex); w.Write(age);
w.Write(age); w.Write(m_Null);
w.Write(m_Null); }
} }
}


部署后在SQL Server 2005中执行下面的语句
 create table UdtTest (Id int not null, p Person not null)
create table UdtTest (Id int not null, p Person not null) insert into UdtTest values(1, 'David,24岁,男')
insert into UdtTest values(1, 'David,24岁,男') select id, convert(nvarchar(25),p) from UdtTest
select id, convert(nvarchar(25),p) from UdtTest drop table UdtTest
drop table UdtTest

结果如下:
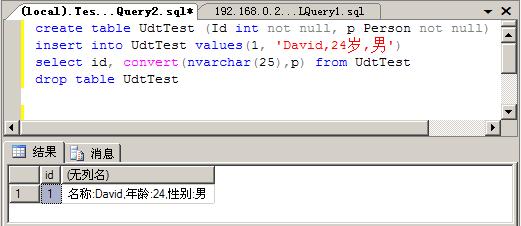
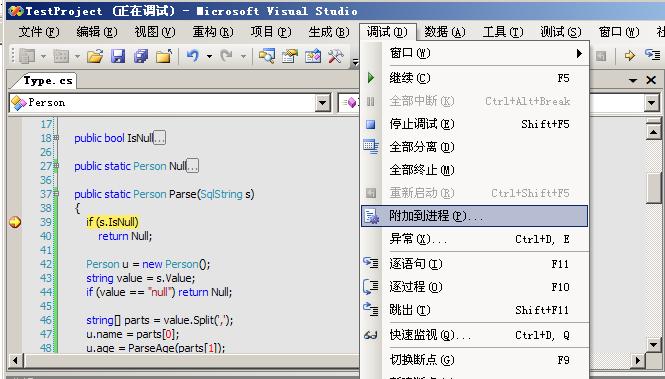
想看清楚SQLCLR在对UDT处理机制可以将项目附加到SQL Server 2005进程,在相应的方法设置断点。
SQLCLR(五)聚合
SQL Server中的聚合,常用的比如max,count之类。 我们现在也可以在SQLCLR里创建自定义的聚合。Visual Studio 2005中提供的聚合模板是一个结构,标注了[Serializable],[SqlUserDefinedAggregate]标签,这将让 SQLCLR知道这是一个聚合函数。看一段代码,这段代码来自SQL Server 2005联机丛书,本来自己想写一段,但突然公司有些事要做,没时间了。示例代码作用是合并同一部书(ID相同)的作者。
 using System;
using System; using System.Data;
using System.Data; using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server;
using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server; using System.Data.SqlTypes;
using System.Data.SqlTypes; using System.IO;
using System.IO; using System.Text;
using System.Text;
 [Serializable]
[Serializable] [SqlUserDefinedAggregate(
[SqlUserDefinedAggregate( Format.UserDefined, //use clr serialization to serialize the intermediate result
Format.UserDefined, //use clr serialization to serialize the intermediate result IsInvariantToNulls = true, //optimizer property
IsInvariantToNulls = true, //optimizer property IsInvariantToDuplicates = false, //optimizer property
IsInvariantToDuplicates = false, //optimizer property IsInvariantToOrder = false, //optimizer property
IsInvariantToOrder = false, //optimizer property MaxByteSize = 8000) //maximum size in bytes of persisted value
MaxByteSize = 8000) //maximum size in bytes of persisted value ]
] public class Concatenate : IBinarySerialize
public class Concatenate : IBinarySerialize {
{ /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// The variable that holds the intermediate result of the concatenation
/// The variable that holds the intermediate result of the concatenation /// </summary>
/// </summary> private StringBuilder intermediateResult;
private StringBuilder intermediateResult;
 /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// Initialize the internal data structures
/// Initialize the internal data structures /// </summary>
/// </summary> public void Init()
public void Init() {
{ this.intermediateResult = new StringBuilder();
this.intermediateResult = new StringBuilder(); }
}
 /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// Accumulate the next value, not if the value is null
/// Accumulate the next value, not if the value is null /// </summary>
/// </summary> /// <param name="value"></param>
/// <param name="value"></param> public void Accumulate(SqlString value)
public void Accumulate(SqlString value) {
{ if (value.IsNull)
if (value.IsNull) {
{ return;
return; }
}
 this.intermediateResult.Append(value.Value).Append(',');
this.intermediateResult.Append(value.Value).Append(','); }
}
 /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// Merge the partially computed aggregate with this aggregate.
/// Merge the partially computed aggregate with this aggregate. /// </summary>
/// </summary> /// <param name="other"></param>
/// <param name="other"></param> public void Merge(Concatenate other)
public void Merge(Concatenate other) {
{ this.intermediateResult.Append(other.intermediateResult);
this.intermediateResult.Append(other.intermediateResult); }
}
 /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// Called at the end of aggregation, to return the results of the aggregation.
/// Called at the end of aggregation, to return the results of the aggregation. /// </summary>
/// </summary> /// <returns></returns>
/// <returns></returns> public SqlString Terminate()
public SqlString Terminate() {
{ string output = string.Empty;
string output = string.Empty; //delete the trailing comma, if any
//delete the trailing comma, if any if (this.intermediateResult != null
if (this.intermediateResult != null && this.intermediateResult.Length > 0)
&& this.intermediateResult.Length > 0) {
{ output = this.intermediateResult.ToString(0, this.intermediateResult.Length - 1);
output = this.intermediateResult.ToString(0, this.intermediateResult.Length - 1); }
}
 return new SqlString(output);
return new SqlString(output); }
}
 public void Read(BinaryReader r)
public void Read(BinaryReader r) {
{ intermediateResult = new StringBuilder(r.ReadString());
intermediateResult = new StringBuilder(r.ReadString()); }
}
 public void Write(BinaryWriter w)
public void Write(BinaryWriter w) {
{ w.Write(this.intermediateResult.ToString());
w.Write(this.intermediateResult.ToString()); }
} }
}这里有几个比较重要的方法:Terminate,这个方法是聚合最后调用的方法,它返回最后的值。可以是SQL Server的任何标量。;Accumulate,聚合每处理一行数据的时候都会调用一次,并将要处理的数据传给方法。可以在函数内部进行比如比较,合并 之类的处理。;
 CREATE TABLE BookAuthors
CREATE TABLE BookAuthors (
( BookID int NOT NULL,
BookID int NOT NULL, AuthorName nvarchar(200) NOT NULL
AuthorName nvarchar(200) NOT NULL )
)
 INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(1, 'Johnson')
INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(1, 'Johnson') INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(2, 'Taylor')
INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(2, 'Taylor') INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(3, 'Steven')
INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(3, 'Steven') INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(2, 'Mayler')
INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(2, 'Mayler') INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(3, 'Roberts')
INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(3, 'Roberts') INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(3, 'Michaels')
INSERT BookAuthors VALUES(3, 'Michaels')
 SELECT BookID, dbo.MyAgg(AuthorName)
SELECT BookID, dbo.MyAgg(AuthorName) FROM BookAuthors
FROM BookAuthors GROUP BY BookID
GROUP BY BookID
| BookID | Author Names |
|---|---|
| 1 | Johnson |
| 2 | Taylor, Mayler |
| 3 | Roberts, Michaels, Steven |
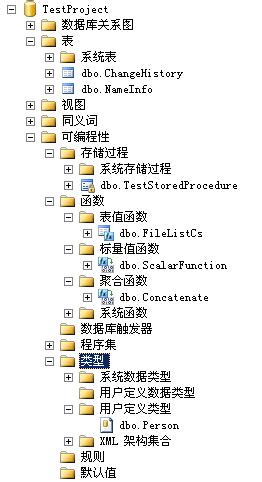
Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio为我们提供了数据库内对象的集中管理功能,前面几篇创建的SQLCLR对象,都可以在数据库的可编程性下相应模块里找到。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
系列文章目录


