Problem Description
For a tree, which nodes and edges are all weighted, the ratio of it is calculated according to the following equation.
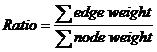
Given a complete graph of n nodes with all nodes and edges weighted, your task is to find a tree, which is a sub-graph of the original graph, with m nodes and whose ratio is the smallest among all the trees of m nodes in the graph.
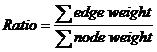
Given a complete graph of n nodes with all nodes and edges weighted, your task is to find a tree, which is a sub-graph of the original graph, with m nodes and whose ratio is the smallest among all the trees of m nodes in the graph.
Input
Input contains multiple test cases. The first line of each test case contains two integers n (2<=n<=15) and m (2<=m<=n), which stands for the number of nodes in the graph and the number of nodes in the minimal ratio tree. Two zeros end the input. The next line contains n numbers which stand for the weight of each node. The following n lines contain a diagonally symmetrical n×n connectivity matrix with each element shows the weight of the edge connecting one node with another. Of course, the diagonal will be all 0, since there is no edge connecting a node with itself.
All the weights of both nodes and edges (except for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix) are integers and in the range of [1, 100].
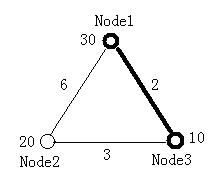
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form the minimal ratio tree.
All the weights of both nodes and edges (except for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix) are integers and in the range of [1, 100].
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form the minimal ratio tree.

Output
For each test case output one line contains a sequence of the m nodes which constructs the minimal ratio tree. Nodes should be arranged in ascending order. If there are several such sequences, pick the one which has the smallest node number; if there's a tie, look at the second smallest node number, etc. Please note that the nodes are numbered from 1 .
Sample Input
3 2
30 20 10
0 6 2
6 0 3
2 3 0
2 2
1 1
0 2
2 0
0 0
30 20 10
0 6 2
6 0 3
2 3 0
2 2
1 1
0 2
2 0
0 0
Sample Output
1 3
1 2
1 2
***************************************************************************************************************************
从n个点抽出m个点,组成最小生成树
***************************************************************************************************************************

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #include<cstdio> 6 using namespace std; 7 int vis1[1001],vis2[1001],ans[1001]; 8 double e[1001][1001],p[1001],dis[1001],minRatio; 9 int n,m,i,j; 10 double prime()//求最小生成树 11 { 12 int u; 13 memset(vis1,0,sizeof(vis1)); 14 int it,jt; 15 u=0; 16 while(!vis2[u]&&u<=n)u++; 17 vis1[u]=1; 18 double psum=0.0,esum=0.0; 19 for(it=1;it<=n;it++) 20 { 21 if(vis2[it]) 22 { 23 dis[it]=e[u][it]; 24 psum+=p[it]; 25 } 26 } 27 for(it=1;it<m;it++) 28 { 29 u=-1; 30 for(jt=1;jt<=n;jt++) 31 { 32 if(vis2[jt]&&!vis1[jt]) 33 if(u==-1||dis[jt]<dis[u]) 34 { 35 u=jt; 36 } 37 38 } 39 esum+=dis[u]; 40 vis1[u]=1; 41 for(jt=1;jt<=n;jt++) 42 { 43 if(!vis1[jt]&&vis2[jt]) 44 if(dis[jt]>e[u][jt]) 45 dis[jt]=e[u][jt]; 46 } 47 } 48 return esum/psum; 49 } 50 void dfs(int u,int num)//枚举 51 { 52 if(num>m)return; 53 if(u==n+1) 54 { 55 if(num!=m)return; 56 double t=prime(); 57 //cout<<"T:: "<<t<<endl; 58 if(t<minRatio) 59 { 60 minRatio=t; 61 memcpy(ans,vis2,sizeof(vis2));//记录 62 } 63 return; 64 } 65 vis2[u]=1; 66 dfs(u+1,num+1); 67 vis2[u]=0; 68 dfs(u+1,num); 69 70 } 71 int main() 72 { 73 while(scanf("%d %d",&n,&m)!=EOF) 74 { 75 if(n==0&&m==0) 76 break; 77 for(i=1;i<=n;i++) 78 { 79 scanf("%lf",&p[i]); 80 //printf("p::%lf ",p[i]); 81 } 82 for(i=1;i<=n;i++) 83 for(j=1;j<=n;j++) 84 { 85 scanf("%lf",&e[i][j]); 86 } 87 minRatio=10000000.0; 88 memset(vis2,0,sizeof(vis2)); 89 //memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans)); 90 dfs(1,0); 91 bool gs=0; 92 for(i=1;i<=n;i++) 93 { 94 if(ans[i]) 95 { 96 if(gs==0) 97 { 98 printf("%d",i); 99 gs=1; 100 } 101 else 102 { 103 printf(" %d",i); 104 } 105 } 106 } 107 puts(""); 108 } 109 return 0; 110 }
