在关联规则挖掘领域最经典的算法法是Apriori,其致命的缺点是需要多次扫描事务数据库。于是人们提出了各种裁剪(prune)数据集的方法以减少I/O开支,韩嘉炜老师的FP-Tree算法就是其中非常高效的一种。
名词约定
举个例子,设事务数据库为:
A E F G
A F G
A B E F G
E F G
每一行为一个事务,事务由若干个互不相同的项目构成,任意几个项目的组合称为一个模式。
上例中一共有4个事务。
模式{A,F,G}的支持数为3,支持度为3/4。支持数大于阈值minSuport的模式称为频繁模式(Frequent Patten)。
{F,G}的支持度数为4,支持度为4/4。
{A}的支持度数为3,支持度为3/4。
{F,G}=>{A}的置信度为:{A,F,G}的支持度数 除以 {F,G}的支持度数,即3/4
{A}=>{F,G}的置信度为:{A,F,G}的支持度数 除以 {A}的支持度数,即3/3
强关联规则挖掘是在满足一定支持度的情况下寻找置信度达到阈值的所有模式。
FP-Tree算法描述
算法描述:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
输入:事务集合 List<List<String>> transactions输出:频繁模式集合及相应的频数 Map<List<String>,Integer> FrequentPattens初始化 PostModel=[],CPB=transactionsvoid FPGrowth(List<List<String>> CPB,List<String> PostModel){ if CPB为空: return 统计CPB中每一个项目的计数,把计数小于最小支持数minSuport的删除掉,对于CPB中的每一条事务按项目计数降序排列。 由CPB构建FP-Tree,FP-Tree中包含了表头项headers,每一个header都指向了一个链表HeaderLinkList,链表中的每个元素都是FP-Tree上的一个节点,且节点名称与header.name相同。 for header in headers: newPostModel=header.name+PostModel 把<newPostModel, header.count>加到FrequentPattens中。 newCPB=[] for TreeNode in HeaderLinkList: 得到从FP-Tree的根节点到TreeNode的全路径path,把path作为一个事务添加到newCPB中,要重复添加TreeNode.count次。 FPGrowth(newCPB,newPostModel) |
算法的核心是FPGrowth函数,这是一个递归函数。CPB的全称是Conditional Pattern Base(条件模式基),我们可以把CPB理解为算法在不同阶段的事务集合。PostModel称为后缀模式,它是一个List。后文会详细讲CPB和PostModel是如何生成的,初始时令PostModel为空,令CPB就是原始的事务集合。
下面我们举个例子来详细讲解FPGrowth函数的完整实现。
事务数据库如下,一行表示一条购物记录:
牛奶,鸡蛋,面包,薯片
鸡蛋,爆米花,薯片,啤酒
鸡蛋,面包,薯片
牛奶,鸡蛋,面包,爆米花,薯片,啤酒
牛奶,面包,啤酒
鸡蛋,面包,啤酒
牛奶,面包,薯片
牛奶,鸡蛋,面包,黄油,薯片
牛奶,鸡蛋,黄油,薯片
令minSuport=3,统计每一个项目出现的次数,把次数低于minSuport的项目删除掉,剩下的项目按出现的次数降序排列,得到F1:
薯片:7 鸡蛋:7 面包:7 牛奶:6 啤酒:4
对于每一条事务,按照F1中的顺序重新排序,不在F1中的被删除掉。这样整个事务集合变为:
薯片,鸡蛋,面包,牛奶
薯片,鸡蛋,啤酒
薯片,鸡蛋,面包
薯片,鸡蛋,面包,牛奶,啤酒
面包,牛奶,啤酒
鸡蛋,面包,啤酒
薯片,面包,牛奶
薯片,鸡蛋,面包,牛奶
薯片,鸡蛋,牛奶
上面的事务集合即为当前的CPB,当前的PostModel依然为空。由CPB构建FP-Tree的步骤如下。
插入第一条事务(薯片,鸡蛋,面包,牛奶)之后

插入第二条事务(薯片,鸡蛋,啤酒)

插入第三条记录(面包,牛奶,啤酒)

估计你也知道怎么插了,最终生成的FP-Tree是:

上图中左边的那一叫做表头项,树中相同名称的节点要链接起来,链表的第一个元素就是表头项里的元素。不论是表头项节点还是FP-Tree中有节点,它们至少有2个属性:name和count。
现在我们已进行完算法描述的第10行。go on
遍历表头项中的每一项,我们拿“牛奶:6”为例。
新的PostModel为“表头项+老的PostModel”,现在由于老的PostModel还是空list,所以新的PostModel为:[牛奶]。新的PostModel就是一条频繁模式,它的支持数即为表头项的count:6,所以此处可以输出一条频繁模式<[牛奶], 6>
从表头项“牛奶”开始,找到FP-Tree中所有的“牛奶”节点,然后找到从树的根节点到“牛奶”节点的路径。得到4条路径:
薯片:7,鸡蛋:6,牛奶:1
薯片:7,鸡蛋:6,面包:4,牛奶:3
薯片:7,面包:1,牛奶:1
面包:1,牛奶:1
对于每一条路径上的节点,其count都设置为牛奶的count
薯片:1,鸡蛋:1,牛奶:1
薯片:3,鸡蛋:3,面包:3,牛奶:3
薯片:1,面包:1,牛奶:1
面包:1,牛奶:1
因为每一项末尾都是牛奶,可以把牛奶去掉,得到新的CPB:
薯片:1,鸡蛋:1
薯片:3,鸡蛋:3,面包:3
薯片:1,面包:1
面包:1
然后递归调用FPGrowth(新的CPB,新的PostModel),当发现新有CPB为空时递归就可以退出了。
几点说明
- 可以在构建FP-Tree之前就把CPB中低于minSuport的项目删掉,也可以先不删,而是在构建FP-Tree的过程当中如果遇到低于minSuport的项目不把它插入到FP-Tree中就可以了。FP-Tree算法之所以高效,就是因为它在每次FPGrowth递归时都对数据进行了这种裁剪。
- 没必要每次FPGrowth递归时都把CPB中的事务按F1做一次重排序,只需要第一次构建CPB时按F1做一次排序,以后每次构建新的CPB时保持与老的CPB各项目顺序不变就可以了。
- 对于FP-Tree已经是单枝的情况,就没有必要再递归调用FPGrowth了,直接输出整条路径上所有节点的各种组合+postModel就可了。例如当FP-Tree为:
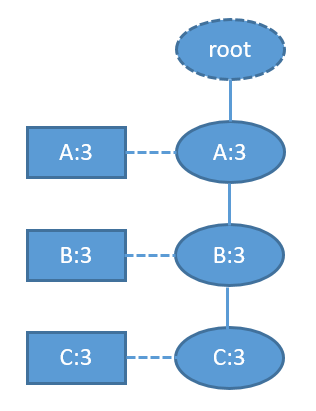
树上只有一条路径{A-B-C},在保证A-B-C这种顺序的前提下,这三个节点的所有组合是:A,B,C,AB,AC,BC,ABC。每一种组合与postModel拼接形成一条频繁模式,模式的支持数即为表头项的计数(单枝的情况下所有表头项和所有树节点的计数都是相同的)。
Java实现
StrongAssociationRule.java

import java.util.List;
public class StrongAssociationRule {
public List<String> condition;
public String result;
public int support;
public double confidence;
}
TreeNode.java

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
*
* @Description: FP树的节点
* @Author orisun
* @Date Jun 23, 2016
*/
class TreeNode {
/**节点名称**/
private String name;
/**频数**/
private int count;
private TreeNode parent;
private List<TreeNode> children;
/**下一个节点(由表头项维护的那个链表)**/
private TreeNode nextHomonym;
/**末节点(由表头项维护的那个链表)**/
private TreeNode tail;
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
public TreeNode() {
}
public TreeNode(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getCount() {
return this.count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public TreeNode getParent() {
return this.parent;
}
public void setParent(TreeNode parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public List<TreeNode> getChildren() {
return this.children;
}
public void addChild(TreeNode child) {
if (getChildren() == null) {
List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
list.add(child);
setChildren(list);
} else {
getChildren().add(child);
}
}
public TreeNode findChild(String name) {
List<TreeNode> children = getChildren();
if (children != null) {
for (TreeNode child : children) {
if (child.getName().equals(name)) {
return child;
}
}
}
return null;
}
public void setChildren(List<TreeNode> children) {
this.children = children;
}
public void printChildrenName() {
List<TreeNode> children = getChildren();
if (children != null) {
for (TreeNode child : children)
System.out.print(child.getName() + " ");
} else
System.out.print("null");
}
public TreeNode getNextHomonym() {
return this.nextHomonym;
}
public void setNextHomonym(TreeNode nextHomonym) {
this.nextHomonym = nextHomonym;
}
public void countIncrement(int n) {
this.count += n;
}
public TreeNode getTail() {
return tail;
}
public void setTail(TreeNode tail) {
this.tail = tail;
}
}
FPTree.java

import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
/**
*
* @Description: FPTree强关联规则挖掘算法
* @Author orisun
* @Date Jun 23, 2016
*/
public class FPTree {
/**频繁模式的最小支持数**/
private int minSuport;
/**关联规则的最小置信度**/
private double confident;
/**事务项的总数**/
private int totalSize;
/**存储每个频繁项及其对应的计数**/
private Map<List<String>, Integer> frequentMap = new HashMap<List<String>, Integer>();
/**关联规则中,哪些项可作为被推导的结果,默认情况下所有项都可以作为被推导的结果**/
private Set<String> decideAttr = null;
public int getMinSuport() {
return this.minSuport;
}
/**
* 设置最小支持数
*
* @param minSuport
*/
public void setMinSuport(int minSuport) {
this.minSuport = minSuport;
}
public double getConfident() {
return confident;
}
/**
* 设置最小置信度
*
* @param confident
*/
public void setConfident(double confident) {
this.confident = confident;
}
/**
* 设置决策属性。如果要调用{@linkplain #readTransRocords(String[])},需要在调用{@code readTransRocords}之后再调用{@code setDecideAttr}
*
* @param decideAttr
*/
public void setDecideAttr(Set<String> decideAttr) {
this.decideAttr = decideAttr;
}
/**
* 获取频繁项集
*
* @return
* @Description:
*/
public Map<List<String>, Integer> getFrequentItems() {
return frequentMap;
}
public int getTotalSize() {
return totalSize;
}
/**
* 根据一条频繁模式得到若干关联规则
*
* @param list
* @return
*/
private List<StrongAssociationRule> getRules(List<String> list) {
List<StrongAssociationRule> rect = new LinkedList<StrongAssociationRule>();
if (list.size() > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String result = list.get(i);
if (decideAttr.contains(result)) {
List<String> condition = new ArrayList<String>();
condition.addAll(list.subList(0, i));
condition.addAll(list.subList(i + 1, list.size()));
StrongAssociationRule rule = new StrongAssociationRule();
rule.condition = condition;
rule.result = result;
rect.add(rule);
}
}
}
return rect;
}
/**
* 从若干个文件中读入Transaction Record,同时把所有项设置为decideAttr
*
* @param filenames
* @return
* @Description:
*/
public List<List<String>> readTransRocords(String[] filenames) {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<String>();
List<List<String>> transaction = null;
if (filenames.length > 0) {
transaction = new LinkedList<List<String>>();
for (String filename : filenames) {
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(filename);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
try {
String line = null;
// 一项事务占一行
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
if (line.trim().length() > 0) {
// 每个item之间用","分隔
String[] str = line.split(",");
//每一项事务中的重复项需要排重
Set<String> record = new HashSet<String>();
for (String w : str) {
record.add(w);
set.add(w);
}
List<String> rl = new ArrayList<String>();
rl.addAll(record);
transaction.add(rl);
}
}
} finally {
br.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println("Read transaction records failed." + ex.getMessage());
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
this.setDecideAttr(set);
return transaction;
}
/**
* 生成一个序列的各种子序列。(序列是有顺序的)
*
* @param residualPath
* @param results
*/
private void combine(LinkedList<TreeNode> residualPath, List<List<TreeNode>> results) {
if (residualPath.size() > 0) {
//如果residualPath太长,则会有太多的组合,内存会被耗尽的
TreeNode head = residualPath.poll();
List<List<TreeNode>> newResults = new ArrayList<List<TreeNode>>();
for (List<TreeNode> list : results) {
List<TreeNode> listCopy = new ArrayList<TreeNode>(list);
newResults.add(listCopy);
}
for (List<TreeNode> newPath : newResults) {
newPath.add(head);
}
results.addAll(newResults);
List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
list.add(head);
results.add(list);
combine(residualPath, results);
}
}
private boolean isSingleBranch(TreeNode root) {
boolean rect = true;
while (root.getChildren() != null) {
if (root.getChildren().size() > 1) {
rect = false;
break;
}
root = root.getChildren().get(0);
}
return rect;
}
/**
* 计算事务集中每一项的频数
*
* @param transRecords
* @return
*/
private Map<String, Integer> getFrequency(List<List<String>> transRecords) {
Map<String, Integer> rect = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
for (List<String> record : transRecords) {
for (String item : record) {
Integer cnt = rect.get(item);
if (cnt == null) {
cnt = new Integer(0);
}
rect.put(item, ++cnt);
}
}
return rect;
}
/**
* 根据事务集合构建FPTree
*
* @param transRecords
* @Description:
*/
public void buildFPTree(List<List<String>> transRecords) {
totalSize = transRecords.size();
//计算每项的频数
final Map<String, Integer> freqMap = getFrequency(transRecords);
//先把频繁1项集添加到频繁模式中
// for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : freqMap.entrySet()) {
// String name = entry.getKey();
// int cnt = entry.getValue();
// if (cnt >= minSuport) {
// List<String> rule = new ArrayList<String>();
// rule.add(name);
// frequentMap.put(rule, cnt);
// }
// }
//每条事务中的项按F1排序
for (List<String> transRecord : transRecords) {
Collections.sort(transRecord, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return freqMap.get(o2) - freqMap.get(o1);
}
});
}
FPGrowth(transRecords, null);
}
/**
* FP树递归生长,从而得到所有的频繁模式
*
* @param cpb 条件模式基
* @param postModel 后缀模式
*/
private void FPGrowth(List<List<String>> cpb, LinkedList<String> postModel) {
// System.out.println("CPB is");
// for (List<String> records : cpb) {
// System.out.println(records);
// }
// System.out.println("PostPattern is " + postPattern);
Map<String, Integer> freqMap = getFrequency(cpb);
Map<String, TreeNode> headers = new HashMap<String, TreeNode>();
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : freqMap.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
int cnt = entry.getValue();
//每一次递归时都有可能出现一部分模式的频数低于阈值
if (cnt >= minSuport) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(name);
node.setCount(cnt);
headers.put(name, node);
}
}
TreeNode treeRoot = buildSubTree(cpb, freqMap, headers);
//如果只剩下虚根节点,则递归结束
if ((treeRoot.getChildren() == null) || (treeRoot.getChildren().size() == 0)) {
return;
}
//如果树是单枝的,则直接把“路径的各种组合+后缀模式”添加到频繁模式集中。这个技巧是可选的,即跳过此步进入下一轮递归也可以得到正确的结果
if (isSingleBranch(treeRoot)) {
LinkedList<TreeNode> path = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode currNode = treeRoot;
while (currNode.getChildren() != null) {
currNode = currNode.getChildren().get(0);
path.add(currNode);
}
//调用combine时path不宜过长,否则会OutOfMemory
if (path.size() <= 20) {
List<List<TreeNode>> results = new ArrayList<List<TreeNode>>();
combine(path, results);
for (List<TreeNode> list : results) {
int cnt = 0;
List<String> rule = new ArrayList<String>();
for (TreeNode node : list) {
rule.add(node.getName());
cnt = node.getCount();//cnt最FPTree叶节点的计数
}
if (postModel != null) {
rule.addAll(postModel);
}
frequentMap.put(rule, cnt);
}
return;
} else {
System.err.println("length of path is too long: " + path.size());
}
}
for (TreeNode header : headers.values()) {
List<String> rule = new ArrayList<String>();
rule.add(header.getName());
if (postModel != null) {
rule.addAll(postModel);
}
//表头项+后缀模式 构成一条频繁模式(频繁模式内部也是按照F1排序的),频繁度为表头项的计数
frequentMap.put(rule, header.getCount());
//新的后缀模式:表头项+上一次的后缀模式(注意保持顺序,始终按F1的顺序排列)
LinkedList<String> newPostPattern = new LinkedList<String>();
newPostPattern.add(header.getName());
if (postModel != null) {
newPostPattern.addAll(postModel);
}
//新的条件模式基
List<List<String>> newCPB = new LinkedList<List<String>>();
TreeNode nextNode = header;
while ((nextNode = nextNode.getNextHomonym()) != null) {
int counter = nextNode.getCount();
//获得从虚根节点(不包括虚根节点)到当前节点(不包括当前节点)的路径,即一条条件模式基。注意保持顺序:你节点在前,子节点在后,即始终保持频率高的在前
LinkedList<String> path = new LinkedList<String>();
TreeNode parent = nextNode;
while ((parent = parent.getParent()).getName() != null) {//虚根节点的name为null
path.push(parent.getName());//往表头插入
}
//事务要重复添加counter次
while (counter-- > 0) {
newCPB.add(path);
}
}
FPGrowth(newCPB, newPostPattern);
}
}
/**
* 把所有事务插入到一个FP树当中
*
* @param transRecords
* @param F1
* @return
*/
private TreeNode buildSubTree(List<List<String>> transRecords,
final Map<String, Integer> freqMap,
final Map<String, TreeNode> headers) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode();//虚根节点
for (List<String> transRecord : transRecords) {
LinkedList<String> record = new LinkedList<String>(transRecord);
TreeNode subTreeRoot = root;
TreeNode tmpRoot = null;
if (root.getChildren() != null) {
//延已有的分支,令各节点计数加1
while (!record.isEmpty()
&& (tmpRoot = subTreeRoot.findChild(record.peek())) != null) {
tmpRoot.countIncrement(1);
subTreeRoot = tmpRoot;
record.poll();
}
}
//长出新的节点
addNodes(subTreeRoot, record, headers);
}
return root;
}
/**
* 往特定的节点下插入一串后代节点,同时维护表头项到同名节点的链表指针
*
* @param ancestor
* @param record
* @param headers
*/
private void addNodes(TreeNode ancestor, LinkedList<String> record,
final Map<String, TreeNode> headers) {
while (!record.isEmpty()) {
String item = (String) record.poll();
//单个项的出现频数必须大于最小支持数,否则不允许插入FP树。达到最小支持度的项都在headers中。每一次递归根据条件模式基本建立新的FPTree时,把要把频数低于minSuport的排除在外,这也正是FPTree比穷举法快的真正原因
if (headers.containsKey(item)) {
TreeNode leafnode = new TreeNode(item);
leafnode.setCount(1);
leafnode.setParent(ancestor);
ancestor.addChild(leafnode);
TreeNode header = headers.get(item);
TreeNode tail=header.getTail();
if(tail!=null){
tail.setNextHomonym(leafnode);
}else{
header.setNextHomonym(leafnode);
}
header.setTail(leafnode);
addNodes(leafnode, record, headers);
}
// else {
// System.err.println(item + " is not F1");
// }
}
}
/**
* 获取所有的强规则
*
* @return
*/
public List<StrongAssociationRule> getAssociateRule() {
assert totalSize > 0;
List<StrongAssociationRule> rect = new ArrayList<StrongAssociationRule>();
//遍历所有频繁模式
for (Entry<List<String>, Integer> entry : frequentMap.entrySet()) {
List<String> items = entry.getKey();
int count1 = entry.getValue();
//一条频繁模式可以生成很多关联规则
List<StrongAssociationRule> rules = getRules(items);
//计算每一条关联规则的支持度和置信度
for (StrongAssociationRule rule : rules) {
if (frequentMap.containsKey(rule.condition)) {
int count2 = frequentMap.get(rule.condition);
double confidence = 1.0 * count1 / count2;
if (confidence >= this.confident) {
rule.support = count1;
rule.confidence = confidence;
rect.add(rule);
}
} else {
System.err.println(rule.condition + " is not a frequent pattern, however "
+ items + " is a frequent pattern");
}
}
}
return rect;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String infile = "trolley.txt";
FPTree fpTree = new FPTree();
fpTree.setConfident(0.6);
fpTree.setMinSuport(3);
if (args.length >= 2) {
double confidence = Double.parseDouble(args[0]);
int suport = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
fpTree.setConfident(confidence);
fpTree.setMinSuport(suport);
}
List<List<String>> trans = fpTree.readTransRocords(new String[] { infile });
Set<String> decideAttr = new HashSet<String>();
decideAttr.add("鸡蛋");
decideAttr.add("面包");
fpTree.setDecideAttr(decideAttr);
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
fpTree.buildFPTree(trans);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("buildFPTree use time " + (end - begin));
Map<List<String>, Integer> pattens = fpTree.getFrequentItems();
String outfile = "pattens.txt";
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(outfile));
System.out.println("模式 频数");
bw.write("模式 频数");
bw.newLine();
for (Entry<List<String>, Integer> entry : pattens.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue());
bw.write(joinList(entry.getKey()) + " " + entry.getValue());
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
System.out.println();
List<StrongAssociationRule> rules = fpTree.getAssociateRule();
outfile = "rule.txt";
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(outfile));
System.out.println("条件 结果 支持度 置信度");
bw.write("条件 结果 支持度 置信度");
bw.newLine();
DecimalFormat dfm = new DecimalFormat("#.##");
for (StrongAssociationRule rule : rules) {
System.out.println(rule.condition + "->" + rule.result + " " + dfm.format(rule.support)
+ " " + dfm.format(rule.confidence));
bw.write(rule.condition + "->" + rule.result + " " + dfm.format(rule.support) + " "
+ dfm.format(rule.confidence));
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
private static String joinList(List<String> list) {
if (list == null || list.size() == 0) {
return "";
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String ele : list) {
sb.append(ele);
sb.append(",");
}
//把最后一个逗号去掉
return sb.substring(0, sb.length() - 1);
}
}
输入trolley.txt
牛奶,鸡蛋,面包,薯片
鸡蛋,爆米花,薯片,啤酒
鸡蛋,面包,薯片
牛奶,鸡蛋,面包,爆米花,薯片,啤酒
牛奶,面包,啤酒
鸡蛋,面包,啤酒
牛奶,面包,薯片
牛奶,鸡蛋,面包,黄油,薯片
牛奶,鸡蛋,黄油,薯片
输出pattens.txt
模式 频数
面包,啤酒 3
鸡蛋,牛奶 4
面包,薯片 5
薯片,鸡蛋 6
啤酒 4
薯片 7
面包,薯片,鸡蛋,牛奶 3
鸡蛋,啤酒 3
面包,牛奶 5
薯片,鸡蛋,牛奶 4
面包,鸡蛋,牛奶 3
面包 7
牛奶 6
面包,薯片,鸡蛋 4
薯片,牛奶 5
鸡蛋 7
面包,鸡蛋 5
面包,薯片,牛奶 4
输出rule.txt
条件 结果 支持度 置信度
[啤酒]->面包 3 0.75
[牛奶]->鸡蛋 4 0.67
[薯片]->面包 5 0.71
[薯片]->鸡蛋 6 0.86
[薯片, 鸡蛋, 牛奶]->面包 3 0.75
[面包, 薯片, 牛奶]->鸡蛋 3 0.75
[啤酒]->鸡蛋 3 0.75
[牛奶]->面包 5 0.83
[薯片, 牛奶]->鸡蛋 4 0.8
[鸡蛋, 牛奶]->面包 3 0.75
[面包, 牛奶]->鸡蛋 3 0.6
[薯片, 鸡蛋]->面包 4 0.67
[面包, 薯片]->鸡蛋 4 0.8
[鸡蛋]->面包 5 0.71
[面包]->鸡蛋 5 0.71
[薯片, 牛奶]->面包 4 0.8
MapReduce实现
在上面的代码我们把整个事务数据库放在一个List<List<String>>里面传给FPGrowth,在实际中这是不可取的,因为内存不可能容下整个事务数据库,我们可能需要从关系关系数据库中一条一条地读入来建立FP-Tree。但无论如何 FP-Tree是肯定需要放在内存中的,但内存如果容不下怎么办?另外FPGrowth仍然是非常耗时的,你想提高速度怎么办?解决办法:分而治之,并行计算。
按照论文《FP-Growth 算法MapReduce 化研究》中介绍的方法,把以相同项目结尾的patten输出一个Reducer里面去,在Reducer中仅对这一部分patten建立FPTree,这种FPTree会小很多,一般不会占用太多的内存。另外论文中的方法不需要维护表头项。
结束语
在实践中,关联规则挖掘可能并不像人们期望的那么有用。一方面是因为支持度置信度框架会产生过多的规则,并不是每一个规则都是有用的。另一方面大部分的关联规则并不像“啤酒与尿布”这种经典故事这么普遍。关联规则分析是需要技巧的,有时需要用更严格的统计学知识来控制规则的增殖。
原文来自:博客园(华夏35度)http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangchaoyang 作者:Orisun
