SqueezeNet
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07360
和别的轻量级模型一样,模型的设计目标就是在保证精度的情况下尽量减少模型参数.核心是论文提出的一种叫"fire module"的卷积方式.
设计策略
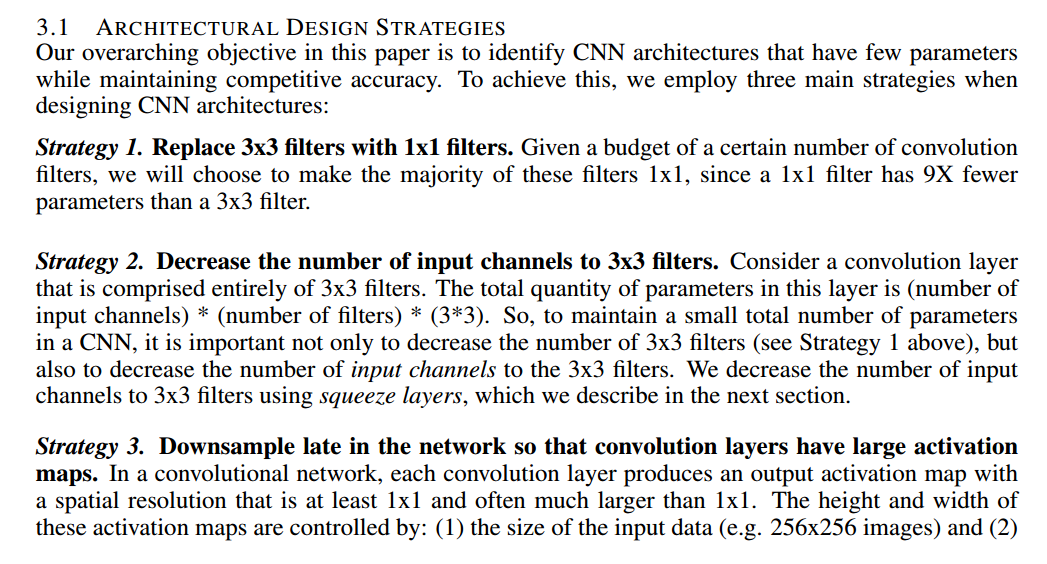
- 主要用1x1卷积核,而不是3x3.
- 减少3x3卷积核作用的channel.
- 推迟下采样的时间.以获取更大尺寸的feature map.这一点是处于精度的考虑.毕竟feature map的resolution越大,信息越丰富.下采样主要通过pool来完成或者卷积的时候控制stride大小.
Fire Module
这个就是网络的核心组件了.
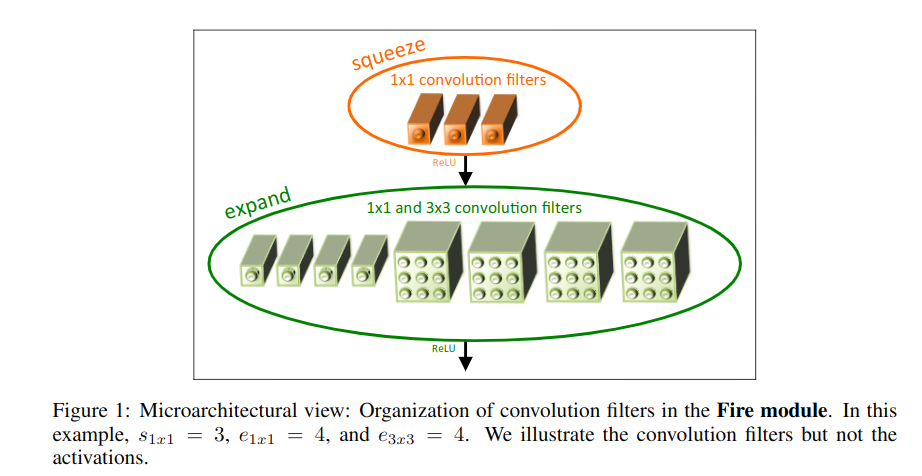
分2部分:
- squeeze convolution layer
- expand layer
其中squeeze只有1x1filter,expand layer由1x1和3x3filter组成.
在squeeze层卷积核数记为(s_{1x1}),在expand层,记1x1卷积核数为(e_{1x1}),而3x3卷积核数为(e_{3x3}),这三个属于超参数,可调。为了尽量降低3x3的输入通道数,让(s_{1x1}<e_{1x1}+e_{3x3})。
这两层的设计分别体现了策略1(多用1x1filter)和策略2(减少3x3filter作用channel).
首先,squeeze convolution layer通过控制1x1卷积核数量达到把输入的channel数目降低的目的.这个是降低参数的最关键的一步.
然后,分别用1x1卷积核和3x3卷积核去做卷积.然后得到不同depth的输出,concat起来.([x,x,depth1],[x,x,depth2]-->[x,x,depth1+depth2])
代码实现
torch的官方实现:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torchvision/models/squeezenet.html
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class Fire(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplanes, squeeze_planes,
expand1x1_planes, expand3x3_planes):
super(Fire, self).__init__()
self.inplanes = inplanes
self.squeeze = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, squeeze_planes, kernel_size=1)
self.squeeze_activation = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.expand1x1 = nn.Conv2d(squeeze_planes, expand1x1_planes,
kernel_size=1)
self.expand1x1_activation = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.expand3x3 = nn.Conv2d(squeeze_planes, expand3x3_planes,
kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.expand3x3_activation = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.squeeze_activation(self.squeeze(x))
print(x.shape)
e_1 = self.expand1x1(x)
print(e_1.shape)
e_3 = self.expand3x3(x)
print(e_3.shape)
return torch.cat([
self.expand1x1_activation(e_1),
self.expand3x3_activation(e_3)
], 1)
很显然地,squeeze convolution layer把channel数量降下来了,所以参数少了很多.
以输入tensor为[n,c,h,w]=[1,96,224,224]举例,假设fire module的squeeze layer的卷积核数量为6,expand layer中1x1卷积核数量为5,3x3卷积核数量为4.
则fire module的参数数量为1x1x96x6 + 1x1x6x5 + 3x3x6x4=822.
普通的3x3卷积,得到depth=9的feature map的话需要3x3x96x9=7776个参数.
所以模型才可以做到很小.
网络结构

基本就是fire module的堆叠.中间穿插了一些maxpool对feature map下采样. 注意一下最后用了dropout以及全局平均池化而不是全连接来完成分类.
最左边的就是类似vgg的堆叠式的结构.中间和右边的参考了resnet的skip-connection.
class SqueezeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, version='1_0', num_classes=1000):
super(SqueezeNet, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
if version == '1_0':
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 96, kernel_size=7, stride=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(96, 16, 64, 64),
Fire(128, 16, 64, 64),
Fire(128, 32, 128, 128),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(256, 32, 128, 128),
Fire(256, 48, 192, 192),
Fire(384, 48, 192, 192),
Fire(384, 64, 256, 256),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(512, 64, 256, 256),
)
elif version == '1_1':
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(64, 16, 64, 64),
Fire(128, 16, 64, 64),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(128, 32, 128, 128),
Fire(256, 32, 128, 128),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True),
Fire(256, 48, 192, 192),
Fire(384, 48, 192, 192),
Fire(384, 64, 256, 256),
Fire(512, 64, 256, 256),
)
else:
# FIXME: Is this needed? SqueezeNet should only be called from the
# FIXME: squeezenet1_x() functions
# FIXME: This checking is not done for the other models
raise ValueError("Unsupported SqueezeNet version {version}:"
"1_0 or 1_1 expected".format(version=version))
# Final convolution is initialized differently from the rest
final_conv = nn.Conv2d(512, self.num_classes, kernel_size=1)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
final_conv,
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
if m is final_conv:
init.normal_(m.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.01)
else:
init.kaiming_uniform_(m.weight)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.classifier(x)
return torch.flatten(x, 1)
https://pytorch.org/hub/pytorch_vision_squeezenet/
这里有一个用torch中的模型做推理的例子,
.....
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(input_batch)
# Tensor of shape 1000, with confidence scores over Imagenet's 1000 classes
print(output[0])
# The output has unnormalized scores. To get probabilities, you can run a softmax on it.
print(torch.nn.functional.softmax(output[0], dim=0))
CNN结构设计的探索
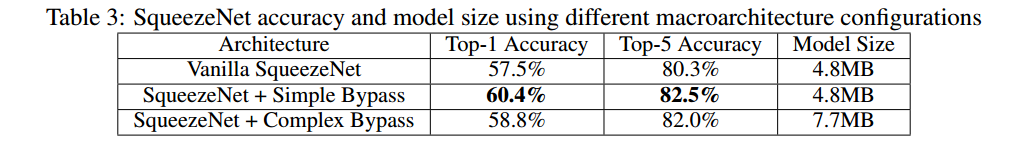
主要从2个方面做实验探讨了不同结构对模型精度和模型大小的影响.

- fire module怎么设计,squeeze layer和expand layer的filter数量怎么设计
- fire module怎么串起来形成一个网络,是简单堆叠还是引入bypass
关于第一点fire module中各种filter占比的实验结果如下图:

这里的sr指的是squeeze layer的卷积核数量/expand layer比例.3x3filter比例指expand layer里3x3filter比例.
具体设计参考论文:

一点思考:
1x1的卷积核关联了某个位置的feature所有channel上的信息.3x3的卷积核关联了多个位置的feature的所有channel的信息.按道理说3x3的越多应该模型精度越好,但实验数据显示并非如此.可能有些是噪音,3x3卷积参考太多周围的feature反而导致精度下降. 这也是深度学习现在被比较多诟病的一点,太黑盒了.只知道能work,为啥work不好解释.不同的数据集可能不同的参数表现会不一样,很难讲哪个最优,调参比较依赖经验.
关于第二点在layer之间采用不同的连接方式,实验结果如下: