前言
- pytest默认按字母顺序去执行的(小写英文--->大写英文--->0-9数字)
- 用例之间的顺序是文件之间按照ASCLL码排序,文件内的用例按照从上往下执行。
- setup_module->setup_claas->setup_function->testcase->teardown_function->teardown_claas->teardown_module
- 可以通过第三方插件
pytest-ordering实现自定义用例执行顺序 - 官方文档: https://pytest-ordering.readthedocs.io/en/develop/
- 注意:一旦设置了自定义的执行顺序,就必须得延伸
@pytest.mark.run(order=1)里面得order字段
代码实现
安装插件
pip install pytest-ordering
目录结构
- 为了演示,新建了个项目,目录结构。
- 新建用例必须严格遵守pytest的规范创建。

# test_login.py
def test_login02():
assert 1 == 1
def test_login01():
assert True
# test_project.py
def test_01():
assert True
# test_three.py
def test_02():
assert True
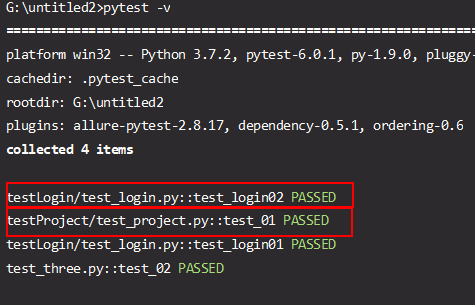
执行结果
- 用例执行顺序:test_three.py > testLogin/test_login.py > testProject/test_project
- 在.py文件内是从上往下执行,不管大小排序。

pytest-ordering使用
方式一
- 第一个执行:
@ pytest.mark.first - 第二个执行:
@ pytest.mark.second - 倒数第二个执行:
@ pytest.mark.second_to_last - 最后一个执行:
@pytest.mark.last
方式二
- 第一个执行:
@ pytest.mark.run('first') - 第二个执行:
@ pytest.mark.run('second') - 倒数第二个执行:
@ pytest.mark.run('second_to_last') - 最后一个执行:
@ pytest.mark.run('last')
方式三
- 第一个执行:
@ pytest.mark.run(order=1) - 第二个执行:
@ pytest.mark.run(order=2) - 倒数第二个执行:
@ pytest.mark.run(order=-2) - 最后一个执行:
@ pytest.mark.run(order=-1)
以上三种方式可以自行尝试,以下情况需要特别注意,我们就那上面的文件举例说明。
# test_login.py
@pytest.mark.run(order=1)
def test_login02():
assert 1 == 1
@pytest.mark.run(order=2)
def test_login01():
assert True
# test_project.py
@pytest.mark.run(order=1)
def test_01():
assert True
# test_three.py
def test_02():
assert True
已经改变了用例执行规则,针对于是全局的,会先执行完@pytest.mark.run(order=1)才会执行order=2的用例
其实总体来说,这个插件的实用场景不是很多,如果需要指定某个用例第一个执行和最后执行,可以用该插件实现。
如果要按照你指定的顺序执行下去,需要在每个用例前都加上@pytest.mark.run(order=1),其中order中的数字需递增。