普通对象的结构如下,按64位机器的长度计算
1. 对象头(_mark), 8个字节
2. Oop指针,如果是32G内存以下的,默认开启对象指针压缩,4个字节
3. 数据区
4.Padding(内存对齐),按照8的倍数对齐
数组对象结构是
1. 对象头(_mark), 8个字节
2. Oop指针,如果是32G内存以下的,默认开启对象指针压缩,4个字节
3. 数组长度,4个字节
4. 数据区
5. Padding(内存对齐),按照8的倍数对齐
清楚了对象在内存的基本布局后,咱们说两种计算Java对象大小的方法
1. 通过java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation的getObjectSize(obj)直接获取对象的大小
2. 通过sun.misc.Unsafe对象的objectFieldOffset(field)等方法结合反射来计算对象的大小
java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation.getObjectSize()的方式
先讲讲java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation.getObjectSize()的方式,这种方法得到的是Shallow Size,即遇到引用时,只计算引用的长度,不计算所引用的对象的实际大小。如果要计算所引用对象的实际大小,可以通过递归的方式去计算。
java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation的实例必须通过指定javaagent的方式才能获得,具体的步骤如下:
1. 定义一个类,提供一个premain方法: public static void premain(String agentArgs, Instrumentation instP)
2. 创建META-INF/MANIFEST.MF文件,内容是指定PreMain的类是哪个: Premain-Class: sizeof.ObjectShallowSize
3. 把这个类打成jar,然后用java -javaagent XXXX.jar XXX.main的方式执行
下面先定义一个类来获得java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation的实例,并提供了一个static的sizeOf方法对外提供Instrumentation的能力
- package sizeof;
- import java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation;
- public class ObjectShallowSize {
- private static Instrumentation inst;
- public static void premain(String agentArgs, Instrumentation instP){
- inst = instP;
- }
- public static long sizeOf(Object obj){
- return inst.getObjectSize(obj);
- }
- }
定义META-INF/MANIFEST.MF文件
- Premain-Class: sizeof.ObjectShallowSize
打成jar包
- cd 编译后的类和META-INF文件夹所在目录
- jar cvfm java-agent-sizeof.jar META-INF/MANIFEST.MF .
准备好了这个jar之后,我们可以写测试类来测试Instrumentation的getObjectSize方法了。在这之前我们先来看对象在内存中是按照什么顺序排列的
有如下这个类,字段的定义按如下顺序
- private static class ObjectA {
- String str; // 4
- int i1; // 4
- byte b1; // 1
- byte b2; // 1
- int i2; // 4
- ObjectB obj; //4
- byte b3; // 1
- }
按照我们之前说的方法来计算一下这个对象所占大小,注意按8对齐
8(_mark) + 4(oop指针) + 4(str) + 4(i1) + 1(b1) + 1(b2) + 2(padding) + 4(i2) + 4(obj) + 1(b3) + 7(padding) = 40 ?
但事实上是这样的吗? 我们来用Instrumentation的getObjectSize来计算一下先:
- package test;
- import sizeof.ObjectShallowSize;
- public class SizeofWithInstrumetation {
- private static class ObjectA {
- String str; // 4
- int i1; // 4
- byte b1; // 1
- byte b2; // 1
- int i2; // 4
- ObjectB obj; //4
- byte b3; // 1
- }
- private static class ObjectB {
- }
- public static void main(String[] args){
- System.out.println(ObjectShallowSize.sizeOf(new ObjectA()));
- }
- }
得到的结果是32!不是会按8对齐吗,b3之前的数据加起来已经是32了,多了1个b3,为33,应该对齐到40才对啊。事实上,HotSpot创建的对象的字段会先按照给定顺序排列一下,默认的顺序如下,从长到短排列,引用排最后: long/double --> int/float --> short/char --> byte/boolean --> Reference
这个顺序可以使用JVM参数: -XX:FieldsAllocationSylte=0(默认是1)来改变。
我们使用sun.misc.Unsafe对象的objectFieldOffset方法来验证一下:
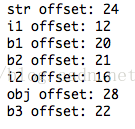
- Field[] fields = ObjectA.class.getDeclaredFields();
- for(Field f: fields){
- System.out.println(f.getName() + " offset: " +unsafe.objectFieldOffset(f));
- }
可以看到确实是按照从长到短,引用排最后的方式在内存中排列的。按照这种方法我们来重新计算下ObjectA创建的对象的长度:
8(_mark) + 4(oop指针) + 4(i1) + + 4(i2) + 1(b1) + 1(b2) + 1(b3) + 1(padding) + 4(str) + 4(obj) = 32
得到的结果和java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation.getObjectSize()的结果是一样的,证明我们的计算方式是正确的。
sun.misc.Unsafe的方式
下面说一下通过sun.misc.Unsafe对象的objectFieldOffset(field)等方法结合反射来计算对象的大小。基本的思路如下:
1. 通过反射获得一个类的Field
2. 通过Unsafe的objectFieldOffset()获得每个Field的offSet
3. 对Field按照offset排序,取得最大的offset,然后加上这个field的长度,再加上Padding对齐
上面三步就可以获得一个对象的Shallow size。可以进一步通过递归去计算所引用对象的大小,从而可以计算出一个对象所占用的实际大小。
如何获得Unsafe对象已经在这篇中聊聊序列化(二)使用sun.misc.Unsafe绕过new机制来创建Java对象说过了,可以通过反射的机制来获得.
Oop指针是4还是未压缩的8也可以通过unsafe.arrayIndexScale(Object[].class)来获得,这个方法返回一个引用所占用的长度
- static {
- try {
- Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
- field.setAccessible(true);
- unsafe = (Unsafe) field.get(null);
- objectRefSize = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(Object[].class);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
下面的源码摘自 http://java-performance.info/memory-introspection-using-sun-misc-unsafe-and-reflection/, 原文中的代码在计算对象大小的时候有问题,我做了微调,并加上了内存对齐的方法,这样计算出的结果和Instrumentation的getObjectSize方法是一样的。
- package test;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Collections;
- import java.util.Comparator;
- import java.util.List;
- /**
- * This class contains object info generated by ClassIntrospector tool
- */
- public class ObjectInfo {
- /** Field name */
- public final String name;
- /** Field type name */
- public final String type;
- /** Field data formatted as string */
- public final String contents;
- /** Field offset from the start of parent object */
- public final int offset;
- /** Memory occupied by this field */
- public final int length;
- /** Offset of the first cell in the array */
- public final int arrayBase;
- /** Size of a cell in the array */
- public final int arrayElementSize;
- /** Memory occupied by underlying array (shallow), if this is array type */
- public final int arraySize;
- /** This object fields */
- public final List<ObjectInfo> children;
- public ObjectInfo(String name, String type, String contents, int offset, int length, int arraySize,
- int arrayBase, int arrayElementSize)
- {
- this.name = name;
- this.type = type;
- this.contents = contents;
- this.offset = offset;
- this.length = length;
- this.arraySize = arraySize;
- this.arrayBase = arrayBase;
- this.arrayElementSize = arrayElementSize;
- children = new ArrayList<ObjectInfo>( 1 );
- }
- public void addChild( final ObjectInfo info )
- {
- if ( info != null )
- children.add( info );
- }
- /**
- * Get the full amount of memory occupied by a given object. This value may be slightly less than
- * an actual value because we don't worry about memory alignment - possible padding after the last object field.
- *
- * The result is equal to the last field offset + last field length + all array sizes + all child objects deep sizes
- * @return Deep object size
- */
- public long getDeepSize()
- {
- //return length + arraySize + getUnderlyingSize( arraySize != 0 );
- return addPaddingSize(arraySize + getUnderlyingSize( arraySize != 0 ));
- }
- long size = 0;
- private long getUnderlyingSize( final boolean isArray )
- {
- //long size = 0;
- for ( final ObjectInfo child : children )
- size += child.arraySize + child.getUnderlyingSize( child.arraySize != 0 );
- if ( !isArray && !children.isEmpty() ){
- int tempSize = children.get( children.size() - 1 ).offset + children.get( children.size() - 1 ).length;
- size += addPaddingSize(tempSize);
- }
- return size;
- }
- private static final class OffsetComparator implements Comparator<ObjectInfo>
- {
- @Override
- public int compare( final ObjectInfo o1, final ObjectInfo o2 )
- {
- return o1.offset - o2.offset; //safe because offsets are small non-negative numbers
- }
- }
- //sort all children by their offset
- public void sort()
- {
- Collections.sort( children, new OffsetComparator() );
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- toStringHelper( sb, 0 );
- return sb.toString();
- }
- private void toStringHelper( final StringBuilder sb, final int depth )
- {
- depth( sb, depth ).append("name=").append( name ).append(", type=").append( type )
- .append( ", contents=").append( contents ).append(", offset=").append( offset )
- .append(", length=").append( length );
- if ( arraySize > 0 )
- {
- sb.append(", arrayBase=").append( arrayBase );
- sb.append(", arrayElemSize=").append( arrayElementSize );
- sb.append( ", arraySize=").append( arraySize );
- }
- for ( final ObjectInfo child : children )
- {
- sb.append( ' ' );
- child.toStringHelper(sb, depth + 1);
- }
- }
- private StringBuilder depth( final StringBuilder sb, final int depth )
- {
- for ( int i = 0; i < depth; ++i )
- sb.append( " ");
- return sb;
- }
- private long addPaddingSize(long size){
- if(size % 8 != 0){
- return (size / 8 + 1) * 8;
- }
- return size;
- }
- }
- package test;
- import java.lang.reflect.Array;
- import java.lang.reflect.Field;
- import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Arrays;
- import java.util.Collections;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.Map;
- import sun.misc.Unsafe;
- /**
- * This class could be used for any object contents/memory layout printing.
- */
- public class ClassIntrospector {
- private static final Unsafe unsafe;
- /** Size of any Object reference */
- private static final int objectRefSize;
- static {
- try {
- Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
- field.setAccessible(true);
- unsafe = (Unsafe) field.get(null);
- objectRefSize = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(Object[].class);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- /** Sizes of all primitive values */
- private static final Map<Class, Integer> primitiveSizes;
- static {
- primitiveSizes = new HashMap<Class, Integer>(10);
- primitiveSizes.put(byte.class, 1);
- primitiveSizes.put(char.class, 2);
- primitiveSizes.put(int.class, 4);
- primitiveSizes.put(long.class, 8);
- primitiveSizes.put(float.class, 4);
- primitiveSizes.put(double.class, 8);
- primitiveSizes.put(boolean.class, 1);
- }
- /**
- * Get object information for any Java object. Do not pass primitives to
- * this method because they will boxed and the information you will get will
- * be related to a boxed version of your value.
- *
- * @param obj
- * Object to introspect
- * @return Object info
- * @throws IllegalAccessException
- */
- public ObjectInfo introspect(final Object obj)
- throws IllegalAccessException {
- try {
- return introspect(obj, null);
- } finally { // clean visited cache before returning in order to make
- // this object reusable
- m_visited.clear();
- }
- }
- // we need to keep track of already visited objects in order to support
- // cycles in the object graphs
- private IdentityHashMap<Object, Boolean> m_visited = new IdentityHashMap<Object, Boolean>(
- 100);
- private ObjectInfo introspect(final Object obj, final Field fld)
- throws IllegalAccessException {
- // use Field type only if the field contains null. In this case we will
- // at least know what's expected to be
- // stored in this field. Otherwise, if a field has interface type, we
- // won't see what's really stored in it.
- // Besides, we should be careful about primitives, because they are
- // passed as boxed values in this method
- // (first arg is object) - for them we should still rely on the field
- // type.
- boolean isPrimitive = fld != null && fld.getType().isPrimitive();
- boolean isRecursive = false; // will be set to true if we have already
- // seen this object
- if (!isPrimitive) {
- if (m_visited.containsKey(obj))
- isRecursive = true;
- m_visited.put(obj, true);
- }
- final Class type = (fld == null || (obj != null && !isPrimitive)) ? obj
- .getClass() : fld.getType();
- int arraySize = 0;
- int baseOffset = 0;
- int indexScale = 0;
- if (type.isArray() && obj != null) {
- baseOffset = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(type);
- indexScale = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(type);
- arraySize = baseOffset + indexScale * Array.getLength(obj);
- }
- final ObjectInfo root;
- if (fld == null) {
- root = new ObjectInfo("", type.getCanonicalName(), getContents(obj,
- type), 0, getShallowSize(type), arraySize, baseOffset,
- indexScale);
- } else {
- final int offset = (int) unsafe.objectFieldOffset(fld);
- root = new ObjectInfo(fld.getName(), type.getCanonicalName(),
- getContents(obj, type), offset, getShallowSize(type),
- arraySize, baseOffset, indexScale);
- }
- if (!isRecursive && obj != null) {
- if (isObjectArray(type)) {
- // introspect object arrays
- final Object[] ar = (Object[]) obj;
- for (final Object item : ar)
- if (item != null)
- root.addChild(introspect(item, null));
- } else {
- for (final Field field : getAllFields(type)) {
- if ((field.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) != 0) {
- continue;
- }
- field.setAccessible(true);
- root.addChild(introspect(field.get(obj), field));
- }
- }
- }
- root.sort(); // sort by offset
- return root;
- }
- // get all fields for this class, including all superclasses fields
- private static List<Field> getAllFields(final Class type) {
- if (type.isPrimitive())
- return Collections.emptyList();
- Class cur = type;
- final List<Field> res = new ArrayList<Field>(10);
- while (true) {
- Collections.addAll(res, cur.getDeclaredFields());
- if (cur == Object.class)
- break;
- cur = cur.getSuperclass();
- }
- return res;
- }
- // check if it is an array of objects. I suspect there must be a more
- // API-friendly way to make this check.
- private static boolean isObjectArray(final Class type) {
- if (!type.isArray())
- return false;
- if (type == byte[].class || type == boolean[].class
- || type == char[].class || type == short[].class
- || type == int[].class || type == long[].class
- || type == float[].class || type == double[].class)
- return false;
- return true;
- }
- // advanced toString logic
- private static String getContents(final Object val, final Class type) {
- if (val == null)
- return "null";
- if (type.isArray()) {
- if (type == byte[].class)
- return Arrays.toString((byte[]) val);
- else if (type == boolean[].class)
- return Arrays.toString((boolean[]) val);
- else if (type == char[].class)
- return Arrays.toString((char[]) val);
- else if (type == short[].class)
- return Arrays.toString((short[]) val);
- else if (type == int[].class)
- return Arrays.toString((int[]) val);
- else if (type == long[].class)
- return Arrays.toString((long[]) val);
- else if (type == float[].class)
- return Arrays.toString((float[]) val);
- else if (type == double[].class)
- return Arrays.toString((double[]) val);
- else
- return Arrays.toString((Object[]) val);
- }
- return val.toString();
- }
- // obtain a shallow size of a field of given class (primitive or object
- // reference size)
- private static int getShallowSize(final Class type) {
- if (type.isPrimitive()) {
- final Integer res = primitiveSizes.get(type);
- return res != null ? res : 0;
- } else
- return objectRefSize;
- }
- }
先一个测试类来验证一下Unsafe的方式计算出的结果
- public class ClassIntrospectorTest
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException {
- final ClassIntrospector ci = new ClassIntrospector();
- ObjectInfo res;
- res = ci.introspect( new ObjectA() );
- System.out.println( res.getDeepSize() );
- }
- private static class ObjectA {
- String str; // 4
- int i1; // 4
- byte b1; // 1
- byte b2; // 1
- int i2; // 4
- ObjectB obj; //4
- byte b3; // 1
- }
- private static class ObjectB {
- }
- }
计算结果如下:
32
和我们之前计算结果是一致的,证明是正确的。
最后再来测试一下数组对象的长度。有两个类如下:
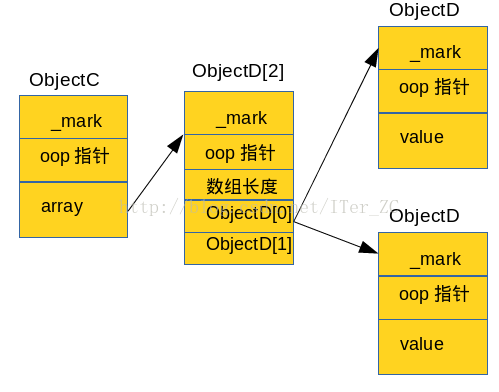
- private static class ObjectC {
- ObjectD[] array = new ObjectD[2];
- }
- private static class ObjectD {
- int value;
- }
它们在内存的大体分布如下图:
我们可以手工计算一下ObjectC obj = new ObjectC()的大小:
ObjectC的Shallow size = 8(_mark) + 4(oop指针) + 4(ObjectD[]引用) = 16
new ObjectD[2]数组的长度 = 8(_mark) + 4(oop指针) + 4(数组长度占4个字节) + 4(ObjectD[0]引用) + 4(ObjectD[1]引用) = 24
由于ObjectD[]数组没有指向具体的对象大小,所以我们手工计算的结果是16 + 24 = 40
使用Unsafe对象的方式来计算一下:
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException {
- final ClassIntrospector ci = new ClassIntrospector();
- ObjectInfo res;
- res = ci.introspect( new ObjectC() );
- System.out.println( res.getDeepSize() );
- }
计算结果如下,和我们计算的结果是一致的,证明是正确的:
40
再给ObjectD[]数组指向具体的ObjectD对象,再测试一下结果:
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException {
- final ClassIntrospector ci = new ClassIntrospector();
- ObjectInfo res;
- res = ci.introspect( new ObjectC() );
- System.out.println( res.getDeepSize() );
- }
- private static class ObjectC {
- ObjectD[] array = new ObjectD[2];
- public ObjectC(){
- array[0] = new ObjectD();
- array[1] = new ObjectD();
- }
- }
- private static class ObjectD {
- int value;
- }
我们可以手工计算一下ObjectC obj = new ObjectC()的大小:
ObjectC的Shallow size = 8(_mark) + 4(oop指针) + 4(ObjectD[]引用) = 16
new ObjectD[2]数组的长度 = 8(_mark) + 4(oop指针) + 4(数组长度占4个字节) + 4(ObjectD[0]引用) + 4(ObjectD[1]引用) = 24
ObjectD对象长度 = 8(_mark) + 4(oop指针) + 4(value) = 16
所以ObjectC实际占用的空间 = 16 + 24 + 2 * 16 = 72
使用Unsafe的方式计算的结果也是72,和我们手工计算的方式一致。