java.io包中定义了各式各样的“流(stream)” 类型(类或抽象类),通过标准的方法实现对于数据的输入/输出操作。
一、流类型分类
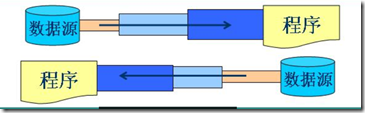
以从不同的角度对其进行分类:按数据流的方向不同,可以分为 输入流 和 输出流(相对于程序来说的);按处理数据单位不同,可以分为 字节流 和 字符流 ;按功能不同,可以分为 节点流 和 处理流,处理流需要套接在节点流之上使用。
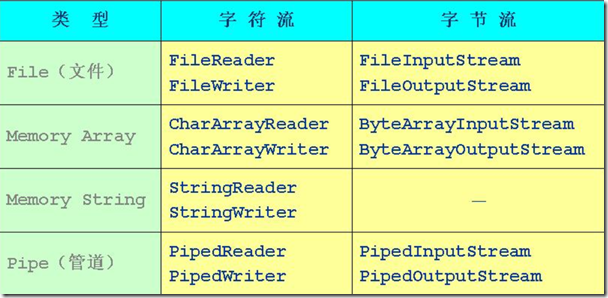
1、节点流
节点流位可以从一个特定的数据源(节点)读写数据(如:文件、内存)。
常见的节点流类型如下:
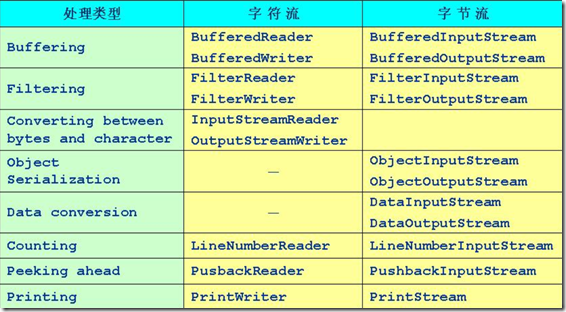
2、处理流
处理流是 “连接/” 在已存在的流(节点流或处理流)之上,通过对数据的处理为程序提供更为强大的读写功能,
常见的处理流类型如下:
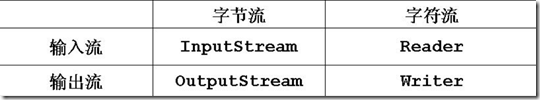
二、流的继承架构
java.io包中所有的流类型,都分别继承以下四种抽象流类型。
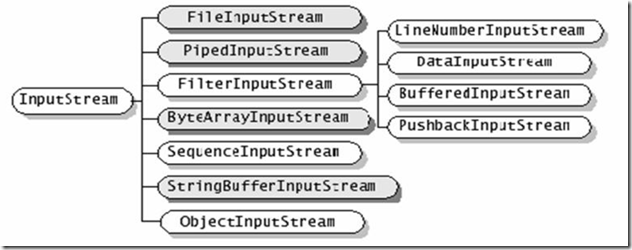
1、InputStream
继承自InputStream的流都是 向程序中输入数据,且数 据的单位为字节(8bit)。
(1)InputStream的子类
下图中深色为节点流、浅色为处理流。
(2)InputStream的基本方法
1 //读取一个字节并以整数的形式返回(0 ~ 255) 2 //若果返回-1,表示已经到了输入流的末尾 3 int read() throws IOException; 4 5 //读取一系列字节并存储到一个数组buffer 6 //返回实际读取的字节数;若果返回-1,表示已经到了输入流的末尾 7 int read (byte [] buffer) throws IOException; 8 9 //从offset位置开始,读取length个字节,并存储到一个字节数组buffer 10 //返回实际读取的字节数;若果返回-1,表示已经到了输入流的末尾 11 int read (byte [] buffer,int offset,int length) throws IOException; 12 13 //关闭流释放内存资源 14 void close () throws IOException ; 15 16 //跳过n个字节不读,返回实际跳过的字节数 17 long skip(long n) throws IOException;
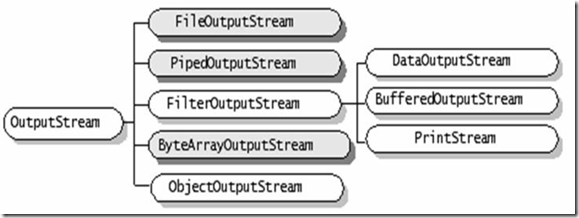
2、OutputStream
继承自OutputStream的流是用于从程序中输出数据,且数据的单位为字节(8bit)。
(1)OutputStream的子类
下图中深色为节点流、浅色为处理流。
(2)OutputStream的基本方法
1 //向输出流中写入一个字节数据,该字节数据为参数b的低8位 2 void write(iunt b) throws IOException; 3 4 //将一个字节类型的数组中的数据写入输出流 5 void write(byte [] b) throws IOException; 6 7 //将一个字节类型的数组中,从off位置开始的len个字节写入到输出流 8 int write (byte [] b,int off,int len) throws IOException; 9 10 //关闭流释放内存资源 11 void close () throws IOException ; 12 13 //将输入流中缓存的数据全部写入到目的地 14 long flush(long n) throws IOException;
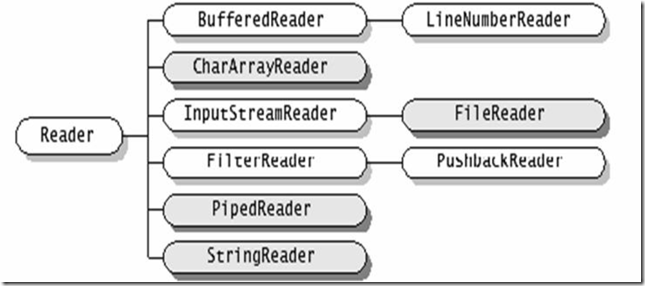
3、Reader
继承自Reader的流都是向程序中输入数据,且数据的单位为字符(16bit)。
(1)Reader的子类
下图中深色为节点流、浅色为处理流。
(2)Reader的基本方法
1 //读取一个字符并以整数的形式返回(0 ~ 255) 2 //若果返回-1,表示已经到了输入流的末尾 3 int read() throws IOException; 4 5 //读取一系列字符并存储到一个数组buffer 6 //返回实际读取的字符数;若果返回-1,表示已经到了输入流的末尾 7 int read (char [] cbuf) throws IOException; 8 9 //从offset位置开始,读取length个字符,并存储到一个字符数组buffer 10 //返回实际读取的字符数;若果返回-1,表示已经到了输入流的末尾 11 int read (char [] cbuf,int offset,int length) throws IOException; 12 13 //关闭流释放内存资源 14 void close () throws IOException ; 15 16 //跳过n个字符不读,返回实际跳过的字符数 17 long skip(long n) throws IOException;
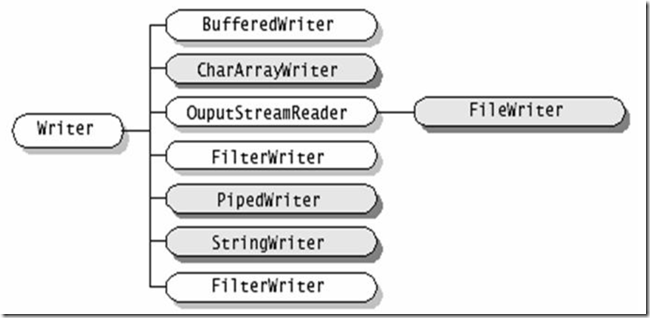
4、Writer
继承自Writer的流是用于从程序中输出数据,且数据的单位为字符(16bit)。
(1)Writer的子类
下图中深色为节点流、浅色为处理流。
(2)Writer的基本方法
1 //向输出流中写入一个字符数据,该字节数据为参数b的低16位 2 void write(int b) throws IOException; 3 4 //将一个字符类型的数组中的数据写入输出流 5 void write(char [] cbuf) throws IOException; 6 7 //将一个字符类型的数组中,从off位置开始的len个字节写入到输出流 8 int write (char [] cbuf,int off,int len) throws IOException; 9 10 //将一个字符串中的字符写入到输出流 11 void write(String str) throws IOException; 12 13 //将一个字符串从offset位置开始的length个字符写入输出流 14 void write (String str ,int offset,int length) throws IOException; 15 16 //关闭流释放内存资源 17 void close () throws IOException ; 18 19 //将输入流中缓存的数据全部写入到目的地 20 long flush(long n) throws IOException;
三、流的详细用法
1、文件流 类型
1 import java.io.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 int b = 0; 5 FileReader in = null;//输入字符流,若采用FileinputStream则不能读取中文 6 FileWriter out = null;//输出字符流,若采用FileOutputStream则不能写入中文 7 8 try { 9 in = new FileReader("file.txt"); //若没有该文件,则抛出FileNotFoundException 10 out = new FileWriter("copy.txt"); //若没有该文件,则会自动创建copy.java 11 while((b=in.read())!=-1){ 12 System.out.print((char)b); //必须进行类型转换,否则打印的是Unicode码 13 out.write(b);//以字节为单位,向输出流写入数据 14 } 15 } catch (FileNotFoundException e1) { 16 System.out.println("找不到指定文件"); System.exit(-1); 17 } catch (IOException e2) { 18 System.out.println("文件复制错误"); System.exit(-1); 19 }finally{ 20 try { 21 in.close(); 22 out.close(); 23 } catch (IOException e) { 24 System.out.println("连接已关闭失败!");System.exit(-1); 25 } 26 } 27 System.out.println("文件已复制"); 28 } 29 } 30
2、数据流 类型
DataInputStream 和DataOutputStream 属于处理流,提供了可以存取与机器无关的JAVA原始类型数据(如:long、double、UTF)等的方法,多用于进行网络数据传输。
(1)构造方法
DataInputStream (InputStream in)
DataOutputStream (OutputStream out)
(2)举例
1 import java.io.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //字节数组输出流 6 ByteArrayInputStream bais = null;//字节数组输入流 7 8 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(baos);//输出流 9 DataInputStream dis = null;//输入流 10 11 try { 12 dos.writeDouble(Math.random());//向字节数组写入一个随机数 13 dos.writeBoolean(true);//向字节数组写入一个布尔变量 14 15 bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray()); 16 dis = new DataInputStream(bais); 17 18 System.out.println(bais.available());//字符数组大小 19 System.out.println(dis.readDouble());//先写的先读 20 System.out.println(dis.readBoolean()); 21 22 } catch (IOException e) { 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 }finally { 25 try { 26 dos.close(); 27 dis.close(); 28 } catch (IOException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 }
3、缓冲流 类型
缓冲流是 “套接” 在相应的节点流之上,对读取的数据提供缓冲的功能,提高读写效率,同时也增加了一些新的方法,如readLine阻塞式方法等。
(1)常用构造方法
1 BufferedReader(Reader in) 2 BufferedReader(Reader in,int sz) //sz为自定义缓冲大小 3 4 BufferedWriter(Writer out) 5 BufferedWriter(Writer out,int sz) 6 7 BufferedInputStream(InputStream out) 8 BufferedInputStream(InputStream out,int sz) 9 10 BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) 11 BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out,int sz)
(2)使用readLine和write读写数据
BufferedReader提供了readLine方法用于读取一行字符串(以 或 分隔)、newLine用于写入一行分隔符、flush方法用于将先在内存中缓存的数据立刻写出。
1 import java.io.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 String s = null; 5 BufferedReader br = null;//输入字符流,若采用BufferedInputStream则不能读取中文 6 BufferedWriter bw = null;//输入字符流,若采用BufferedOutputStream则不能写入中文 7 try { 8 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("file.txt")); 9 bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("copy.txt")); 10 11 while((s=br.readLine())!=null){ 12 System.out.println(s); 13 bw.write(s); 14 bw.newLine(); 15 } 16 bw.flush(); 17 18 } catch (IOException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 }finally { 21 try { 22 br.close(); 23 bw.close(); 24 } catch (IOException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 }
(3)使用mark和reset方法
mark(int readlimit)方法标记当前位置,并保证在mark以后最多可以读取readlimit字节数据,mark标记仍有效。如果在mark后读取超过readlimit字节数据,mark标记就会失效,调用reset()方法会有异常。但实际上只要在mark标记后读取的数据没有超出缓冲区的大小,mark标记就不会失效,仍然能正确调用reset方法重置。 。
1 import java.io.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 int c = 0; 5 String s = null; 6 BufferedReader br = null; 7 8 try { 9 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("file.txt")); 10 11 for(int i=0;i<=15 && (c=br.read())!=-1;i++){ 12 if(c == 'd') br.mark(5); 13 System.out.print((char)c+" ");//包含了回车换行符 14 } 15 br.reset(); 16 17 while((s=br.readLine())!=null){ 18 System.out.println(s); 19 } 20 21 } catch (IOException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 }finally { 24 try { 25 br.close(); 26 } catch (IOException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 }
4、转换流 类型
InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter用于字节数据转换到字符数据,转换流在构造时可以指定其编码集合。
1 import java.io.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String args[]) { 4 BufferedReader istr = null; 5 OutputStreamWriter ostr = null; 6 String s = null; 7 8 try { 9 istr = new BufferedReader( 10 new InputStreamReader( new FileInputStream("file.txt"))); 11 ostr = new OutputStreamWriter( 12 new FileOutputStream("copy.txt", true),"utf-8"); // ISO8859_1 13 14 ostr.write(ostr.getEncoding()); 15 while((s=istr.readLine())!=null){ 16 System.out.println(s); 17 ostr.write(s); 18 } 19 ostr.flush(); 20 21 } catch (IOException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 }finally { 24 try { 25 istr.close(); 26 ostr.close(); 27 } catch (IOException e) { 28 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 }
5、Print流 类型
PrintWriter和PrintStream都属于输出流,处理数据的单位分别是字符和字节。PrintWriter和PrintStream提供了重载的print和println方法用于多种数据类型的输出 以及 在关闭连接之前可以自动flush的功能。另外,Print流的操作不会抛出异常,用户通过检测错误状态获取错误信息。
注:System.in和System.out默认是键盘输入输出。
(1)构造方法
PrintWriter( Writer out )
PrintWriter( Writer out , boolean autoFlush) //true表示以追加的方式写入
PrintWriter( OutputStream out )
PrintWriter( OutputStream out , boolean autoFlush)
PrintWriter( OutputStream out )
PrintWriter( OutputStream out ,,boolean autoFlush)
(2)举例
1 import java.util.*; 2 import java.io.*; 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 String s = null; 6 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 7 8 PrintWriter log1 = null; 9 PrintStream log2 = null; 10 11 try { 12 log1 = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter ("file.txt", true)); 13 log2 = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream ("file.txt", true)); 14 15 if(log2 != null){ 16 System.setOut(log2); //将System.out输出目的地设置成文件 17 } 18 19 while ((s = br.readLine())!=null) { 20 if(s.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) break; 21 22 //在文件file中换行打印 23 log1.println(s.toUpperCase()); 24 log2.println(s.toUpperCase()); 25 System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());//默认立即flush 26 } 27 log1.println("==="+new Date()+"==="); 28 log1.flush();//显式写出默认的flush方式,即在循环完成后一起flush 29 log2.flush();//也可写在循环中达到立即flush的效果 30 31 } catch (IOException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 }finally { 34 log1.close(); //不会抛出异常 35 log2.close(); 36 } 37 } 38 }
6、Object流 类型
Object流可以直接将Object写入或写出,但Object类必须实现序列化接口。
(1)序列化接口
Serializable是序列化接口,标记类可以被序列化,无需重写方法,序列化过程由JRE控制。Externalizable是外部化接口,是Serializable的子接口,提供了readExternal和writeExternal方法,程序员可以重写这两个方法控制序列化过程。
(2)举例
1 import java.io.*; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception { 5 T t = new T(); 6 7 //保存类 8 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream( 9 new FileOutputStream("file.dat")); 10 oos.writeObject(t); 11 oos.flush(); 12 oos.close(); 13 14 //读取类 15 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream( 16 new FileInputStream("file.dat")); 17 T tReaded = (T)ois.readObject(); 18 System.out.println(tReaded.i + " " + tReaded.j + " " + 19 tReaded.d + " " + tReaded.k); 20 21 } 22 } 23 24 class T implements Serializable 25 { 26 int i = 10; 27 int j = 9; 28 double d = 2.3; 29 transient int k = 15;//transient修饰的成员变量在序列化时不予考虑,显示默认值0 30 }