年后到现在一直很忙,都没什么时间记录东西了,其实之前工作中积累了很多知识点,一直都堆在备忘录里,只是因为近几个月经历了一些事情,没有太多的经历来写了,但是一些重要的东西,我还是希望能坚持记录下来。正好最近公司用到了一些本篇文章的知识点,所以就抽空记录一下。
本文代码github地址:https://github.com/shaweiwei/RibbonTest/tree/master
简介
ribbon 是一个客户端负载均衡器,它和nginx的负载均衡相比,区别是一个是客户端负载均衡,一个是服务端负载均衡。ribbon可以单独使用,也可以配合eureka使用。
使用
单独使用
1.首先我们先在原来的基础上新建一个Ribbon模块,如下图:
现在我们单独使用ribbon,在Ribbon模块下添加依赖,如下图所示:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-ribbon</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
修改application.yml文件,如下所示:
server:
port: 8082
spring:
application:
name: Ribbon-Consumer
#providers这个是自己命名的,ribbon,listOfServer这两个是规定的
providers:
ribbon:
listOfServers: localhost:8080,localhost:8081
在Ribbon模块下新建一个测试类如下代码 * Created by cong on 2018/5/8. */
@RestController
public class ConsumerController {
//注入负载均衡客户端
@Autowired
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient;
@RequestMapping("/consumer")
public String helloConsumer() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//这里是根据配置文件的那个providers属性取的
ServiceInstance serviceInstance = loadBalancerClient.choose("providers");
//负载均衡算法默认是轮询,轮询取得服务
URI uri = URI.create(String.format("http://%s:%s", serviceInstance.getHost(), serviceInstance.getPort()));
return uri.toString();
}
运行结果如下:
会轮询的获取到两个服务的URL 访问第一次,浏览器出现http://localhost:8080 访问第二次就会出现http://localhost:8081
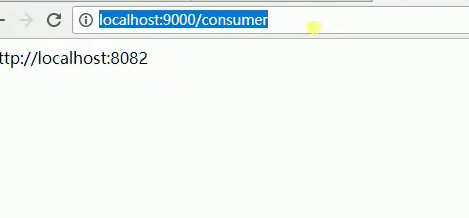
在eureka环境下使用
下面这个例子是在之前这篇文章的例子上改的,Spring Cloud(二):Spring Cloud Eureka Server高可用注册服务中心的配置
先看下写好的结构

先介绍下大致功能,EurekaServer提供服务注册功能,RibbonServer里会调用ServiceHello里的接口,ServiceHello和ServiceHello2是同样的服务,只是为了方便分布式部署。
EurekaServer
pom依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
BootApplication
@SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaServer public class BootApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(BootApplication.class, args); } }
application.properties
server.port=8760 spring.application.name=eureka-server #eureka.instance.hostname=peer1 eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:${server.port}/eureka
RibbonServer

BootApplication
红色部分代码是关键
@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient @RestController @RibbonClients(value={ @RibbonClient(name="service-hi",configuration=RibbonConfig.class) }) public class BootApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(BootApplication.class, args); } }
RibbonConfig
@Configuration public class RibbonConfig { @Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate restTemplate(){ return new RestTemplate(); } @Bean public IRule ribbonRule() { return new RoundRobinRule(); } }
TestController
@RestController public class TestController { @Autowired @LoadBalanced private RestTemplate restTemplate; @Autowired SpringClientFactory springClientFactory; @RequestMapping("/consumer") public String helloConsumer() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = springClientFactory.getLoadBalancer("service-hi"); List<Server> servers = loadBalancer.getReachableServers(); System.out.println(",......"+servers.size()); return restTemplate.getForEntity("http://service-hi/hi",String.class).getBody(); } }
application.properties
server.port=8618 spring.application.name=ribbon-service eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8760/eureka/
ServiceHello

BootApplication
@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient @RestController public class BootApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(BootApplication.class, args); } @RequestMapping(value="/hi",method=RequestMethod.GET) public String hi(){ return "hi"; } }
application.properties
server.port=8788 spring.application.name=service-hi eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8760/eureka/ #service-hi.ribbon.NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName=com.netflix.loadbalancer.RoundRobinRule
ServiceHello2
和ServiceHello一样,只是端口不同,另外为了区分,接口hi返回的值也改成不一样。
查看结果
然后就是分别启动各个服务。
查看eureka信息,可以看到服务都启动了。
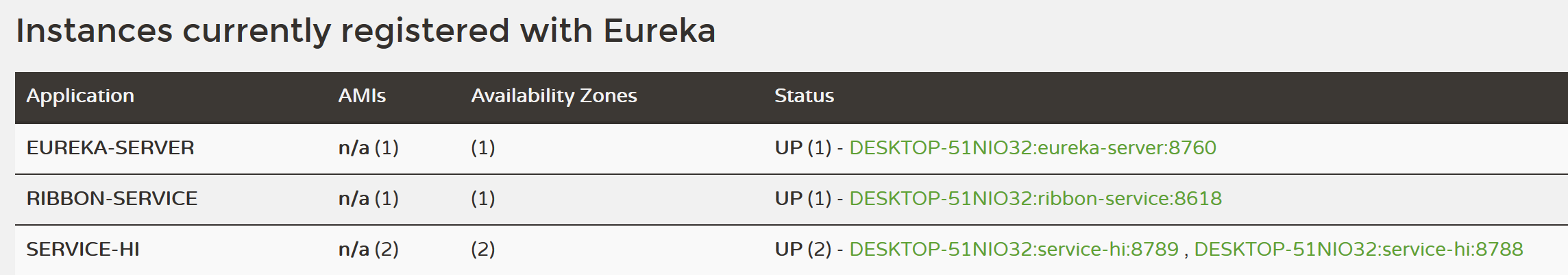
浏览器里输入http://localhost:8618/consumer,多调用几次,可以看到分别结果是hi和hi2交替出现。
这说明负载均衡实现了,而且我选择的负载均衡策略是轮询,所以hi和hi2肯定是交替出现。
负载均衡策略
Ribbon的核心组件是IRule,是所有负载均衡算法的父接口,其子类有:


每一个类就是一种负载均衡算法
RoundRobinRule 轮询
RandomRule 随机
AvailabilityFilteringRule 会先过滤掉由于多次访问故障而处于断路器跳闸状态的服务,还有并发的连接数超过阈值的服务,然后对剩余的服务列表进行轮询
WeightedResponseTimeRule 权重 根据平均响应时间计算所有服务的权重,响应时间越快服务权重越大被选中的概率越高。刚启动时,如果统计信息不足,则使用轮询策略,等信息足够,切换到 WeightedResponseTimeRule
RetryRule 重试 先按照轮询策略获取服务,如果获取失败则在指定时间内重试,获取可用服务
BestAvailableRule 选过滤掉多次访问故障而处于断路器跳闸状态的服务,然后选择一个并发量最小的服务
ZoneAvoidanceRule 符合判断server所在区域的性能和server的可用性选择服务
原理与源码分析
ribbon实现的关键点是为ribbon定制的RestTemplate,ribbon利用了RestTemplate的拦截器机制,在拦截器中实现ribbon的负载均衡。负载均衡的基本实现就是利用applicationName从服务注册中心获取可用的服务地址列表,然后通过一定算法负载,决定使用哪一个服务地址来进行http调用。
Ribbon的RestTemplate
RestTemplate中有一个属性是List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> interceptors,如果interceptors里面的拦截器数据不为空,在RestTemplate进行http请求时,这个请求就会被拦截器拦截进行,拦截器实现接口ClientHttpRequestInterceptor,需要实现方法是
ClientHttpResponse intercept(HttpRequest request, byte[] body, ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException;
也就是说拦截器需要完成http请求,并封装一个标准的response返回。
ribbon中的拦截器
在Ribbon 中也定义了这样的一个拦截器,并且注入到RestTemplate中,是怎么实现的呢?
在Ribbon实现中,定义了一个LoadBalancerInterceptor,具体的逻辑先不说,ribbon就是通过这个拦截器进行拦截请求,然后实现负载均衡调用。
拦截器定义在org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.LoadBalancerInterceptorConfig#ribbonInterceptor
@Configuration @ConditionalOnMissingClass("org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate") static class LoadBalancerInterceptorConfig { @Bean //定义ribbon的拦截器 public LoadBalancerInterceptor ribbonInterceptor( LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient, LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) { return new LoadBalancerInterceptor(loadBalancerClient, requestFactory); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean //定义注入器,用来将拦截器注入到RestTemplate中,跟上面配套使用 public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer( final LoadBalancerInterceptor loadBalancerInterceptor) { return restTemplate -> { List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> list = new ArrayList<>( restTemplate.getInterceptors()); list.add(loadBalancerInterceptor); restTemplate.setInterceptors(list); }; } }
ribbon中的拦截器注入到RestTemplate
定义了拦截器,自然需要把拦截器注入到、RestTemplate才能生效,那么ribbon中是如何实现的?上面说了拦截器的定义与拦截器注入器的定义,那么肯定会有个地方使用注入器来注入拦截器的。
在org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration#loadBalancedRestTemplateInitializerDeprecated方法里面,进行注入,代码如下。
@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass(RestTemplate.class) @ConditionalOnBean(LoadBalancerClient.class) @EnableConfigurationProperties(LoadBalancerRetryProperties.class) public class LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration { @LoadBalanced @Autowired(required = false) private List<RestTemplate> restTemplates = Collections.emptyList(); @Bean public SmartInitializingSingleton loadBalancedRestTemplateInitializerDeprecated( final ObjectProvider<List<RestTemplateCustomizer>> restTemplateCustomizers) { //遍历context中的注入器,调用注入方法。 return () -> restTemplateCustomizers.ifAvailable(customizers -> { for (RestTemplate restTemplate : LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.this.restTemplates) { for (RestTemplateCustomizer customizer : customizers) { customizer.customize(restTemplate); } } }); } //...... }
遍历context中的注入器,调用注入方法,为目标RestTemplate注入拦截器,注入器和拦截器都是我们定义好的。
还有关键的一点是:需要注入拦截器的目标restTemplates到底是哪一些?因为RestTemplate实例在context中可能存在多个,不可能所有的都注入拦截器,这里就是@LoadBalanced注解发挥作用的时候了。
LoadBalanced注解
严格上来说,这个注解是spring cloud实现的,不是ribbon中的,它的作用是在依赖注入时,只注入实例化时被@LoadBalanced修饰的实例。
例如我们定义Ribbon的RestTemplate的时候是这样的
@Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate rebbionRestTemplate(){ return new RestTemplate(); }
因此才能为我们定义的RestTemplate注入拦截器。
那么@LoadBalanced是如何实现这个功能的呢?其实都是spring的原生操作,@LoadBalance的源码如下
/** * Annotation to mark a RestTemplate bean to be configured to use a LoadBalancerClient * @author Spencer Gibb */ @Target({ ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @Qualifier public @interface LoadBalanced { }
很明显,‘继承’了注解@Qualifier,我们都知道以前在xml定义bean的时候,就是用Qualifier来指定想要依赖某些特征的实例,这里的注解就是类似的实现,restTemplates通过@Autowired注入,同时被@LoadBalanced修饰,所以只会注入@LoadBalanced修饰的RestTemplate,也就是我们的目标RestTemplate。
拦截器逻辑实现
LoadBalancerInterceptor源码如下。
public class LoadBalancerInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor { private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer; private LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory; public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer, LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) { this.loadBalancer = loadBalancer; this.requestFactory = requestFactory; } public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer) { // for backwards compatibility this(loadBalancer, new LoadBalancerRequestFactory(loadBalancer)); } @Override public ClientHttpResponse intercept(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body, final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException { final URI originalUri = request.getURI(); String serviceName = originalUri.getHost(); Assert.state(serviceName != null, "Request URI does not contain a valid hostname: " + originalUri); return this.loadBalancer.execute(serviceName, requestFactory.createRequest(request, body, execution)); } }
拦截请求执行
@Override public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException { ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(serviceId); //在这里负载均衡选择服务 Server server = getServer(loadBalancer); if (server == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId); } RibbonServer ribbonServer = new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server, serviceId), serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server)); //执行请求逻辑 return execute(serviceId, ribbonServer, request); }
我们重点看getServer方法,看看是如何选择服务的
protected Server getServer(ILoadBalancer loadBalancer) { if (loadBalancer == null) { return null; } // return loadBalancer.chooseServer("default"); // TODO: better handling of key }
代码配置随机loadBlancer,进入下面代码
public Server chooseServer(Object key) { if (counter == null) { counter = createCounter(); } counter.increment(); if (rule == null) { return null; } else { try { //使用配置对应负载规则选择服务 return rule.choose(key); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error choosing server for key {}", name, key, e); return null; } } }
这里配置的是RandomRule,所以进入RandomRule代码
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) { if (lb == null) { return null; } Server server = null; while (server == null) { if (Thread.interrupted()) { return null; } //获取可用服务列表 List<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers(); List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers(); //随机一个数 int serverCount = allList.size(); if (serverCount == 0) { /* * No servers. End regardless of pass, because subsequent passes * only get more restrictive. */ return null; } int index = rand.nextInt(serverCount); server = upList.get(index); if (server == null) { /* * The only time this should happen is if the server list were * somehow trimmed. This is a transient condition. Retry after * yielding. */ Thread.yield(); continue; } if (server.isAlive()) { return (server); } // Shouldn't actually happen.. but must be transient or a bug. server = null; Thread.yield(); } return server; }
随机负载规则很简单,随机整数选择服务,最终达到随机负载均衡。我们可以配置不同的Rule来实现不同的负载方式。
