1、介绍
Ridge 回归通过对系数的大小施加惩罚来解决 普通最小二乘法 的一些问题。 岭系数最小化的是带罚项的残差平方和,
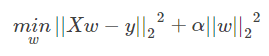
其中,α≥0α≥0 是控制系数收缩量的复杂性参数: αα 的值越大,收缩量越大,这样系数对共线性的鲁棒性也更强。
2、参数
alpha:{float,array-like},shape(n_targets)
正则化强度; 必须是正浮点数。 正则化改善了问题的条件并减少了估计的方差。 较大的值指定较强的正则化。 Alpha对应于其他线性模型(如Logistic回归或LinearSVC)中的C^-1。
如果传递数组,则假定惩罚被特定于目标。 因此,它们必须在数量上对应。
copy_X:boolean,可选,默认为True
如果为True,将复制X; 否则,它可能被覆盖。
fit_intercept:boolean
是否计算此模型的截距。 如果设置为false,则不会在计算中使用截距(例如,数据预期已经居中)。
max_iter:int,可选
共轭梯度求解器的最大迭代次数。 对于’sparse_cg’和’lsqr’求解器,默认值由scipy.sparse.linalg确定。 对于’sag’求解器,默认值为1000。
normalize:boolean,可选,默认为False
如果为真,则回归X将在回归之前被归一化。 当fit_intercept设置为False时,将忽略此参数。 当回归量归一化时,注意到这使得超参数学习更加鲁棒,
并且几乎不依赖于样本的数量。 相同的属性对标准化数据无效。 然而,如果你想标准化,请在调用normalize = False训练估计器之前,使用preprocessing.StandardScaler处理数据。
solver:{‘auto’,’svd’,’cholesky’,’lsqr’,’sparse_cg’,’sag’}
用于计算的求解方法:
‘auto’根据数据类型自动选择求解器。
‘svd’使用X的奇异值分解来计算Ridge系数。对于奇异矩阵比’cholesky’更稳定。
‘cholesky’使用标准的scipy.linalg.solve函数来获得闭合形式的解。
‘sparse_cg’使用在scipy.sparse.linalg.cg中找到的共轭梯度求解器。作为迭代算法,这个求解器比大规模数据(设置tol和max_iter的可能性)的“cholesky”更合适。
‘lsqr’使用专用的正则化最小二乘常数scipy.sparse.linalg.lsqr。它是最快的,但可能不是在旧的scipy版本可用。它还使用迭代过程。
‘sag’使用随机平均梯度下降。它也使用迭代过程,并且当n_samples和n_feature都很大时,通常比其他求解器更快。注意,“sag”快速收敛仅在具有近似相同尺度的特征上被保证。
可以使用sklearn.preprocessing的缩放器预处理数据。
所有最后四个求解器支持密集和稀疏数据。但是,当fit_intercept为True时,只有’sag’支持稀疏输入。
新版本0.17支持:随机平均梯度下降解算器。
tol:float 解的精度。
random_state:int seed,RandomState实例或None(默认)
伪随机数生成器的种子,当混洗数据时使用。 仅用于’sag’求解器。
新版本0.17:random_state支持随机平均渐变。
3、返回值
coef_:array,shape(n_features,)或(n_targets,n_features)
4、权重向量。
intercept_:float | array,shape =(n_targets,)
决策函数的独立项,即截距。 如果fit_intercept = False,则设置为0.0。
n_iter_:array或None,shape(n_targets,)
每个目标的实际迭代次数。 仅适用于sag和lsqr求解器。 其他求解器将返回None。在版本0.17中出现。
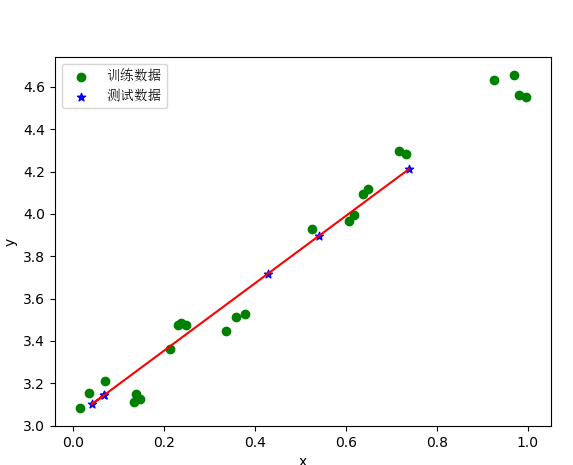
5、实例代码
print(__doc__) from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge,RidgeCV import matplotlib.font_manager as fm myfont = fm.FontProperties(fname='C:WindowsFontssimsun.ttc') data=[ [0.607492, 3.965162], [0.358622, 3.514900], [0.147846, 3.125947], [0.637820, 4.094115], [0.230372, 3.476039], [0.070237, 3.210610], [0.067154, 3.190612], [0.925577, 4.631504], [0.717733, 4.295890], [0.015371, 3.085028], [0.067732, 3.176513], [0.427810, 3.816464], [0.995731, 4.550095], [0.738336, 4.256571], [0.981083, 4.560815], [0.247809, 3.476346], [0.648270, 4.119688], [0.731209, 4.282233], [0.236833, 3.486582], [0.969788, 4.655492], [0.335070, 3.448080], [0.040486, 3.167440], [0.212575, 3.364266], [0.617218, 3.993482], [0.541196, 3.891471], [0.526171, 3.929515], [0.378887, 3.526170], [0.033859, 3.156393], [0.132791, 3.110301], [0.138306, 3.149813] ] #生成X和y矩阵 dataMat = np.array(data) # X = dataMat[:,0:1] # 变量x X = dataMat[:,0:1] # 变量x y = dataMat[:,1] #变量y X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y ,train_size=0.8) # model = Ridge(alpha=0.5) model = RidgeCV(alphas=[0.1, 1.0, 10.0]) # 通过RidgeCV可以设置多个参数值,算法使用交叉验证获取最佳参数值 model.fit(X_train, y_train) # 线性回归建模 # print('系数矩阵: ',model.coef_) # print('线性回归模型: ',model) # print('交叉验证最佳alpha值',model.alpha_) # 只有在使用RidgeCV算法时才有效 # 使用模型预测 y_predicted = model.predict(X_test) plt.scatter(X_train, y_train, marker='o',color='green',label='训练数据') # 绘制散点图 参数:x横轴 y纵轴 plt.scatter(X_test, y_predicted, marker='*',color='blue',label='测试数据') plt.legend(loc=2,prop=myfont) plt.plot(X_test, y_predicted,c='r') # 绘制x轴和y轴坐标 plt.xlabel("x") plt.ylabel("y") # 显示图形 plt.show()
6、显示图形
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/luanpeng825485697/article/details/79829778