课程:Python面向对象
进度:day4
上次内容回顾
1. 运算符重载
1)算术运算符重载
__add__(self,rhs) obj+3
__sub__(self,rhs) obj-3
__mul__(self,rhs) obj*3
__truediv__(self,rhs) obj/3
__floordiv__(self,rhs) obj//3
__mod__(self,rhs) obj%3
__pow__(self,rhs) obj**3
反向算术运算符: 3+obj
复合算术运算符: obj += 3
2)比较运算符
__lt__(self,rhs) obj < 3
__gt__(self,rhs) obj > 3
__eq__(self,rhs) obj == 3
__ne__(self,rhs) obj != 3
__ge__(self,rhs) obj >= 3
__le__(self,rhs) obj <= 3
3)一元运算符:带一个操作数
__neg__(self) -obj
__pos__(self) +obj
__invert__(self) ~obj
4)in,not in
__contains__(self,e)
5)索引运算符重载
__getitem__(self,i) x=obj[i]
__setitem__(self,i,val) obj[i]=x
__delitem__(self,i) del obj[i]
2. 对象的内置属性
__dict__: 绑定对象的变量
__class__:绑定创建本对象的类
今天的内容
1. 类属性和类方法
1)类属性(类变量)
- 什么是类属性:属于类,而不是对象
- 可以通过类访问,也可通过对象访问
ClassName.attribute 通过类访问
objectName.attribute 通过对象访问
- 定义:在类的所有方法之外定义
- 特征:类变量为所有实例所共享
2)类方法:属于类而不属于对象
- 定义方式:需要在方法前加@classmethod装饰器
- 特征:第一个参数不是self, 而是cls
绑定调用该方法的类而不是对象
类方法不能访问对象属性
- 访问:类.方法(), 或
3)静态方法
- 什么是静态方法:主要处理一些逻辑,
跟类有一定的相关性,跟类没有数据交互
(不操作类的属性)
- 如何定义静态方法:通过@staticmethod
装饰器进行定义,不需要传入self和cls
- 调用:可以通过类或对象进行调用
- 意义:对一些独立的功能或操作进行
归类存放
2. 类的预置属性
1)__slots__属性
作用:用来限定属性的范围,示例化对象时,
不允许对象设置__slots__限定外的属性
从而防止因属性填写错误导致的程序错误
类型:允许的属性名称(字符串)构成的列表
含有__slots__属性的类创建的对象
没有__dict__内置属性
2)__doc__属性
作用:绑定类中第一个没有赋值的字符串,
可以通过help函数进行查看。__doc__
属性主要存放类的描述信息
示例:见staff.py
查看:进入python交互模式,执行
from staff import *
help(Staff)

1 # staff.py 2 # 员工类,演示__slots__属性示例 3 class Staff: 4 "这是一个员工类" 5 __slots__ = ["no", "name", "position"] 6 7 def __init__(self, no, name, position): 8 self.no = no #员工编号 9 self.name = name #员工姓名 10 self.position = position #职位 11 #self.salary = 8000 #不允许 12 13 def __str__(self): 14 ret = "编号:%s, 姓名:%s, 职位:%s" % 15 (self.no, self.name, self.position) 16 return ret 17 18 def work(self): #员工工作方法 19 print("%s正在工作" % self.name) 20 21 #定义机器人类,继承自Staff类 22 class ServiceRobot(Staff): 23 def __init__(self, no, name, position): 24 super().__init__(no, name, position) 25 26 def work(self): #重写工作方法 27 print("%s的工作,扫地" % self.name) 28 29 if __name__ == "__main__": 30 staff = Staff("0001", "Jerry", "经理") 31 #如果没有__slots__属性,则创建一个新属性 32 #执行不会报错,但没有起到给属性赋值的作用 33 #staff.positino = "副总经理" 34 print(staff) 35 36 robot = ServiceRobot("0002","多啦A梦","服务员") 37 print(robot) 38 robot.work()
3. 类的关系设计(理解)
1)继承关系
- 描述子类、父类之间的关系
- 子类和父类是"是一个XX"的关系
2)组合关系
- 一个对象中嵌入了另一个对象
描述"有一个"的关系
整体包含部分的关系
3)关联关系
- 一个类中嵌套了另一个类,但是这两个
类是平等关系,而不是局部和整体的关系
- 关联可以是单向,也可是双向
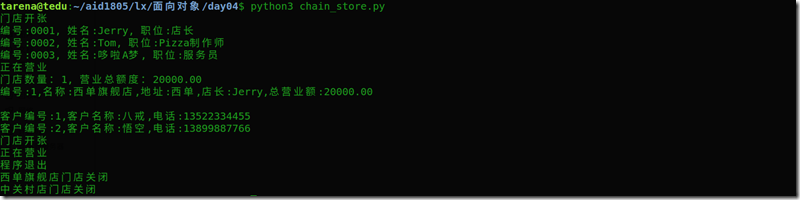
示例代码:见chain_store.py

1 # staff.py 2 # 员工类,演示__slots__属性示例 3 class Staff: 4 "这是一个员工类" 5 __slots__ = ["no", "name", "position"] 6 7 def __init__(self, no, name, position): 8 self.no = no #员工编号 9 self.name = name #员工姓名 10 self.position = position #职位 11 # self.salary = 8000 #不允许 12 13 def __str__(self): 14 ret = "编号:%s, 姓名:%s, 职位:%s" % 15 (self.no, self.name, self.position) 16 return ret 17 18 def work(self): #员工工作方法 19 print("%s正在工作" % self.name) 20 21 #定义机器人类,继承自Staff类 22 class ServiceRobot(Staff): 23 def __init__(self, no, name, position): 24 super().__init__(no, name, position) 25 26 def work(self): #重写工作方法 27 print("%s的工作,扫地" % self.name) 28 29 if __name__ == "__main__": 30 staff = Staff("0001", "Jerry", "经理") 31 #如果没有__slots__属性,则创建一个新属性 32 #执行不会报错,但没有起到给属性赋值的作用 33 # staff.positino = "副总经理" 34 print(staff) 35 36 robot = ServiceRobot("0002","多啦A梦","服务员") 37 print(robot) 38 robot.work()

1 # customer.py 2 # 客户类 3 class Customer: #客户类 4 def __init__(self,cust_id,cust_name,tel_no): 5 self.cust_id = cust_id 6 self.cust_name = cust_name 7 self.tel_no = tel_no 8 9 def __str__(self): 10 ret = "客户编号:%s,客户名称:%s,电话:%s" 11 %(self.cust_id, self.cust_name, self.tel_no) 12 return ret

1 # chain_store.py 2 # 连锁店类,类属性/类方法示例 3 from staff import * 4 from customer import * 5 6 class ChainStore: 7 #类属性 8 store_num = 0 #连锁店门店数量 9 total_income = 0 #所有门店总营业额 10 store_list = [] #所有门店对象列表 11 cust_list = [] #所有会员列表 12 13 def __init__(self,store_no,store_name, 14 address, manager): 15 print("门店开张") 16 self.store_no = store_no #编号 17 self.store_name = store_name #名称 18 self.address = address #地址 19 self.manager = manager #经理 20 self.myincome = 0 #本店营业额度 21 ChainStore.store_num += 1 #门店开张,总数量加1 22 ChainStore.store_list.append(self)#添加当前对象到列表 23 24 self.staff_list = [] #连锁店包含一组员工,组合关系 25 26 def add_staff(self, staff): #添加员工 27 self.staff_list.append(staff) 28 29 def remove_staff(self, no): #删除员工 30 for staff in self.staff_list: 31 if staff.no == no: 32 self.staff_list.remove(staff) 33 34 def print_all_staff(self): #打印所有员工信息 35 for staff in self.staff_list: 36 print(staff) 37 38 def do_business(self, income): #营业 39 print("正在营业") 40 self.myincome += income #营业额累加 41 # 将本店的营业额度累加到总营业额度 42 ChainStore.total_income += income 43 44 def __str__(self): #重写__str__() 45 ret="编号:%s,名称:%s,地址:%s,店长:%s,总营业额:%.2f" 46 %(self.store_no, self.store_name, 47 self.address,self.manager, self.myincome) 48 return ret 49 50 def __del__(self): #析构函数 51 print("%s门店关闭" % self.store_name) 52 ChainStore.store_num -= 1 #减少一家门店 53 54 @classmethod 55 def print_total(cls): #类方法,打印类的属性 56 print("门店数量:%d, 营业总额度:%.2f" % 57 (cls.store_num, cls.total_income)) 58 for store in cls.store_list: #遍历门店列表 59 print(str(store)) 60 61 @staticmethod 62 def print_regulation(): #静态方法,打印管理条例 63 regulation = ''' 64 --------- 连锁店管理条例 --------- 65 第一条 考勤 66 第一款 不迟到,不早退,不旷工 67 第二款 有事向经理请假 68 ... 69 70 第二条 服务规范 71 ... 72 ''' 73 print(regulation) 74 75 def cust_reg(self, cust): #会员注册 76 ChainStore.cust_list.append(cust) 77 78 def print_cust_info(self): #打印会员 79 for cust in ChainStore.cust_list: 80 print(cust) 81 82 if __name__ == "__main__": 83 # 第一家分店 84 store1 = ChainStore("1","西单旗舰店","西单","Jerry") 85 store1.add_staff(Staff("0001","Jerry","店长")) 86 store1.add_staff(Staff("0002","Tom","Pizza制作师")) 87 store1.add_staff(ServiceRobot("0003","哆啦A梦","服务员")) 88 store1.print_all_staff() #打印所有员工信息 89 90 store1.do_business(20000) #营业 91 ChainStore.print_total() #调用类方法 92 print("") 93 store1.cust_reg(Customer("1","八戒","13522334455")) 94 store1.cust_reg(Customer("2","悟空","13899887766")) 95 store1.print_cust_info() #打印会员信息 96 97 # print("") 98 # # 第二家分店 99 store2 = ChainStore("2","中关村店","中关村","李小小") 100 store2.do_business(25000) #营业 101 del store2 #销毁store2对象 102 103 print("程序退出") 104 # ChainStore.print_total() #调用类方法 105 106 # ChainStore.print_regulation() #通过类调用静态方法 107 # store2.print_regulation() #通过对象调用静态方法 108
4. with语句
1)作用:在访问某些资源时,不管有没有发生
异常,都确保能够执行必须的清理操作,
并释放资源(类似于try-finally作用)
2)语法
with 表达式1 [as 变量1][,表达式2 [as 变量2]]
语句块
例如:文件打开后自动关闭
线程资源的释放(系统编程阶段学习)
3)实现原理:环境资源管理器(上下文管理器)
- 定义了__enter__()和__exit__()方法的
对象称为环境资源管理器
- 调用时机:__enter__()方法在with语句被
执行时调用
__exit__()方法with语句结束时被调用
- 格式:
__enter__(self) 略
__exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb)
参数:exc_type 异常类型,没有异常为None
exc_val 绑定异常对象,没有异常为None
exc_tb 绑定TrackBack对象,没有异常为None

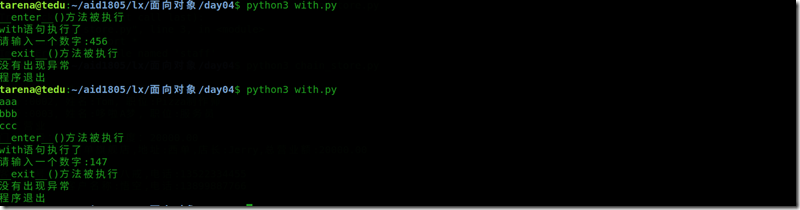
1 aaa 2 bbb 3 ccc 4

1 # with.py 2 # with语句示例 3 # try: 4 # #f = open("aaa.txt", "rt") 5 # # 使用with语句,不管以下的操作是否 6 # # 发生异常,都能保证文件被正确关闭 7 # with open("a.txt", "rt") as f: 8 # for line in f: 9 # print(line,end="") 10 # # with语句结束 11 # except: 12 # print("文件操作失败") 13 14 class A: #自定义资源管理器 15 def __init__(self, name): 16 self.name = name 17 18 def __enter__(self): 19 print("__enter__()方法被执行") 20 return self 21 22 def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val,exc_tb): 23 print("__exit__()方法被执行") 24 if exc_type is None: #没有出现异常 25 print("没有出现异常") 26 else: # 出现异常 27 print("错误类型:", exc_type) 28 print("错误对象:", exc_val) 29 print("TraceBack:", exc_tb) 30 31 if __name__ == "__main__": 32 with A("test_name") as a: 33 print("with语句执行了") 34 # 制造或不制造异常 35 a = int(input("请输入一个数字:")) 36 37 print("程序退出")
作业:
编写一个程序,模拟扫福,各种福的概率如下:
爱国福 30%
敬业福 10%
和谐福 30%
友善福 20%
富强福 10%
编写代码进行模拟