一、什么是链表
链表是线性表的一种,它不像顺序表一样连续存储数据,而是在每一个节点中存储下一个节点的位置信息(下一个节点的链接地址)。那么为什么需要链表呢?
- 顺序表需要预先知道数据的大小用来申请连续的内存空间
- 顺序表进行扩充时需要进行数据搬迁
这样很不灵活,而链表可以充分利用内存空间,因为它可以不连续的在内存空间中排列。链表的种类有:
- 单向链表
- 单向循环链表
- 双向链表
- 双向循环链表
二、单向链表
(一)什么是单向链表
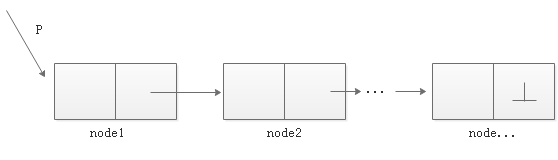
链表包括:
- p变量,用于指向链表的头节点
- 每一个节点node
- 最后一个节点的链接域指向空值
每一个节点的构成包含两部分:
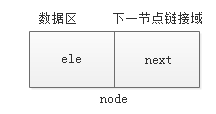
- 数据区,用来存放该节点具体数据
- 下一节点链接域,用来指向下一个节点的连接地址
(二)单向链表的实现
单向链表是由一个个的节点链接而成的,所以需要先实现节点:
class Node: def __init__(self, item): # 存储节点的数据 self.item = item # 节点中指向下一个节点的链接域 self.next = None def __str__(self): """打印node对象的返回值""" return "%s" % self.item
链表实现:
class SingleLink: def __init__(self, node=None): # 每一个实例就是一个链表,让p变量标示指向第一个头节点 self.__head = node def is_empty(self): """判断链表是否为空""" return self.__head is None def length(self): """计算链表的长度""" cur = self.__head count = 0 while cur: count += 1 cur = cur.next return count def travel(self): """遍历链表""" cur = self.__head while cur: cur = cur.next print(cur, end=" ") def add(self, item): """链表头部添加元素""" node = Node(item) node.next = self.__head self.__head = node def append(self, item): """链表尾节点添加节点""" node = Node(item) # 如果是空链表直接添加 if self.is_empty(): self.__head = node return # 如果不是空链表做以下操作 cur = self.__head # 循环查找出尾节点的位置 while cur.next: cur = cur.next # 循环退出后cur就是尾节点的位置 cur.next = node def insert(self, pos, item): """在指定的位置前插入元素""" # 如果插入的位置在第一位或者之前使用头插法 if pos <= 0: self.add(item) # 如果插入的位置在最后一位或者更靠后使用尾插法 elif pos > (self.length() - 1): self.append(item) # 在中间位置的情况 else: # 判断是中间位置 # 中间找到pos前一个位置 node = Node(item) count = 0 pre = self.__head while count < (pos - 1): count += 1 pre = pre.next node.next = pre.next pre.next = node def remove(self, item): """删除指定节点""" cur = self.__head pre = None while cur: if cur.item == item: # 如果第一个就是需要删除的元素 if not pre: self.__head = cur.next else: pre.next = cur.next break else: # 继续移动链表节点 pre = cur cur = cur.next def search(self, item): """查看节点是否存在""" cur = self.__head while cur: if cur.item == item: return True cur = cur.next return False
三、单向循环链表
单向循环链表与单向循环链表的区别是最后一个节点next域不再指向空而是指向头节点:
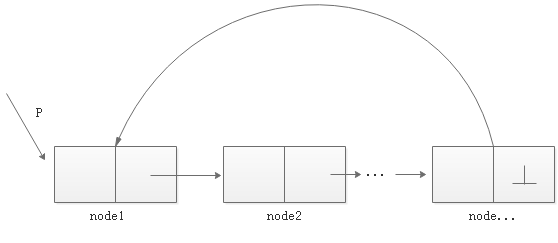
- 节点的实现
class Node: def __init__(self, item): # 存储节点的数据 self.item = item # 节点中指向下一个节点的链接域 self.next = None def __str__(self): """打印node对象的返回值""" return "%s" % self.item
- 单向循环链表实现
class SingleCycleLink: def __init__(self, node=None): # 每一个实例就是一个链表,让p变量标示指向第一个头节点,并且让唯一的节点指向自己 self.__head = node if node: node.next = node def is_empty(self): """判断链表是否为空""" return self.__head is None def length(self): """计算链表的长度""" if self.is_empty(): return 0 cur = self.__head count = 1 while cur.next != self.__head: count += 1 cur = cur.next return count def travel(self): """遍历链表""" if self.is_empty(): return cur = self.__head while cur.next != self.__head: cur = cur.next print(cur, end=" ") # 最后一个节点不要遗忘了 print(cur, end=" ") def add(self, item): """链表头部添加元素""" node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): self.__head = node node.next = node return cur = self.__head # 找出尾部元素位置 while cur.next != self.__head: cur = cur.next # 退出循环,cur指向尾节点 node.next = self.__head self.__head = node cur.next = node def append(self, item): """链表尾节点添加节点""" node = Node(item) # 如果是空链表直接添加 if self.is_empty(): self.__head = node node.next = node return # 如果不是空链表做以下操作 cur = self.__head # 循环查找出尾节点的位置 while cur.next != self.__head: cur = cur.next # 循环退出后cur就是尾节点的位置 node.next = self.__head cur.next = node def insert(self, pos, item): """在指定的位置前插入元素""" # 如果插入的位置在第一位或者之前使用头插法 if pos <= 0: self.add(item) # 如果插入的位置在最后一位或者更靠后使用尾插法 elif pos > (self.length() - 1): self.append(item) # 在中间位置的情况 else: # 判断是中间位置 # 中间找到pos前一个位置 node = Node(item) count = 0 pre = self.__head while count < (pos - 1): count += 1 pre = pre.next # 当循环退出后,pre指向pos-1位置 node.next = pre.next pre.next = node def remove(self, item): """删除指定节点""" if self.is_empty(): return cur = self.__head pre = None while cur.next != self.__head: if cur.item == item: # 如果第一个节点就是需要删除的元素 if cur == self.__head: # 找到尾节点 rear = self.__head while rear.next != self.__head: rear = rear.next self.__head = cur.next rear.next = self.__head else: # 中间节点 pre.next = cur.next return else: # 继续移动链表节点 pre = cur cur = cur.next # 退出循环后cur指向尾节点,还需要进行判断 if cur.item == item: if cur == self.__head: # 该链表只有一个节点 self.__head = None else: pre.next = cur.next def search(self, item): """查看节点是否存在""" if self.is_empty(): return False cur = self.__head while cur.next != self.__head: if cur.item == item: return True cur = cur.next # 退出循环,cur指向尾节点 if cur.item == item: return True return False
四、双向链表
一种更复杂的链表是“双向链表”或“双面链表”。每个节点有两个链接:一个指向前一个节点,当此节点为第一个节点时,指向空值;而另一个指向下一个节点,当此节点为最后一个节点时,指向空值。
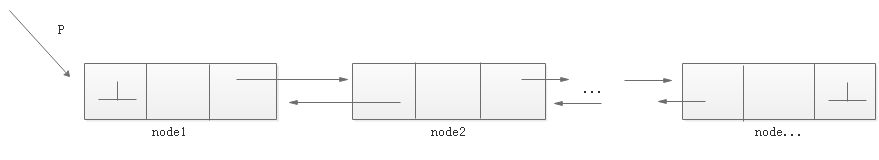
节点实现:
class Node: def __init__(self, item): # 存储节点的数据 self.item = item # 节点中指向下一个节点的链接域 self.next = None # 节点中指向前一个节点的链接域 self.prev = None def __str__(self): """打印node对象的返回值""" return "%s" % self.item
双向链表实现:
class DoubleLink: def __init__(self, node=None): # 每一个实例就是一个链表,让p变量标示指向第一个头节点 self.__head = node def is_empty(self): """判断链表是否为空""" return self.__head is None def length(self): """计算链表的长度""" cur = self.__head count = 0 while cur: count += 1 cur = cur.next return count def travel(self): """遍历链表""" cur = self.__head while cur: cur = cur.next print(cur, end=" ") def add(self, item): """链表头部添加元素""" node = Node(item) node.next = self.__head self.__head = node node.next.prev = node def append(self, item): """链表尾节点添加节点""" node = Node(item) # 如果是空链表直接添加 if self.is_empty(): self.__head = node return # 如果不是空链表做以下操作 cur = self.__head # 循环查找出尾节点的位置 while cur.next: cur = cur.next # 循环退出后cur就是尾节点的位置 cur.next = node node.prev = cur def insert(self, pos, item): """在指定的位置前插入元素""" # 如果插入的位置在第一位或者之前使用头插法 if pos <= 0: self.add(item) # 如果插入的位置在最后一位或者更靠后使用尾插法 elif pos > (self.length() - 1): self.append(item) # 在中间位置的情况 else: node = Node(item) count = 0 cur = self.__head while count < pos: count += 1 cur = cur.next # 当循环退出后,cur指向pos位置 node.next = cur node.prev = cur.prev cur.prev.next = node cur.prev = node def remove(self, item): """删除指定节点""" cur = self.__head while cur: if cur.item == item: # 如果第一个就是需要删除的元素 if cur == self.__head: self.__head = cur.next if cur.next: cur.next.prev = None else: cur.next.prev = cur.next if cur.next: cur.next.prev = cur.prev break else: # 继续移动链表节点 cur = cur.next def search(self, item): """查看节点是否存在""" cur = self.__head while cur: if cur.item == item: return True cur = cur.next return False