一、大纲

二、吞吐 VS 响应
响应需要上下文切换,其实时间很短,主要问题在于cache miss(代码和数据)。

linux系统是吞吐和响应兼顾的系统,可以在内核配置Preemption Model:1)No Forced Preemption(Server),非强制抢占,服务器,基本没有抢占调度; 2)Voluntary Kernel Preemption(Desktop), 自愿内核抢占,内核不能抢; 3)Preemptible Kernel(Low_Latency Desktop)抢占-手机 内核也可以抢。
二、I/O消耗型 VS. CPU消耗型

IO消耗型进程主要工作都在IO,CPU消耗不多,所以对于CPU要求不高,要求能够及时调度使用CPU,即使CPU性能差一点也没有关系。所以可以设计几个性能差一点的CPU服务IO消耗型进程,几个性能高的CPU服务CPU消耗型,这就是big.LITTLE,节能。4LITTLE+4个big=7.xbig。
三、调度器
早期2.6,内核空间优先级0~139,0-99是RT,100-139是普通进程。
RT进程:内核空间优先级=99-x(用户空间优先级)。
nice值:-20(nice值)-->100(内核优先级)19(nice值)->139(内核优先级),nice值越大,优先级越低。
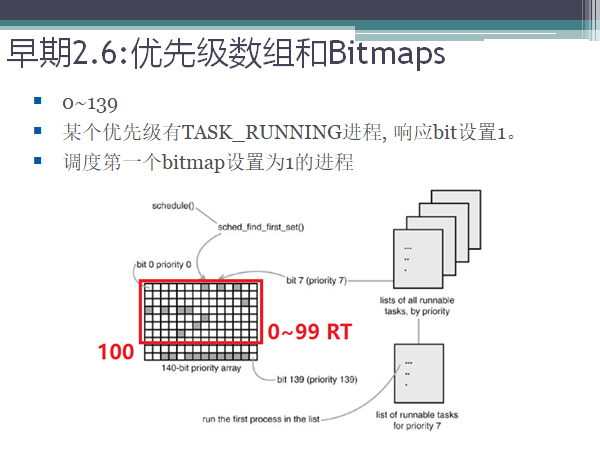
1)实时进程调度:区别在同一优先级

RR:Round Robin
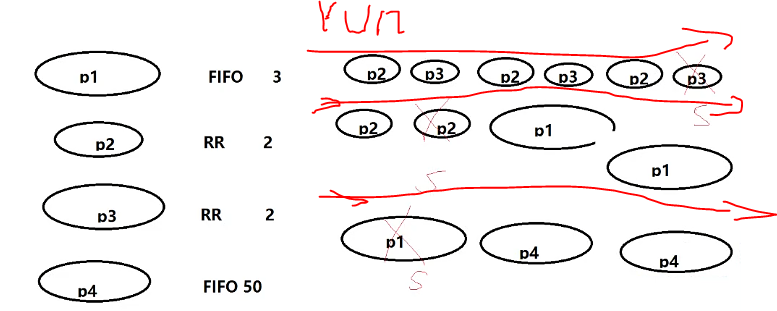
在0-99跑完后,都睡眠了,才跑100-139的进程。
-20-->100
19->139
2)早期2.6 普通进程调度

普通进程越睡,nice越低,优先级越高,越容易得到调度。这有利于IO消耗型进程能够快速得到调度。
3)rt门限

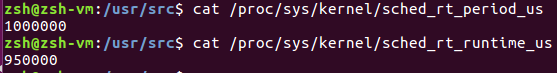
在1000,000us周期里面rt进程最多跑950,000us,剩余时间留给普通进程。
如果RT里面的进程有bug,普通进程就完全没有办法跑,所以上面补丁非常有用。
4)2.6之后普通进程CFS:完全公平调度算法 completely fair scheduler
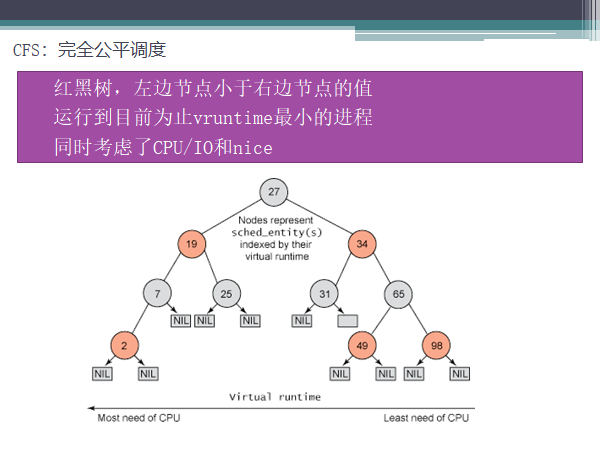
vruntime = phyruntime/weight * NICE_0_LOAD, weight为自身的权重。
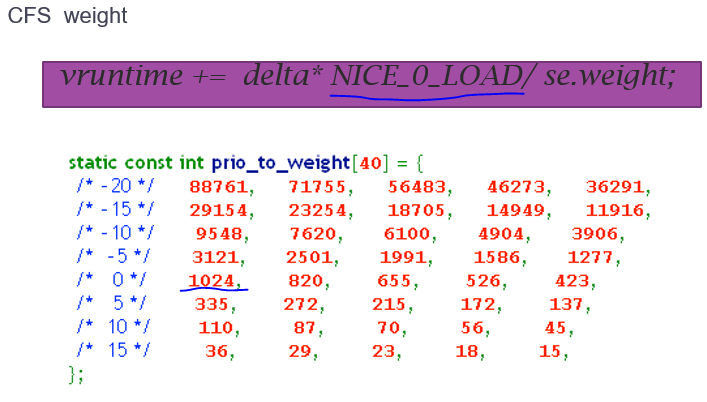
随便一个RT进程都能抢占普通进程。
同一个进程里面的线程优先级可以不同。
例子:renice -n -5 -g pid -n: -5为新的nice值 -g:所有线程 -p单个线程

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <pthread.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <sys/syscall.h> 5 6 static pid_t gettid() 7 { 8 return syscall(__NR_gettid); 9 } 10 11 static void *thread_fun(void *param) 12 { 13 printf("threadid: %d, tid: %d, thread_self(): %d ", getpid(), gettid(), pthread_self()); 14 while(1); 15 return NULL; 16 } 17 18 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 19 { 20 pthread_t tid1, tid2; 21 int ret; 22 23 printf("threadid: %d, tid: %d, thread_self(): %d ", getpid(), gettid(), pthread_self()); 24 25 ret = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread_fun, NULL); 26 if(ret == -1) 27 { 28 perror("can not create new thread"); 29 return -1; 30 } 31 32 ret = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread_fun, NULL); 33 if(ret == -1) 34 { 35 perror("can not create new thread"); 36 return -1; 37 } 38 39 if(pthread_join(tid1, NULL) != 0) 40 { 41 perror("call thread_jion function fail"); 42 return -1; 43 } 44 45 if(pthread_join(tid2, NULL) != 0) 46 { 47 perror("call thread_jion function fail"); 48 return -1; 49 } 50 51 return 0; 52 }
运行结果
例子:设置


三、工具
1)chrt
设置SCHED_FIFO和50RT优先级:chrt -f -a -p 50 pid
普通进程跑死循环这样设置后cpu利用率会下降,是因为前述RT补丁限制的。
设置nice:renice -n -5 -g pid 或者nice -n 5 ./a.out
四、答疑
1、关于0-139优先级,新内核有变化:不是很强调0-139优先级,查一下新内核的优先级。nice值-20~19是普通进程,RT进程为rt进程。下面是ubuntu的top显示:

2、MAX_USER_RT_PRIO=100:内核优先级 MAX_USER_RT_PRIO - 1 - 用户空间设置的优先级
3、LMbench工具,制造了切换时cache miss的场景。
4、
