这是对Flattened Promise Chains的翻译,水平有限请见谅^ ^。
Promises对于解决复杂异步请求与响应问题堪称伟大。AngularJS提供了$q和$http来实现它;还有很多类似技术这里不做展开。
Promises允许开发者很容易得将请求通知与异步请求进行绑定,而它还有另外两个重要的忒性:
- 在后续请求处理函数被通知前对传参进行转换
- 在响应中可以触发更多的promise式的异步请求
但是比以上更重要的是,Promises支持自定义链式活动或计算,管理异步调用链是一个非常困难和复杂的行为,Promise令人惊奇的做到了这一点。
但是这依然隐藏了一些反模式,后面我将对其进行讨论。
The FlightDashboard
看下Travel Service,它载入即将出发的用户信息,下面的代码一个远程服务返回了一个json格式响应数据,另外请注意这是一个promise式的异步请求。
var TravelService = function($http) {
return {
getDeparture: function(user) {
return $http.get(
URL_LAST_FLIGHT,
{userID : user.email}
)
}
}
}
现在让我使用该服务区载入用户的预定航班:
var FlightDashboard = function($scope, user, travelService) {
travelService
.getDeparture(user)
.then(function(departure) {
// Publish the departure details to the view
$scope.departure = departure
})
$scope.departure = null
}
非常棒,这里没有什么让我们感到陌生的新知识,下面我们再来些更加贴近实际的复杂场景。
嵌套Promise调用链
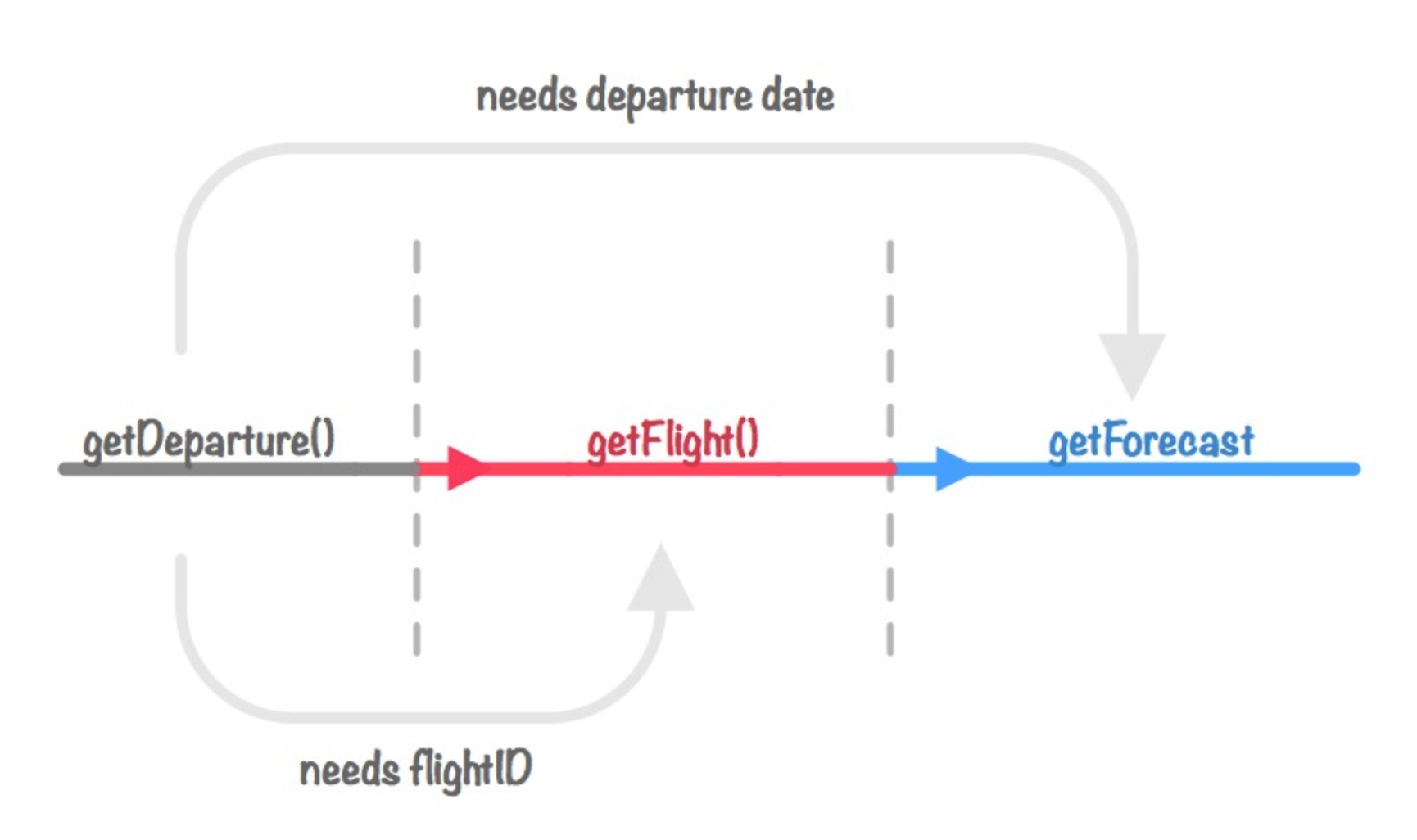
现在我们假设,当我们收到航班信息,就查看天气预报和航班状态,这个场景有三个序列的级联:getDeparture() -> getFlight() -> getForecast()
var FlightDashboard = function($scope, user, travelService, weatherService) {
// level 1
travelService
.getDeparture(user.email)
.then(function(departure) {
$scope.departure = departure
// level2
travelService
.getFlight(departure.flightId)
.then(function(flight) {
$scope.flight = flight
// level 3
weatherService
.getForecast(departure.date)
.then(function(weather) {
$scope.weather = weather
})
})
})
}
以上代码展示了我们不断在成功回调函数调用下一级请求。
这里出现了一个深层嵌套的序列化的、级联的三级调用链。请求载入用户即将搭乘的航班、航班信息和天气情况。
注意这里没有考虑错误处理,任意的嵌套rejection可能并不会像你想的那样传播下去。
扁平化promises调用链
如果每级逻辑都很复杂,那么这种深层嵌套是难以管理的,而且开发者还要细心考虑每级调用链的错误处理。
我个人认为这种嵌套是**anti-pattern**的,这里我从错误处理、代码简洁和可维护性角度权衡后对对上述代码进行了重构,实际一个promise回调可以返回以下内容:
- 一个值 - 我们可以将它向下分发并通过resolve回调处理。
- 一个promise - 它将创建一个异步分支。
- 一个异常 - rejection后续promise活动。
- 一个rejected promise - 向下分发病通过reject回调处理。
由于promise回调可以返回promises,让我们重构上述代码。1218
var FlightDashboard = function ($scope, user, flightService, weatherService) {
travelService
.getDeparture(user)
.then(function (departure) {
$scope.departure = departure
return travelService.getFlight(departure.flightId)
})
.then(function (flight) {
$scope.flight = flight
return weatherService.getForecast($scope.departure.date)
})
.then(function (weather) {
$scope.weather = weather
})
$scope.flight = null;
$scope.planStatus = null;
$scope.forecast = null;
}
这里最重要的改变就是每个response回调都返回的是promise。
请记住成功回调中可以返回一个值、跑出一个异常或者返回一个promise
对于之前的深层嵌套这是一个不错的解决方法,但是我并不喜欢在成功回调中去调用另一个promise式API,如果可以将这些冗余的函数剔除那就更好了。
这里有两个很明显的anti-pattern:
- 我们在每级修改$scope变量改为在每个成功回调中修改,
- 我们用
$scope.departure.date代替以前的直接参数传递。
更好的重构
如果我们自处理request-response呢?
var FlightDashboard = function ($scope, user, flightService, weatherService) {
travelService
.getDeparture(user)
.then(function (departure) {
$scope.departure = departure
return travelService.getFlight(departure.flightId)
})
.then(function (flight) {
$scope.flight = flight
return weatherService.getForecast($scope.departure.date)
})
.then(function (weather) {
$scope.weather = weather
})
$scope.flight = null;
$scope.planStatus = null;
$scope.forecast = null;
}
var FlightDashboard = function ($scope, user, travelService, weatherService) {
var loadDeparture = function (user) {
return travelService
.getDeparture(user.email) // Request #1
.then(function (departure) {
$scope.departure = departure; // Response Handler #1
return departure.flightID;
});
},
loadFlight = function (flightID) {
return travelService
.getFlight(flightID) // Request #2
.then(function (flight) {
$scope.flight = flight; // Response Handler #2
return flight;
});
},
loadForecast = function () {
return weatherService
.getForecast($scope.departure.date) // Request #3
.then(function (weather) {
$scope.weather = weather; // Response Handler #3
return weather;
});
};
loadDeparture(user)
.then(loadFlight)
.then(loadForecast)
$scope.user = user;
$scope.departure = null;
$scope.flight = null;
$scope.weather = null;
}
可以看到这里仍然存在anti-pattern (2)。
最后
这里我们再考虑下级与级之前的依赖关系,获取航班信息和天气情况其实不需要有层级关系而是平级的,因此最后我们对代码再进行下处理。
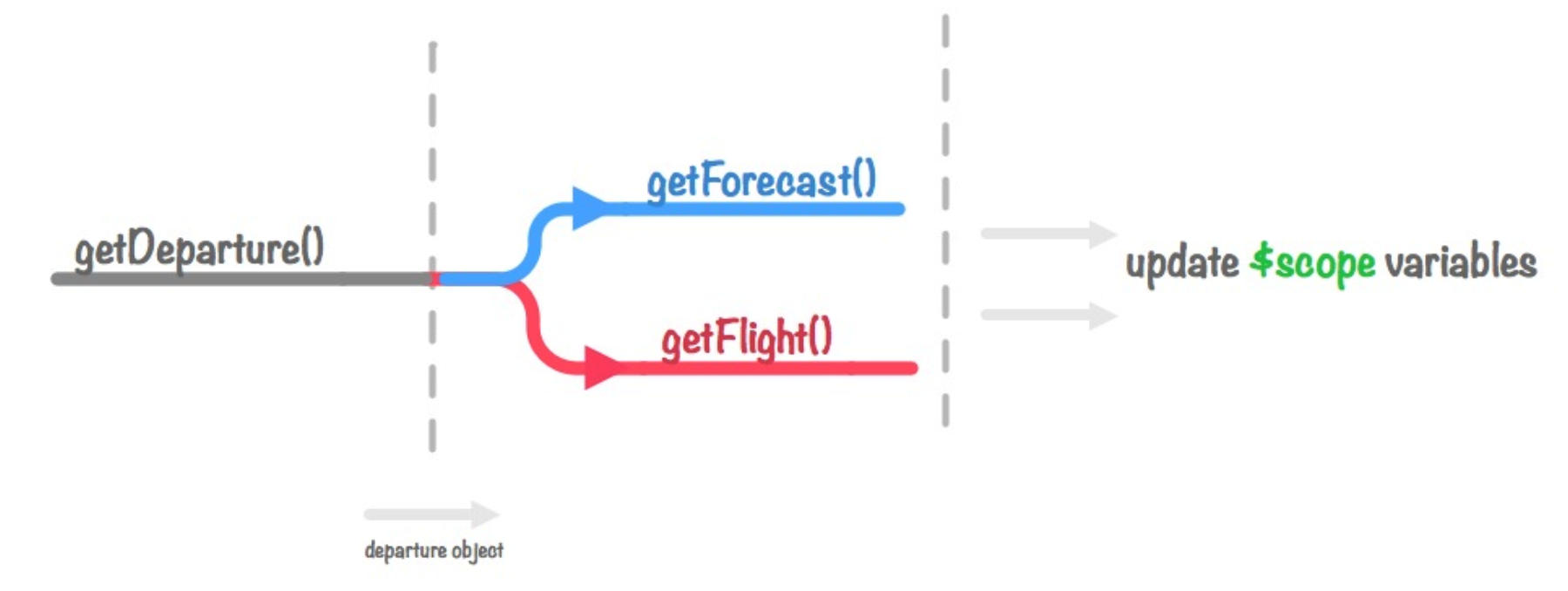
var FlightDashboard = function( $scope, user, travelService, weatherService, $q, $log )
{
var loadFlight = function( user )
{
return travelService.getDeparture( user.email ); // Request #1
},
parallelLoad = function ( departure )
{
// Execute #2 & #3 in parallel...
return $q.all([
travelService.getFlight( departure.flightID ), // Request #2
weatherService.getForecast( departure.date ) // Request #3
])
.then( $q.spread( function( flight, weather )
{
$scope.departure = departure; // Response Handler #1
$scope.flight = flight; // Response Handler #2
$scope.weather = weather; // Response Handler #3
// Let's force an error to demonstrate the reportProblem() works!
throw( new Error("Just to prove catch() works! ") );
}));
},
reportProblems = function( fault )
{
$log.error( String(fault) );
};
// 3-easy steps to load all of our information...
// and now we can include logging for of problems within ANY of the steps
loadFlight( user )
.then( parallelLoad )
.catch( reportProblems );
};
这里我们将异常处理也加上了。