A. Remove Duplicates
Petya has an array aconsisting of nintegers. He wants to remove duplicate (equal) elements.Petya wants to leave only the rightmost entry (occurrence) for each element of the array. The relative order of the remaining unique elements should not be changed.
Input
The first line contains a single integer n(1≤n≤50) — the number of elements in Petya's array.
The following line contains a sequence a1,a2,…,an(1≤ai≤1000) — the Petya's array.
In the first line print integer x— the number of elements which will be left in Petya's array after he removed the duplicates.In the second line print x
integers separated with a space — Petya's array after he removed the duplicates. For each unique element only the rightmost entry should be left.
6
1 5 5 1 6 1
3
5 6 1
5
2 4 2 4 4
2
2 4
5
6 6 6 6 6
1
6
Note
In the first example you should remove two integers 1, which are in the positions 1 and 4. Also you should remove the integer 5, which is in the position 2.
In the second example you should remove integer 2, which is in the position 1, and two integers 4, which are in the positions 2 and 4.
In the third example you should remove four integers 6, which are in the positions 1, 2, 3 and 4.
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cstdlib> #include <iomanip> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include <ctime> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; #pragma comment(linker, "/stck:1024000000,1024000000") #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) #define max(x,y) (x>=y?x:y) #define min(x,y) (x<=y?x:y) #define MAX 100000000000000000 #define MOD 1000000007 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define ei exp(1) #define PI 3.1415926535897932384626433832 #define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(true) #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define mem(a) ((a,0,sizeof(a))) typedef long long ll; int n,a[56][2]; set<int>s; int main() { scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i][0]); int ans=0; for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--) { if(s.count(a[i][0])) a[i][1]=1; else a[i][1]=0,ans++; s.insert(a[i][0]); } printf("%d ",ans); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { if(!a[i][1]) printf("%d ",a[i][0]); } return 0; }
B. File Name
You can not just take the file and send it. When Polycarp trying to send a file in the social network "Codehorses", he encountered an unexpected problem. If the name of the file contains three or more "x" (lowercase Latin letters "x") in a row,
the system considers that the file content does not correspond to the social network topic. In this case, the file is not sent and an error message is displayed.
Determine the minimum number of characters to remove from the file name so after that the name does not contain "xxx" as a substring. Print 0 if the file name does not initially contain a forbidden substring "xxx".
You can delete characters in arbitrary positions (not necessarily consecutive). If you delete a character, then the length of a string is reduced by 1. For example, if you delete the character in the position 2from the string "exxxii", then the resulting string is "exxii".
The first line contains integer n(3≤n≤100)— the length of the file name.
The second line contains a string of length n
consisting of lowercase Latin letters only — the file name.
Print the minimum number of characters to remove from the file name so after that the name does not contain "xxx" as a substring.
If initially the file name dost not contain a forbidden substring "xxx", print 0.
6
xxxiii
1
5
xxoxx
0
10
xxxxxxxxxx
8
In the first example Polycarp tried to send a file with name contains number 33, written in Roman numerals.
But he can not just send the file, because it name contains three letters "x" in a row. To send the file he needs to remove any one of this letters.
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cstdlib> #include <iomanip> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include <ctime> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; #pragma comment(linker, "/stck:1024000000,1024000000") #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) #define max(x,y) (x>=y?x:y) #define min(x,y) (x<=y?x:y) #define MAX 100000000000000000 #define MOD 1000000007 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define ei exp(1) #define PI 3.1415926535897932384626433832 #define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(true) #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define mem(a) ((a,0,sizeof(a))) typedef long long ll; char a[106]; int n; int main() { scanf("%d",&n); scanf("%s",a); int ans=0,pos=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { if(a[i]=='x') ans++; else { if(ans>=3) pos+=ans-2; ans=0; } } if(ans>=3) pos+=ans-2; printf("%d ",pos); return 0; }
C. Letters

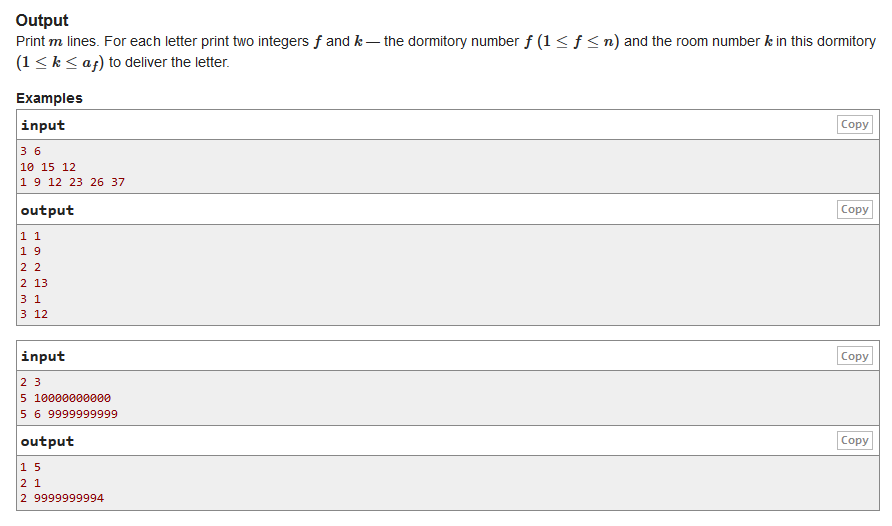

前缀和+二分
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cstdlib> #include <iomanip> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include <ctime> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; #pragma comment(linker, "/stck:1024000000,1024000000") #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) #define max(x,y) (x>=y?x:y) #define min(x,y) (x<=y?x:y) #define MAX 100000000000000000 #define MOD 1000000007 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define ei exp(1) #define PI 3.1415926535897932384626433832 #define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(true) #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define mem(a) ((a,0,sizeof(a))) typedef long long ll; ll a[200005],x,n,m,q; int main() { scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m); a[0]=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%lld",&x); a[i]=a[i-1]+x; } while(m--) { scanf("%lld",&q); ll k=lower_bound(a+1,a+n+1,q)-a; printf("%lld %lld ",k,q-a[k-1]); } return 0; }
D. Almost Arithmetic Progression
Polycarp likes arithmetic progressions. A sequence [a1,a2,…,an]
is called an arithmetic progression if for each i (1≤i<n) the value ai+1−ai is the same. For example, the sequences [42], [5,5,5], [2,11,20,29] and [3,2,1,0] are arithmetic progressions, but [1,0,1], [1,3,9] and [2,3,1]
are not.It follows from the definition that any sequence of length one or two is an arithmetic progression.Polycarp found some sequence of positive integers [b1,b2,…,bn]
. He agrees to change each element by at most one. In the other words, for each element there are exactly three options: an element can be decreased by 1, an element can
beincreased by 1, an element can be left unchanged.Determine a minimum possible number of elements in bwhich can be changed (by exactly one), so that the sequence b
becomes an arithmetic progression, or report that it is impossible.It is possible that the resulting sequence contains element equals 0.
The first line contains a single integer n(1≤n≤100000) — the number of elements in b.
The second line contains a sequence b1,b2,…,bn(1≤bi≤109)
.
If it is impossible to make an arithmetic progression with described operations, print -1. In the other case, print non-negative integer — the minimum number of elements to change to make the given equence becomes an arithmetic progression. The only allowed operation is to add/to subtract one from an element (can't use operation twice tothesameposition).
4
24 21 14 10
3
2
500 500
0
3
14 5 1
-1
5
1 3 6 9 12
1
In the first example Polycarp should increase the first number on 1, decrease the second number on 1, increase the third number on 1, and the fourth number should left
unchanged. So, after Polycarp changed three elements by one, his sequence became equals to [25,20,15,10], which is an arithmetic progression.
In the second example Polycarp should not change anything, because his sequence is an arithmetic progression.
In the third example it is impossible to make an arithmetic progression.In the fourth example Polycarp should change only the first element, he should decrease it on one.
After that his sequence will looks like [0,3,6,9,12], which is an arithmetic progression.
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cstdlib> #include <iomanip> #include <cmath> #include <cassert> #include <ctime> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; #pragma comment(linker, "/stck:1024000000,1024000000") #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) #define max(x,y) (x>=y?x:y) #define min(x,y) (x<=y?x:y) #define MAX 100000000000000000 #define MOD 1000000007 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define ei exp(1) #define PI 3.1415926535897932384626433832 #define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(true) #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define mem(a) ((a,0,sizeof(a))) typedef long long ll; int dir[10][2]={{1,0},{-1,0},{-1,1},{0,1},{1,-1},{0,-1},{0,0},{1,1},{-1,-1}}; int n,ans=INF,a[100005],b[100005],pos,cnt,flag; int main() { scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); if(n<=2) return printf("0 "),0; for(int i=0;i<9;i++) { pos=0;flag=0; if(dir[i][0]!=0) pos++; if(dir[i][1]!=0) pos++; b[0]=a[0]+dir[i][0]; b[1]=a[1]+dir[i][1]; cnt=b[1]-b[0]; for(int j=2;j<n;j++) { if(a[j]+1-b[j-1]==cnt) b[j]=a[j]+1,pos++; else if(a[j]-b[j-1]==cnt) b[j]=a[j]; else if(a[j]-1-b[j-1]==cnt) b[j]=a[j]-1,pos++; else { flag=1; break; } } if(!flag) ans=min(ans,pos); } if(ans==INF) printf("-1 "); else printf("%d ",ans); return 0; }
E. Bus Video System
The busses in Berland are equipped with a video surveillance system. The system records information about changes in the number of passengers in a bus after stops.If x
is the number of passengers in a bus just before the current bus stop and y is the number of passengers in the bus just after current bus stop, the system records the
numbery−x. So the system records show how number of passengers changed.The test run was made for single bus and nbus stops. Thus, the system recorded the sequence of integers a1,a2,…,an (exactly one number for each bus stop), where ai is the record for the bus stop i. The bus stops are numbered from 1 to n
in chronological order.
Determine the number of possible ways how many people could be in the bus before the first bus stop, if the bus has a capacity equals
to w(that is, at any time in the bus thereshould be from 0 to wpassengers inclusive).
The first line contains two integers nand w (1≤n≤1000,1≤w≤109)— the number of bus stops and the capacity of the bus.
The second line contains a sequence a1,a2,…,an
(−106≤ai≤106), where ai equals to the number, which has been recorded by the video system after the i-th bus stop.
Print the number of possible ways how many people could be in the bus before the first bus stop, if the bus has a capacity equals to w. If the situation is contradictory (i.e. for any initial number of passengers there will be a contradiction), print 0.
3 5
2 1 -3
3
2 4
-1 1
4
4 10
2 4 1 2
2
In the first example initially in the bus could be 0, 1 or 2passengers.
In the second example initially in the bus could be 1, 2, 3 or 4passengers.
In the third example initially in the bus could be 0or 1passenger.