Lambda的前世今生
在C#2.0之前,当我们执行委托绑定的方法时,具体如下所示:
public class LambdaDemo { //public delegate void NoReturnNoParam(); public delegate void NoReturnWithParam(int x, int y); //public delegate int WithReturnNoParam(); //public delegate string WithReturnWithParam(int x, ref int y); //Lambda的前世今生 public void Show() { //.net framework 1.0/1.1时代 { //NoReturnNoParam method = new NoReturnNoParam(DoNothing); //method.Invoke(); NoReturnWithParam method1 = new NoReturnWithParam(MethodWithParam); method1.Invoke(1, 2); } private void MethodWithParam(int x, int y) { Console.WriteLine("this is a method with param x,y,without return value"); }
在C# 2.0时代,提出了匿名方法,增加了 一个delegate关键字,可以访问到除了参数以外的局部变量eg此处的float i=100
double i = 100.1; { //2.0时代,匿名方法,增加了 一个delegate关键字,可以访问到除了参数以外的局部变量eg此处的float i=100 NoReturnWithParam method = new NoReturnWithParam(delegate (int x, int y) { Console.WriteLine($"param1 is{x},param2 is {y}"); Console.WriteLine(i); } ); }
在C#3.0时代,去掉了delegate关键字,并在紧跟参数列表后面添加了一个=> goes to
//.net 3.0时代,去掉了delegate关键字,并在紧跟参数列表后面添加了一个=> goes to { NoReturnWithParam method = new NoReturnWithParam((int x, int y) => { Console.WriteLine($"param1 is{x},param2 is {y}"); Console.WriteLine(i); } ); }
到C# 3.0后期,去掉了匿名方法的参数列表的类型。
{ NoReturnWithParam method = new NoReturnWithParam((x, y) => //编译器自动推断来的(语法糖) { Console.WriteLine($"param1 is{x},param2 is {y}"); Console.WriteLine(i); } ); }
该匿名方法在IL中如下:
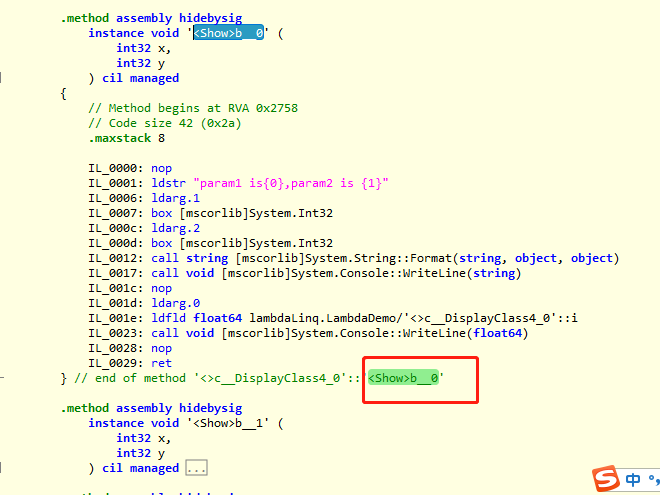
对于以下情况,还可以更加精简:
{ //如果匿名方法体中只有一行代码,可以直接省去方法体的大括号 NoReturnWithParam method = new NoReturnWithParam((x, y) => Console.WriteLine($"param1 is{x},param2 is {y}")); method.Invoke(1, 3); } { //一个参数的时候,无返回值的 Action<string> method = s => Console.WriteLine("with one param of lambda"); method.Invoke("hello"); } //有返回值的情况?如果lambda表达式只有一行代码,且有返回值,则可以省略return { Func<string> func = () => "weiyin"; Func<int, string> func1 = t => t.ToString(); }
Linq的逐步演化
Linq的演化是基于扩展方法来的。
扩展方法的使用
对于扩展方法,此处举个小例子,比如对于实现int与其他类型的相加、字符串截取功能。如下所示:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { LambdaDemo lambdaDemo = new LambdaDemo(); lambdaDemo.Show(); { Student student = new Student() { Id = 1, Name = "weiyin", Age = 28 }; student.StudyMath(); { int i = 1; int? j = 20; //int k = i + j;会报错 int k = i + j.ToInt(); } { string str = "拓展方法实现字符串截取截取截取截取截取截取截取"; Console.WriteLine(str.ToStringLength()); } }
/// <summary> /// 拓展方法的要求 /// </summary> public static class MethdoExtension { public static void StudyMath(this Student stu) { Console.WriteLine("student增加的一个学习数学的拓展方法"); } public static int ToInt(this int ?i) { return i ?? 0;//与下面的语句功能相同。 //if (i == null) //{ // return 0; //} //else //return i.Value; } /// <summary> /// 其实也可以对Object类型进行拓展,拓展Object以后,任何一个类型都可以来调用,因为Object是所有类型的父类---拓展方法可以被继承。 /// 1拓展Oeject 类型以后,会造成类型的方法污染 /// 2 除非需求很明确,否则不要随意的拓展Object或者没有约束的泛型 /// </summary> /// <param name="str"></param> /// <param name="length"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static string ToStringLength(this string str,int length=10) { if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(str)) { return string.Empty; } else if(str.Length>length) { return $"{str.Substring(0,length)}......"; } else { return str; } } }
LINQ演变
此处定义了一个返回List<Student>集合的一个方法,如下:

public static List<Student> GetStudentsList() { List<Student> studentsList = new List<Student>(); Student student1 = new Student() { Id = 1, Name = "weiyin1", Age = 28 }; Student student2 = new Student() { Id = 1, Name = "weiyin2", Age = 29 }; Student student3 = new Student() { Id = 1, Name = "weiyin3", Age = 30 }; Student student4 = new Student() { Id = 1, Name = "weiyin4", Age = 31 }; Student student5 = new Student() { Id = 1, Name = "weiyin5", Age = 32 }; Student student6 = new Student() { Id = 1, Name = "weiyin6", Age = 33 }; studentsList.Add(student1); studentsList.Add(student2); studentsList.Add(student3); studentsList.Add(student4); studentsList.Add(student5); studentsList.Add(student6); return studentsList; }
如果想获取年龄大于30的集合,如何获取呢?最简单的如下:
/// <summary> /// 输入的是 List<Student>,返回的也是 List<Student> /// </summary> /// <param name="stulist"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static List<Student> GetStudentListAgeBiggerthan30(List<Student> stulist) { List<Student> res = new List<Student>(); foreach (var item in stulist) { if (item.Age > 30)//条件的判断其实就是逻辑---就是动作、唯一的区别就是中间这里的条件不一样 { res.Add(item); } } return res; }
如果进一步采用委托将里面的逻辑(动作)抽出来呢【其返回的是一个bool类型,操作的是item Student对象】。如下:
//如果采用拓展函数加委托呢。 /// <summary> /// 使用委托:委托可以把方法当做参数传递;方法其实是逻辑,委托可以把逻辑当做参数传递 /// 委托:应该是返回值为bool的委托,参数是一个Student /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static List<Student> MySelect(this List<Student> resource, Func<Student, bool> func) { List<Student> list = new List<Student>(); foreach (var item in resource) { if (func.Invoke(item)) //if (item.Age > 30)//条件的判断其实就是逻辑---就是动作、、唯一的区别就是中间这里的条件不一样 { list.Add(item); } } return list; }
如果不指定具体的类型Student,Func改为Predicate特定的返回值为bool的委托,则泛型版如下:
/// <summary> /// 泛型拓展方法,满足不同类型需要 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="TSource"></typeparam> /// <param name="resource"></param> /// <param name="func"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static List<TSource> MySelect<TSource>(this List<TSource> resource, Predicate<TSource> tPredicate) { List<TSource> list = new List<TSource>(); foreach (var item in resource) { if (tPredicate.Invoke(item)) //if (item.Age > 30)//条件的判断其实就是逻辑---就是动作、、唯一的区别就是中间这里的条件不一样 { list.Add(item); } } return list; }
如果不想对委托的返回类型约定那么死,想根据用户预想的类型返回。那我们看下Enumerable类下的Select方法签名:

// // 摘要: // 将序列中的每个元素投影到新表单。 // // 参数: // source: // 一个值序列,要对该序列调用转换函数。 // // selector: // 应用于每个元素的转换函数。 // // 类型参数: // TSource: // 中的元素的类型 source。 // // TResult: // 返回的值的类型 selector。 // // 返回结果: // System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable`1 其元素是调用转换函数的每个元素的结果 source。 // // 异常: // T:System.ArgumentNullException: // source 或 selector 为 null。 public static IEnumerable<TResult> Select<TSource, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, TResult> selector);
两者是不是很相像。
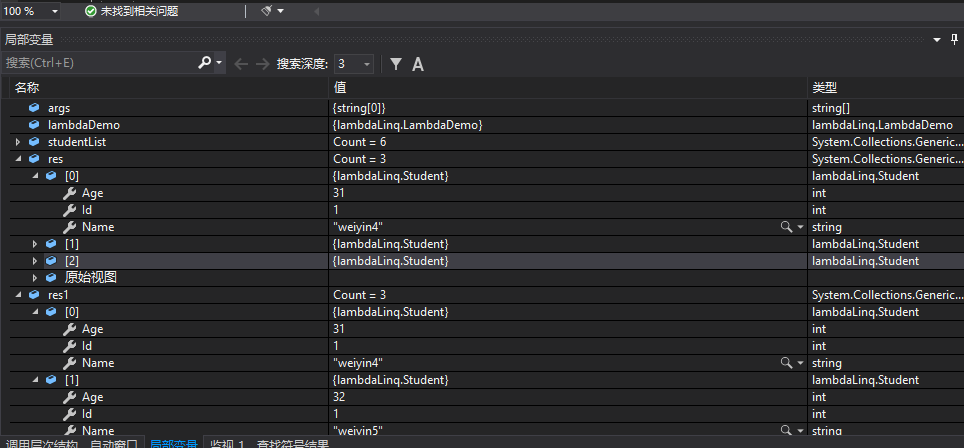
分别用系统内置的Select方法和自定义的MySelect查询数据结果如下:
List<Student> studentList = GetStudentsList(); var res = LinqDemo.GetStudentListAgeBiggerthan30(studentList); //Func<Student, bool> func = item => item.Age > 30; //studentList.Mywhere(func); var res1 = studentList.MySelect(item => item.Age > 30); var result = studentList.Select(t => t.Age > 30);
个人总结:
Lambda表达式是本质是基于匿名方法(在IL中就是一个符合指定签名的方法),经过步步简化后的语法糖,它作为委托实例的参数,绑定了委托实例将要执行的签名方法。
LINQ是基于扩展方法和Lambda表达式,通过执行特定泛型类型的扩展方法(改拓展方法中写明了不变与可变【委托绑定的方法】的部分),通过传入Lambda表达式【委托绑定的方法,委托实例的参数】,执行特定逻辑动作。
