1. new,delete的局部重载:
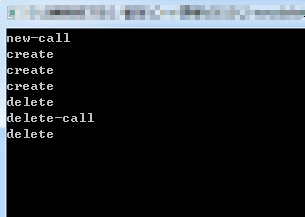
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int objs = 0; class myclass { public: myclass() { //objs++; cout << "create" << endl; } ~myclass() { //objs--; cout << "delete" << endl; } //operator重载,针对new重新作出一种解释,只针对当前类 static void * operator new(size_t size) { objs++; cout << "new-call" << endl; myclass *p = ::new myclass; //全局new return p; } static void operator delete(void *p) { objs--; cout << "delete-call" << endl; ::delete p; } }; //功能1:无法在堆上被创建的类 void main() { myclass *p1 = new myclass; myclass *p2 = new myclass; myclass *p3 = new myclass; delete p1; int *p = new int(5); //此时new重载对于这一句无效 cout << objs << endl; cin.get(); }
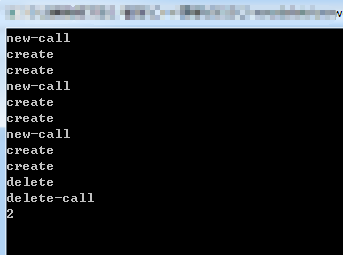
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int objs = 0; void *g_p = nullptr; class myclass { public: myclass() { //objs++; cout << "create" << endl; } ~myclass() { //objs--; cout << "delete" << endl; } //operator重载,针对new重新作出一种解释,只针对当前类 static void * operator new(size_t size) { if (g_p==nullptr) { objs++; cout << "new-call" << endl; myclass *p = ::new myclass; //全局new g_p = p; //单例,堆上创建对象只有一个 return p; } else { return g_p; } } static void operator delete(void *p) { if (g_p!=nullptr) { objs--; cout << "delete-call" << endl; ::delete p; g_p = nullptr; } } }; //功能1:无法在堆上被创建的类 //功能2:实现统计分配内存,释放内存的次数 //实现单例设计模式,实现避免反复delete出错 //new delete在内部,只针对当前类,int double 无影响 void main() { myclass *p1 = new myclass; myclass *p2 = new myclass; delete p1; delete p1; //规避了两次delete的错误 cin.get(); }
2. 全局new,delete重载:
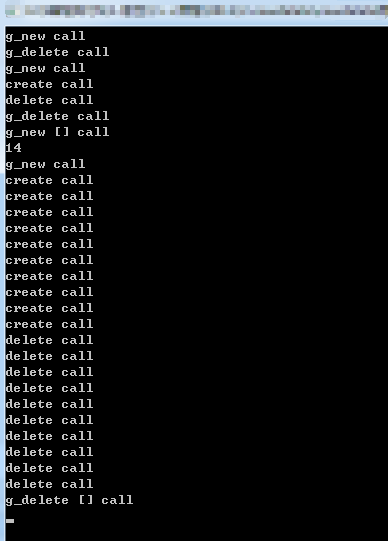
#include <iostream> using namespace std; //全局内存管理,统计释放内存,分配内存 //new new [] delete delete [] //分配内存优先于构造 //析构优先于释放内存 void * operator new(size_t size) { cout << "g_new call" << endl; void *p = malloc(size); //全局的new,只能使用malloc return p; } void * operator new [](size_t size) { cout << "g_new [] call" << endl; cout << size << endl; return operator new(size); //每个元素调用一次new } void operator delete(void *p) { cout << "g_delete call" << endl; free(p); } void operator delete [](void *p) { cout << "g_delete [] call" << endl; free(p); } class myclass { public: myclass() { cout << "create call" << endl; } ~myclass() { cout << "delete call" << endl; } }; void main() { int *p1 = new int(5); delete p1; myclass *p2 = new myclass; delete p2; myclass *px = new myclass[10]; delete[]px; cin.get(); }
3. 绑定类成员函数:
#include <iostream> #include <functional> using namespace std; using namespace std::placeholders;//站位 struct MyStruct { void add1(int a) { cout << a << endl; } void add2(int a, int b) { cout << a << b << endl; } void add3(int a, int b, int c) { cout << a << b << c << endl; } }; void main() { MyStruct my1; //my1.add(10); //绑定包装器,包装类成员函数,用于使用 auto fun1 = bind(&MyStruct::add1, &my1, _1);//有1个参数 函数名、对象地址、参数 fun1(10); auto fun2 = bind(&MyStruct::add2, &my1, _1,_2);//有2个参数 fun2(100,200); auto fun3 = bind(&MyStruct::add3, &my1, _1,_2,_3);//有3个参数 fun3(1000,2000,3000); cin.get(); }
4. 绑定lambda表达式以及仿函数:
#include <iostream> #include <functional> using namespace std; using namespace std::placeholders; int add(int a, int b,int c) { return a + b+c; } struct MyStruct { int operator()(int a,int b) //仿函数 { return a + b; } }; void main() { auto fun1 = bind(add, 10,12, _1);//适配器模式 cout << fun1(1000) << endl; //1022 auto fun2 = bind([](int a, int b)->int {return a + b; }, 100, _1); cout << fun2(123) << endl; //223 MyStruct my1; cout << my1(1, 2) << endl; //3 auto fun3 = bind(my1, 100, _1); //绑定 cout << fun3(100) << endl; //200 cin.get(); }
5. 静态断言:
#include <iostream> #include <cassert> using namespace std; int divv(int a, int b) { assert(b != 0); //断言 return a / b; } void main() { cout << divv(1, 0) << endl; cin.get(); }
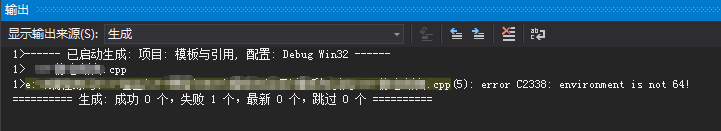
#include <iostream> #include <cassert> using namespace std; static_assert(sizeof(void *) >= 8, "environment is not 64!"); void main() { cin.get(); }
6. 内联函数:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; #define f(x) x*x*x //C语言内联,C++要求类型严格匹配 inline int get(int x) //C++的内联函数 { return x*x*x; } //提高程序运行速度 //inline 只是对于编译器的建议 //一般情况下,我们对内联函数做如下的限制: //(1)不能有递归; //(2)不能包含静态数据; //(3)不能包含循环; //(4)不能包含switch和goto语句; //(5)不能包含数组。 //若一个内联函数定义不满足以上限制,则编译系统把它当做普通函数对待 template<class T> inline T go(T t) { return t*t; } void main() { get(10); go(5); //优化为内联函数 auto fun = []() {}; //lambda表达式实际上也是内联函数 cin.get(); }
7. CPP处理转义字符:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; void main() { //string str(""C:\Program Files (x86)\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe""); string str(R"("C:Program Files (x86)GoogleChromeApplicationchrome.exe")"); // R"(......)" system(str.c_str()); cin.get(); }