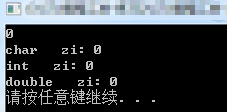
1. 算法容器的使用:
#include <iostream> #include <functional> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> //算法,共包含108个算法 #include <numeric> //整数 using namespace std; using namespace std::placeholders; //用于bind()函数的"_1"参数 struct MyStruct { int operator()(int data) //对()进行重载-->伪函数 { return data % 2 == 1; } }; int get(int data) { return data % 2 == 1; } struct my { int get(int data) { return data % 2 == 1; } }; int main() { vector<int> myint{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11 }; //创建容器 //法一:lambda表达式 int num1 = count_if(myint.begin(), myint.end(), [](int data)->bool {return data % 2 == 0; }); //偶数个数 //法二:伪函数(匿名对象) int num2 = count_if(myint.begin(), myint.end(), MyStruct()); //MyStruct()匿名对象 //法三:有名对象 MyStruct my1; int num3 = count_if(myint.begin(), myint.end(), my1); //法四:函数 int num4 = count_if(myint.begin(), myint.end(), get); //法五:成员函数(函数绑定器) my my2; auto fun = bind(&my::get, &my2, _1); int num5 = count_if(myint.begin(), myint.end(), fun); cout << num1 << endl; //4 cout << num2 << endl; //6 cout << num3 << endl; //6 cout << num4 << endl; //6 cout << num5 << endl; //6 system("pause"); return 0; }
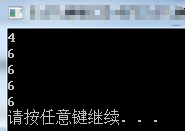
1.1 加入函数模板如下:
#include <iostream> #include <functional> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> //算法,共包含108个算法 #include <numeric> //整数 using namespace std; using namespace std::placeholders; //用于bind()函数的"_1"参数 template<class T> bool getT(T data) { return data % 2 == 1; } int main() { vector<int> myint{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11 }; //创建容器 int num6 = count_if(myint.begin(), myint.end(), getT<int>); cout << num6 << endl; //6 system("pause"); return 0; }

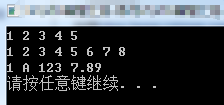
2. 模板的展开 ==> 属于模板元的范畴
#include <iostream> #include <cstdarg> using namespace std; template<class T> void show(T t) { cout << t << " "; } template<class...Args> void all(Args...args) { int arr[] = { (show(args),0)... }; //使用数组进行展开 } template<class...Args> void allIt(Args...args) { int arr[] = { (show(args),0)... }; //int arr[],用来约束展开多少层,保存在数组里面,[]不能省 } int main() { all(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); cout << endl; all(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8); cout << endl; allIt(1, 'A', "123", 7.89); cout << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
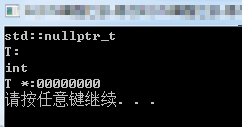
3. 函数模板推理机制:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<typename T> void go(T t) //将类型泛型 { cout << typeid(T).name() << endl; //cout << t << endl; cout << "T:" << endl; } template<int i> //模板之间也可以重载 void go() //数据可以为任意数据(相当于数字模板) { cout << i << endl; } template<typename T> void go(T *t) //将类型泛型 { cout << typeid(T).name() << endl; cout << "T *:" << t << endl; } int main() { /* go(31 - 2); //调用泛型函数模板 go<31 - 2>(); //调用数字模板 go<decltype(10 + 2)>(1234); //调用泛型函数模板,可以用decltype获取数据类型 */ go(nullptr); //nullptr不是指针类型,是一种自定义的数据类型表示空指针而已,调用go(T t) int *p = nullptr; //调用go(T *t) go(p); system("pause"); return 0; }
4. 函数指针与函数模板:
4.1 函数模板赋值给函数指针:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> void show(T t) { cout << t << endl; } struct MyStruct { template<class T> void show(T t) { cout << t << endl; } void go() { show(123); } }; //函数模板赋值给函数指针 int main() { //void(*p)() = show<int>; //无法从“void (__cdecl *)(T)”转换为“void (__cdecl *)(void)” void(*p1)(int i) = show<int>; void(*p2)(double db) = show<double>; system("pause"); return 0; }
4.2 如何调用结构体中的函数模板?
//如何调用结构体中的函数模板? int main() { MyStruct my1; my1.go(); //结构体内部调用结构体中的函数模板 my1.show(12.3); //外部直接调用结构体中的函数模板 my1.show('A'); my1.show<int>('A'); system("pause"); return 0; }

4.3 如何绑定结构体内部的函数模板?
#include <iostream> #include <functional> using namespace std; using namespace std::placeholders; template<class T> void show(T t) { cout << t << endl; } struct MyStruct { template<class T> void show(T t) { cout << t << endl; } template<class T> void showit(T t1, T t2) { cout << t1 << " " << t2 << endl; } void go() { show(123); } }; //如何绑定结构体内部的函数模板? int main() { MyStruct my1; auto fun = bind(&MyStruct::showit<int>, &my1, 1, 2); fun(2); system("pause"); return 0; }

5. 函数模板、模板函数与类模板:
5.1 什么是函数模板?什么是模板函数?
函数模板就是上面所讲的函数模板,而模板函数则是实例化的函数模板。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; /*函数模板,不调用不编译*/ template<class T> T add(T a, T b) { return a + b; } int main() { add(1, 2); /*模板函数,也就是实例化的函数模板,自动根据参数推理*/ add<double>(1, 1.2); /*模板函数*/ system("pause"); return 0; }
5.2 类成员函数模板:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class myclass { public: template<class T> //类成员函数模板 T add(T a, T b) { return a + b; } template<class T> //静态函数模板 static T sub(T a, T b) { return a - b; } }; int main() { myclass *p = nullptr; int num1 = p->add<int>(2, 3); //强行指定的模板函数,当做类成员函数调用 int num2 = p->add(2, 3); //自动推理的模板函数 cout << num1 << endl; cout << num2 << endl; int num3 = myclass::sub(9 , 1); cout << num3 << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
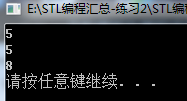
6. 模板在类中的应用:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; class myclass { public: template<class T> T add(T a) { return a; } template<class T> T add(T a,T b) { show(); //函数模板与类成员函数可以互相调用 return a + b; } template<class T> T add(T a, T b,T c) { return a + b + c; } //template<class T> //virtual T add(T a, T b,T c) //error C2898: “T myclass::add(T,T,T)”: 成员函数模板不能是虚拟的 //{ // return a + b + c; //} void show() { cout << add<int>(10) << endl; //指明类型的方式调用 } }; int main() { myclass *p = nullptr; p->add(1, 2); system("pause"); return 0; }
7. 类模板与函数模板对比:
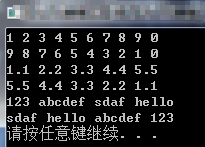
#include <iostream> #include <initializer_list> #include <memory> #include <string> using namespace std; template<class T,int n> class myarray { T *p; public: myarray(initializer_list<T> mylist) { p = new T[n]; //开辟内存 memset(p, 0, sizeof(T)*n); //内存清0 int length = mylist.size(); if (length > n) { abort(); //触发异常 } else { int i = 0; for (auto j : mylist) //数据填充 { p[i] = j; i++; } } } ~myarray() { delete[] p; } void show() //显示数据 { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cout << p[i] << " "; } cout << endl; } void sort() //冒泡排序 { for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n - 1 - i; j++) { if (p[j] < p[j+1]) //从大到小 { T temp = p[j]; p[j] = p[j + 1]; p[j + 1] = temp; } } } } }; int main() { myarray<int, 10> my1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 }; my1.show(); my1.sort(); my1.show(); myarray<double, 5> my2 = { 1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5 }; my2.show(); my2.sort(); my2.show(); myarray<string, 5> my3 = { "123","abcdef","sdaf","hello" }; my3.show(); my3.sort(); my3.show(); system("pause"); return 0; }
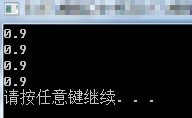
8. 类包装器:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class T,class F> //函数模板 T run(T t, F f) { return f(t); } class fun { public: double operator ()(double data) { return data - 10; } }; template<class T> //类模板 class Tfun { public: T operator ()(T data) { return data - 10; } }; int main() { cout << run(10.9, fun()) << endl; //fun()是匿名对象 fun x; cout << run(10.9, x) << endl; //x是有名对象 cout << run(10.9, Tfun<double>()) << endl; //模板函数的匿名对象,构造函数返回的就是匿名对象 Tfun<double> fang; cout << run(10.9, fang) << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
9. 高级类包装器:
#include <iostream> #include <list> #include <vector> using namespace std; template<class T, class F> //函数模板 T run(T t, F f) { return f(t); } template<class T> //类模板 class Trun { public: T operator ()(T data) { for (auto i:data) { cout << i <<" "; } cout << endl; return data; } }; int main() { list<int> myint; //构建链表,压入数据 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { myint.push_back(i); } run(myint, //lambda表达式 [](list<int> myint)->list<int> { for (auto i : myint) { cout << i << endl; } return myint; } ); system("pause"); return 0; }

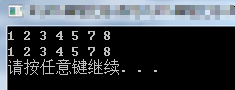
#include <iostream> #include <list> #include <vector> using namespace std; template<class T, class F> //函数模板 T run(T t, F f) { return f(t); } template<class T> //类模板 class Trun { public: T operator ()(T data) { for (auto i:data) { cout << i <<" "; } cout << endl; return data; } }; int main() { vector<int> myv{ 1,2,3,4,5,7,8 }; run(myv, Trun< vector<int> >()); //匿名对象,用完就扔 run(myv, Trun< decltype(myv) >()); system("pause"); return 0; }
10. 类模板间的封装、继承、多态:
10.1 父类为类模板,子类也是类模板:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; //类模板支持封装、继承、多态 template<class T> class Tfu { public: T t; Tfu():t(0) { } void show() { cout << t << endl; } virtual void go() { cout << "fu:" << t << endl; } }; template<class T> class Tzi :public Tfu<T> { public: void go() { cout << "zi:" << t << endl; } }; int main() { Tzi<int> tzi; tzi.t = 109; tzi.show(); Tfu<int> *p = new Tzi<int>; //实现多态 p->go(); system("pause"); return 0; }

10.2 父类为类模板,子类为普通类:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> class Tfu { public: T t; Tfu() :t(0) { } void show() { cout << t << endl; } virtual void go() { cout << "fu:" << t << endl; } }; class zi :public Tfu<int> { public: void go() { cout << "zi:" << t << endl; } }; int main() { zi z1; z1.t = 108; z1.show(); Tfu<int> *p = new zi; //多态 此处只能用int p->go(); system("pause"); return 0; }

10.3 父类为普通类,子类为类模板:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; //类模板支持封装、继承、多态 //T T //类模板 可以实现封装、继承、多态 //T P //类模板与类 可以实现封装、继承、多态 必须明确类型 //P T //类与类模板 可以实现封装、继承、多态 必须明确类型 多态什么类型都可以 //P P //普通类 可以实现封装、继承、多态 class die { public: int t; die() :t(0) { } void show() { cout << t << endl; } virtual void go() { cout << "fu: " << t << endl; } }; template<class T> class er :public die { public: void go() { cout << typeid(T).name() << " zi: " << t << endl; } }; int main() { er<double> boer; boer.show(); die *p1 = new er<char>; die *p2 = new er<int>; die *p3 = new er<double>; p1->go(); p2->go(); p3->go(); system("pause"); return 0; }