muduo库里面的实现日志滚动有两种条件,一种是日志文件大小达到预设值,另一种是时间到达超过当天。滚动日志类的文件是LogFile.cc ,LogFile.h
代码如下:
LogFile.cc
#include <muduo/base/LogFile.h>
#include <muduo/base/Logging.h> // strerror_tl
#include <muduo/base/ProcessInfo.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
using namespace muduo;
//LogFile里面嵌套的File类
// not thread safe
class LogFile::File : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
//传进文件名称,执行打开文件,文件指针保存到fp_
explicit File(const string& filename): fp_(::fopen(filename.data(), "ae")), writtenBytes_(0)
{
assert(fp_);//断言文件已经打开
::setbuffer(fp_, buffer_, sizeof buffer_);//设定文件指针的缓冲区
// posix_fadvise POSIX_FADV_DONTNEED ?
}
~File()
{//析构函数关闭文件指针
::fclose(fp_);
}
//把logline这一行信息添加到文件当中
void append(const char* logline, const size_t len)
{
size_t n = write(logline, len);//这个write是一个内部的成员函数
//计算剩余的字节数,len是要写入的,n是已经写入的
size_t remain = len - n;
while (remain > 0)//大于-则表示没有写完
{//一直写直到写完为止
size_t x = write(logline + n, remain);
if (x == 0)
{
int err = ferror(fp_);
if (err)//写入错误
{
fprintf(stderr, "LogFile::File::append() failed %s
", strerror_tl(err));
}
break;
}
n += x;//更新已经写的个数
remain = len - n; // remain -= x,更新剩余字节数
}
writtenBytes_ += len;//更新已经写的字节数
}
void flush()
{//清空缓冲区
::fflush(fp_);
}
//返回已经写的字节数
size_t writtenBytes() const { return writtenBytes_; }
private:
size_t write(const char* logline, size_t len)
{
#undef fwrite_unlocked
//使用fwrite_unlocked方式写入效率会高一些
return ::fwrite_unlocked(logline, 1, len, fp_);
}
FILE* fp_;//fp_为文件指针
char buffer_[64*1024];//文件指针的缓冲区,64k
size_t writtenBytes_;//已经写入的字节数
};
LogFile::LogFile(const string& basename,
size_t rollSize,
bool threadSafe,
int flushInterval)
: basename_(basename),//日志文件的basename
rollSize_(rollSize),//日志文件写到rollSize_这么大的容量时就换一个新的文件
flushInterval_(flushInterval),//日志写入的间隔时间,默认是3秒钟
count_(0),//计数器初始化为0
mutex_(threadSafe ? new MutexLock : NULL),//如果是线程安全的则构造一个互斥锁
//mutex_是个智能指针能够自动销毁
startOfPeriod_(0),//开始记录日志时间(将会调整至0点时间)
lastRoll_(0),//上一次滚动日志的时间
lastFlush_(0)//上一次日志写入文件的时间
{
assert(basename.find('/') == string::npos);//断言basename不能找到'/'
rollFile();//滚动日志(第一次,产生一个文件)
}
LogFile::~LogFile()
{
}
void LogFile::append(const char* logline, int len)
{
if (mutex_)//如果是线程安全的
{
MutexLockGuard lock(*mutex_);//先加锁
append_unlocked(logline, len);//再添加
}
else//否则直接添加
{
append_unlocked(logline, len);
}
}
void LogFile::flush()
{
if (mutex_)
{
MutexLockGuard lock(*mutex_);
file_->flush();
}
else
{
file_->flush();
}
}
//日志滚动的条件有两种:满,到达第二天
void LogFile::append_unlocked(const char* logline, int len)
{//加入
file_->append(logline, len);
if (file_->writtenBytes() > rollSize_)//如果已经写入的字节数大于rollSize_
{
rollFile();//滚动日志
}
else
{//否则查看计数值count是否超过kCheckTimeRoll_
if (count_ > kCheckTimeRoll_)
{
count_ = 0;//计数值清零
time_t now = ::time(NULL);//取当前时间
time_t thisPeriod_ = now / kRollPerSeconds_ * kRollPerSeconds_;//把时间调整到当天的零点
if (thisPeriod_ != startOfPeriod_)//如果不等,则应该就是第二天的零点
{
rollFile();//滚动日志
}
else if (now - lastFlush_ > flushInterval_)//时间差大于日志写入的间隔时间
{
lastFlush_ = now;
file_->flush();
}
}
else
{
++count_;//计数值增加
}
}
}
//滚动日志
void LogFile::rollFile()
{
time_t now = 0;
string filename = getLogFileName(basename_, &now);//获取文件名,并且返回时间
//这里除以kRollPerSeconds_又乘以kRollPerSeconds_表示对齐至kRollPerSeconds_的整数倍
//即把时间调整到当天的零点
time_t start = now / kRollPerSeconds_ * kRollPerSeconds_;
if (now > lastRoll_)
{//滚动日志
lastRoll_ = now;
lastFlush_ = now;
startOfPeriod_ = start;
file_.reset(new File(filename));//产生一个新的日志文件
}
}
//获取文件名
string LogFile::getLogFileName(const string& basename, time_t* now)
{
string filename;
//string类对象filename预留这么多的空间,basename后面还要加内容,所以再加64
filename.reserve(basename.size() + 64);
filename = basename;
char timebuf[32];
char pidbuf[32];
struct tm tm;
*now = time(NULL);//获取当前时间
//gmtime_r是线程安全的,gmtime不是线程安全的
gmtime_r(now, &tm); // FIXME: localtime_r ?GMT时间也就是UTC时间,保存在tm中
//把时间格式化放在缓冲区timebuf中
strftime(timebuf, sizeof timebuf, ".%Y%m%d-%H%M%S.", &tm);
//时间加入到filename中
filename += timebuf;
filename += ProcessInfo::hostname();//主机名称加入到filename中
//获取进程号pid
snprintf(pidbuf, sizeof pidbuf, ".%d", ProcessInfo::pid());
//pid加入到filename中
filename += pidbuf;
//后缀名加入到filename中
filename += ".log";
//返回filename
return filename;
}
LogFile.h
//日志滚动
#ifndef MUDUO_BASE_LOGFILE_H
#define MUDUO_BASE_LOGFILE_H
#include <muduo/base/Mutex.h>
#include <muduo/base/Types.h>
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <boost/scoped_ptr.hpp>
namespace muduo
{
class LogFile : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
//线程安全默认是true,日志写入的间隔时间是3秒钟
LogFile(const string& basename,size_t rollSize,bool threadSafe = true,int flushInterval = 3);
~LogFile();
//将长度为len的一行添加到日志当中
void append(const char* logline, int len);
//清空缓冲区
void flush();
private:
//以不加锁的方式添加
void append_unlocked(const char* logline, int len);
//获取日志文件的名称
static string getLogFileName(const string& basename, time_t* now);
//滚动日志
void rollFile();
const string basename_;//日志文件的basename
const size_t rollSize_;//日志文件写到rollSize_这么大的容量时就换一个新的文件
const int flushInterval_;//日志写入的间隔时间
int count_;//计数器,当达到kCheckTimeRoll_会去检测一下是否需要写入新文件
boost::scoped_ptr<MutexLock> mutex_;//互斥量的智能指针
time_t startOfPeriod_;//开始记录日志时间(将会调整至0点时间)
time_t lastRoll_;//上一次滚动日志的时间
time_t lastFlush_;//上一次日志写入文件的时间
class File;//File嵌套类
boost::scoped_ptr<File> file_;//File嵌套类的一个智能指针
const static int kCheckTimeRoll_ = 1024;
const static int kRollPerSeconds_ = 60*60*24;//一天的秒数
};
}
#endif // MUDUO_BASE_LOGFILE_H
测试代码则是输出一系列的日志,进行日志滚动,代码如下:
LogFile_test.cc
//日志滚动测试程序
#include <muduo/base/LogFile.h>
#include <muduo/base/Logging.h>
boost::scoped_ptr<muduo::LogFile> g_logFile;
void outputFunc(const char* msg, int len)
{
g_logFile->append(msg, len);
}
void flushFunc()
{
g_logFile->flush();
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char name[256];
strncpy(name, argv[0], 256);
//滚动日志的话肯定就是输出到文件了
g_logFile.reset(new muduo::LogFile(::basename(name), 200*1000));
muduo::Logger::setOutput(outputFunc);
muduo::Logger::setFlush(flushFunc);
muduo::string line = "1234567890 abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ ";
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; ++i)
{//输出日志
LOG_INFO << line << i;
usleep(1000);
}
}
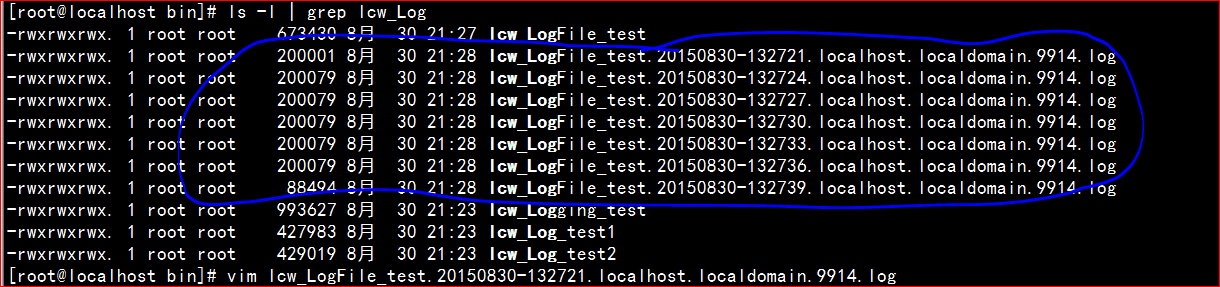
运行结果如下:
另一个文件测试日志的各种性能
Logging_test.cc
#include <muduo/base/Logging.h>
#include <muduo/base/LogFile.h>
#include <muduo/base/ThreadPool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int g_total;
FILE* g_file;//文件指针
boost::scoped_ptr<muduo::LogFile> g_logFile;//智能指针
void dummyOutput(const char* msg, int len)
{
g_total += len;//更新g_total
if (g_file)//最开始g_file,g_logFile都是空的,不执行
{
fwrite(msg, 1, len, g_file);
}
else if (g_logFile)
{
g_logFile->append(msg, len);
}
}
void bench(const char* type)
{
muduo::Logger::setOutput(dummyOutput);//更改默认输出
muduo::Timestamp start(muduo::Timestamp::now());//开始时间
g_total = 0;
int n = 1000*1000;//100w次
const bool kLongLog = false;
muduo::string empty = " ";
muduo::string longStr(3000, 'X');//3000个X
longStr += " ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
LOG_INFO << "Hello 0123456789" << " abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
<< (kLongLog ? longStr : empty)//kLongLog真,输出longStr,假输出empty
<< i;
}
muduo::Timestamp end(muduo::Timestamp::now());//截止时间
double seconds = timeDifference(end, start);//计算时间差
//打印到标准输出
printf("%12s: %f seconds, %d bytes, %10.2f msg/s, %.2f MiB/s
",
type, seconds, g_total, n / seconds, g_total / seconds / (1024 * 1024));
}
void logInThread()
{//线程池当中的线程,更新日志
LOG_INFO << "logInThread";
usleep(1000);
}
int main()
{//获取父进程pid
getppid(); // for ltrace and strace
//建立线程池
muduo::ThreadPool pool("pool");
//线程池启动5个线程
pool.start(5);
//线程池添加5个任务
pool.run(logInThread);
pool.run(logInThread);
pool.run(logInThread);
pool.run(logInThread);
pool.run(logInThread);
//主线程输出日志
LOG_TRACE << "trace";
LOG_DEBUG << "debug";
LOG_INFO << "Hello";
LOG_WARN << "World";
LOG_ERROR << "Error";
LOG_INFO << sizeof(muduo::Logger);
LOG_INFO << sizeof(muduo::LogStream);
LOG_INFO << sizeof(muduo::Fmt);
LOG_INFO << sizeof(muduo::LogStream::Buffer);
//睡眠1秒钟
sleep(1);
//性能测试程序
bench("nop");
char buffer[64*1024];
//空文件,测试数据写入到/dev/null中的性能
g_file = fopen("/dev/null", "w");
setbuffer(g_file, buffer, sizeof buffer);
bench("/dev/null");
fclose(g_file);
//测试数据写入到/tmp/log中的性能
g_file = fopen("/tmp/log", "w");
setbuffer(g_file, buffer, sizeof buffer);
bench("/tmp/log");
fclose(g_file);
g_file = NULL;
//不是线程安全的
g_logFile.reset(new muduo::LogFile("test_log_st", 500*1000*1000, false));
bench("test_log_st");
//线程安全的
g_logFile.reset(new muduo::LogFile("test_log_mt", 500*1000*1000, true));
bench("test_log_mt");
g_logFile.reset();
}
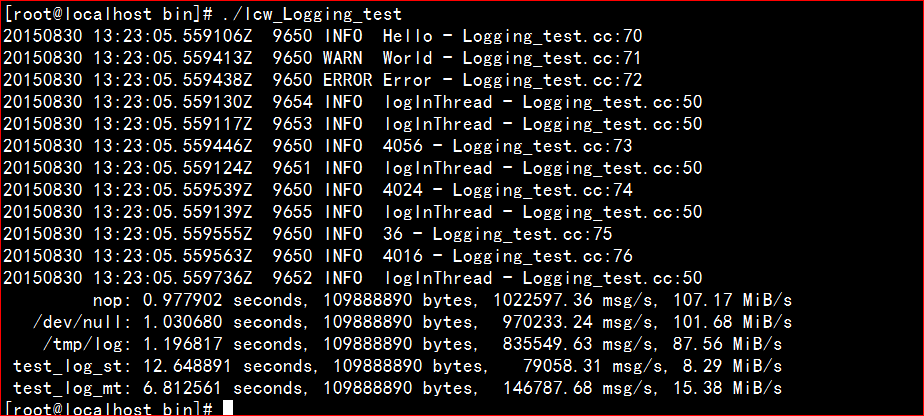
运行结果如下: