muduo源码的互斥锁源码位于muduo/base,Mutex.h,进行了两个类的封装,在实际的使用中更常使用MutexLockGuard类,因为该类可以在析构函数中自动解锁,避免了某些情况忘记解锁。代码如下所示:
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
//
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
//互斥锁
#ifndef MUDUO_BASE_MUTEX_H
#define MUDUO_BASE_MUTEX_H
#include <muduo/base/CurrentThread.h>
#include <boost/noncopyable.hpp>
#include <assert.h>
#include <pthread.h>
namespace muduo
{
class MutexLock : boost::noncopyable//继承自noncopyable,表示不可拷贝
{
public:
MutexLock() : holder_(0)//构造函数,将holder初始化为0,表示该锁没有被任何线程拥有
{
int ret = pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_, NULL);//初始化互斥锁
assert(ret == 0); (void) ret;
}
~MutexLock()//析构函数
{
assert(holder_ == 0);//断言该锁没有被任何线程占用,才可以销毁
int ret = pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_);
assert(ret == 0); (void) ret;
}
bool isLockedByThisThread()//是否当前线程拥有该锁
{
return holder_ == CurrentThread::tid();//只需判断当前线程的tid是否等于holder_
}
void assertLocked()//断言当前线程拥有该锁
{
assert(isLockedByThisThread());
}
// internal usage
void lock()//加锁
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_);
holder_ = CurrentThread::tid();//将当前线程的tid保存至holder_
}
void unlock()//解锁
{
holder_ = 0;//holder_清零
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_);
}
//获取threadMutex对象
pthread_mutex_t* getPthreadMutex() /* non-const */
{
return &mutex_;
}
private:
pthread_mutex_t mutex_;//变量保存
pid_t holder_;//当前使用该锁的线程id
};
//MutexLockGuard类使用RAII技法封装,在实际应用中这个类更常用
class MutexLockGuard : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
//explicit只能显式调用
explicit MutexLockGuard(MutexLock& mutex): mutex_(mutex)
{//构造函数获取资源
mutex_.lock();
}
//在对象生存期结束的时候利用析构函数可以实现自动解锁
~MutexLockGuard()
{//析构函数释放资源
mutex_.unlock();
}
private:
MutexLock& mutex_;//整个对象结束的时候mutex_并没有结束(引用)
};
}
// Prevent misuse like:
// MutexLockGuard(mutex_);
// A tempory object doesn't hold the lock for long!
#define MutexLockGuard(x) error "Missing guard object name"
#endif // MUDUO_BASE_MUTEX_H
测试程序分别使用集中不同的方式往向量中插入数据,从中也可以看出锁的开销,测试代码如下所示:
//互斥锁测试代码
#include <muduo/base/CountDownLatch.h>
#include <muduo/base/Mutex.h>
#include <muduo/base/Thread.h>
#include <muduo/base/Timestamp.h>
#include <boost/bind.hpp>
#include <boost/ptr_container/ptr_vector.hpp>
#include <vector>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace muduo;
using namespace std;
MutexLock g_mutex;//声明锁对象
vector<int> g_vec;//int动态数组(向量)
const int kCount = 10*1000*1000;//常量1千万
void threadFunc()
{
for (int i = 0; i < kCount; ++i)
{
MutexLockGuard lock(g_mutex);//使用锁
g_vec.push_back(i);//往向量中插入1000w个整数
}
}
int main()
{
const int kMaxThreads = 8;//最多8个线程
g_vec.reserve(kMaxThreads * kCount);//预留8千万个整数(这个所占的内存空间有300多M)
Timestamp start(Timestamp::now());//当前时间戳
for (int i = 0; i < kCount; ++i)
{
g_vec.push_back(i);//往向量中插入1000w个整数
}
//输出插入这么多个数的时间
printf("single thread without lock %f
", timeDifference(Timestamp::now(), start));
start = Timestamp::now();//更新当前时间戳
threadFunc();//调用上面的函数
//和上面一样,计算下插入这么多个数的时间
printf("single thread with lock %f
", timeDifference(Timestamp::now(), start));
for (int nthreads = 1; nthreads < kMaxThreads; ++nthreads)
{//ptr_vector指针的vector
boost::ptr_vector<Thread> threads;
g_vec.clear();//先清除g_vec向量
start = Timestamp::now();//更新当前时间戳
for (int i = 0; i < nthreads; ++i)
{
threads.push_back(new Thread(&threadFunc));//创建线程
threads.back().start();//启动线程
}
for (int i = 0; i < nthreads; ++i)
{
threads[i].join();
}
//分别输出1到8个线程执行插入操作的时间
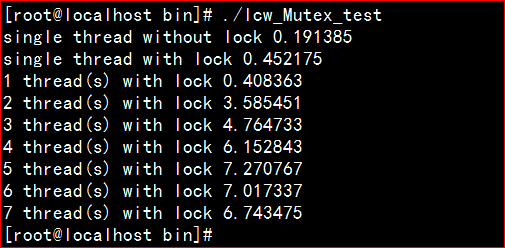
printf("%d thread(s) with lock %f
", nthreads, timeDifference(Timestamp::now(), start));
}
}单独编译后运行结果如下: