SSD目标检测网络
使用SSD检测网络一段时间了,研究过代码,也踩过坑,算是有能力来总结下SSD目标检测网络了。
1. SSD300_Vgg16
最基础的SSD网络是以Vgg16作为backbone, 输入图片尺寸为300x300,这里以其为示例,详细剖析下SSD检测网络。
SSD(Single Shot MultiBox Detector)检测网络可概括为三个特征:one-stage检测器,多个尺度的特征图检测(MultiBox),大量的先验框(Prior Boxes)。相比于YoLo和Faster-RCNN,在准确度和速度上进行了折衷。对于SSD网络的理解主要在于三部分,一是对模型整体结构的理解,二是对于正负样本分配的理解(prior boxes 和gt boxes的匹配策略),三是对于损失函数Multibox_loss函数的理解
1.1 SSD模型结构
SSD模型结构主要包括三部分: VGG-Base, Extra-Layer和Pred-Layer。SSD300的整体网络结构如下图所示,在VGG16基础上加入了四个Extra_layer。 输入300*300图片,依次经过VGG-base和Extra_layer网络层进行卷积特征提取,取VGG-16的两个卷积层输出Feature1和Feature2,以及四个Extra_layer输出Feature3,Feature4, Feature5, Feature6,将这六个尺度特征图分别送入class_predictors和box_predictors预测类别和坐标,将所有尺度预测值进行合并。(注意VGG_Base中红色圈主的部分,是SSD对原始VGG的改变)
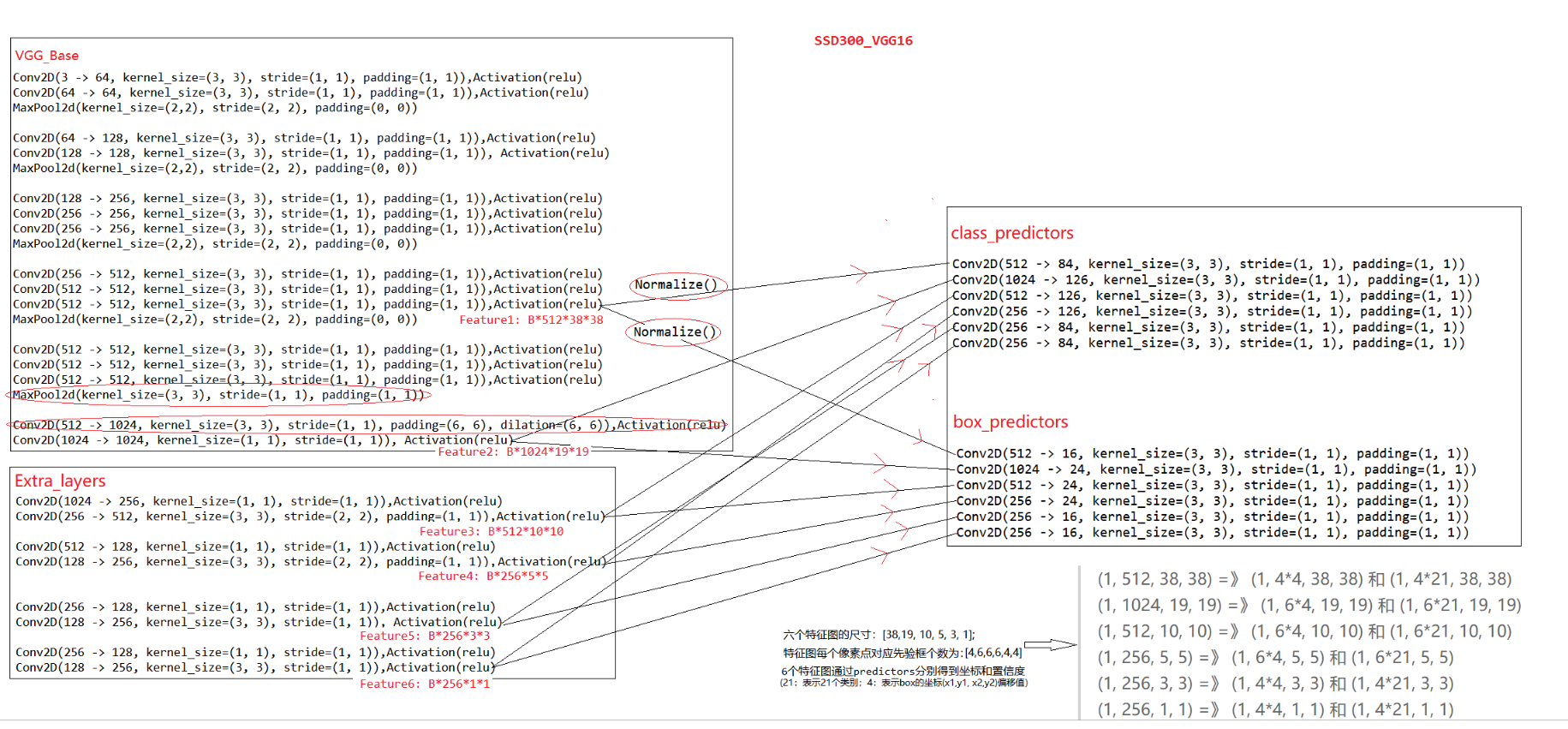
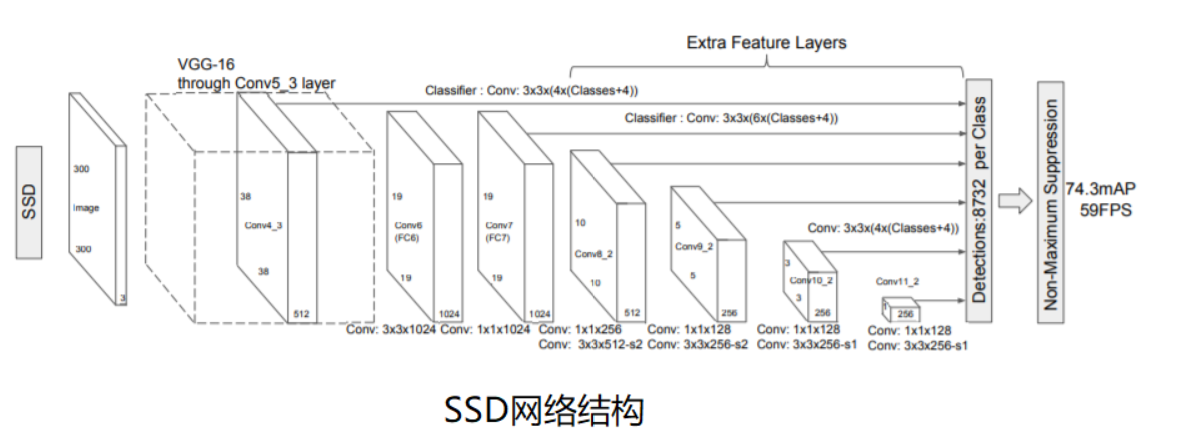
VGG-Base作为基础架构用来提取图像的feature;Extra-layers对VGG的feature做进一步处理,增加模型对图像的感受野,使Pred-Layer得到的特征图承载更多抽象信息。待预测的特征图由6种特征图组成,这6种特征图最终通过Pred-Layers(loc-layer 和conf-layer)来得到预测框的坐标信息(loc-layer),置信度信息(conf-layer)和类别信息(conf-layer)。
对于SSD300,6种特征图的尺寸说明如下:
-
两个来自VGG部分(38, 19),其特点是特征图尺寸大,意味着丢失信息少,可以识别较小目标;处理层数浅,感受野小,意味着抽象信息少,准确度不高。
-
四个来自Extra部分(10, 5, 3, 1),其特点与VGG部分相反,这也是Extra的意义所在——弥补VGG部分的不足。
模型计算流程:
-
模型通过Base部分得到两个特征图(1, 512, 38, 38)和(1, 1024, 19, 19)
-
通过extra部分得到四个特征图(1, 512, 10, 10),(1, 256, 5, 5),(1, 256, 3, 3)和(1, 256, 1, 1)
-
这6个特征图再通过class_predictors和box_predictors分别得到置信度和坐标:
(1, 512, 38, 38) =》 (1, 4x4, 38, 38) 和 (1, 4x21, 38, 38) (1, 1024, 19, 19) =》 (1, 6x4, 19, 19) 和 (1, 6x21, 19, 19) (1, 512, 10, 10) =》 (1, 6x4, 10, 10) 和 (1, 6x21, 10, 10) (1, 256, 5, 5) =》 (1, 6x4, 5, 5) 和 (1, 6x21, 5, 5) (1, 256, 3, 3) =》 (1, 4x4, 3, 3) 和 (1, 4x21, 3, 3) (1, 256, 1, 1) =》 (1, 4x4,1, 1) 和 (1, 4x21, 1, 1)
-
最终得到所有预测框的loc:(1, 8732, 4)和conf:(1, 8732, 21)
训练阶段
-
输出有预测框的loc_p:(1, 8732, 4),con_p:(1, 8732, 21)和先验框anchors:(8732, 4);结合gt_box, gt_id计算loss
测试阶段
-
根据先验框anchors和预测box偏移值,计算真实box坐标值和类别置信度,经过NMS,最后输出预测的box坐标值和置信度
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/70415140?utm_source=wechat_session
1.2 Anchors和gt_boxes匹配策略
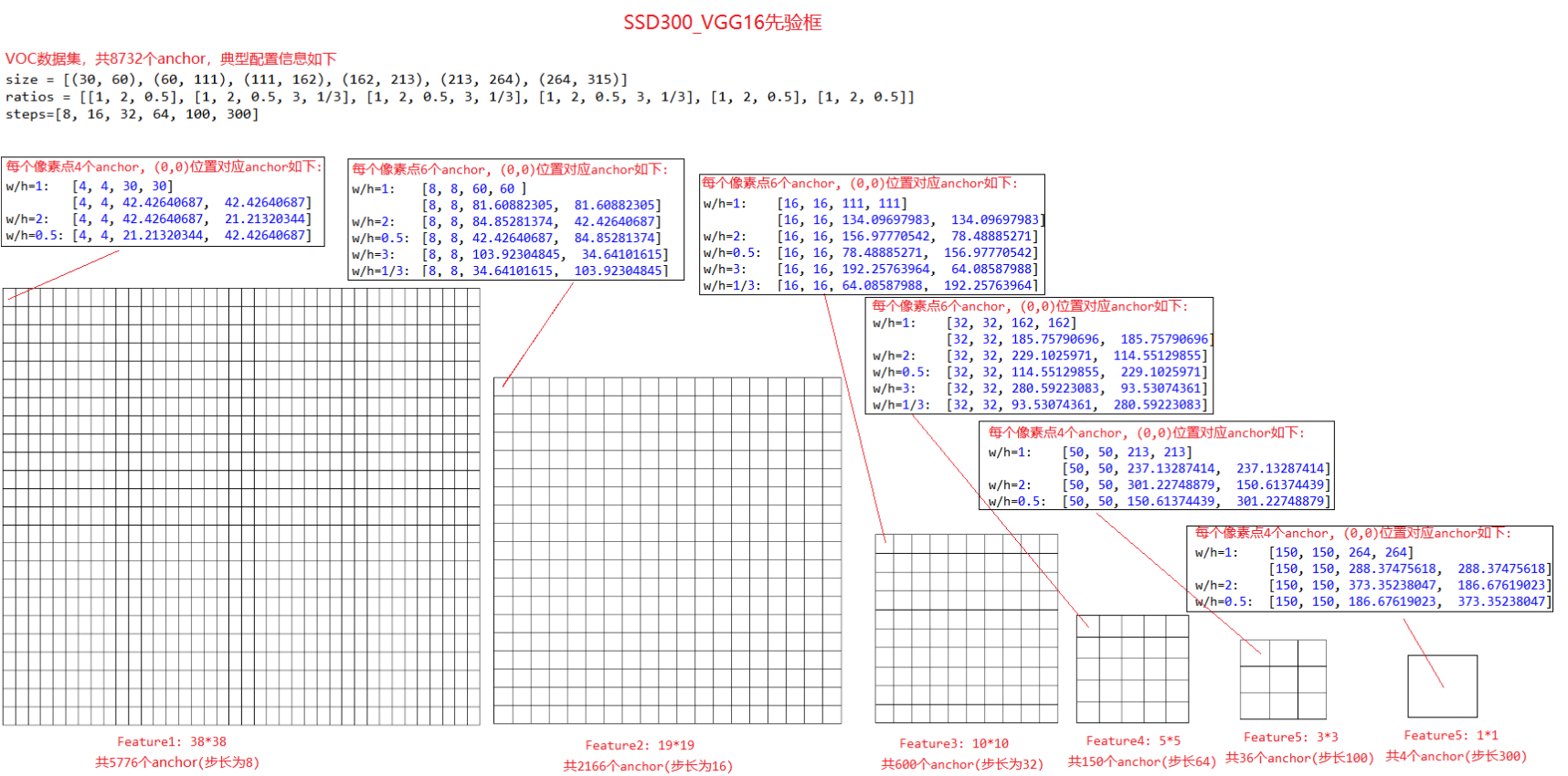
对于SSD300,下图是VOC数据集的典型anchor配置(size, ratio),可以看到不同尺寸的feature上每个像素点都设置了anchor,六张feature总共设置了8732个anchor。
生成anchor的示例代码如下:

import numpy as np # 对于第一张feature_map, 产生anchor box的代码如下: feature_size = (38, 38) offsets = (0.5, 0.5) step = 8 size = (30, 60) ratios = [1, 2, 0.5] anchors = [] for i in range(feature_size[0]): for j in range(feature_size[1]): cy = (i + offsets[0]) * step cx = (j + offsets[1]) * step min = size[0] max = np.sqrt(size[0] * size[1]) anchors.append([cx, cy, min, max]) anchors.append([cx, cy, max, max]) for r in ratios[1:]: sr = np.sqrt(r) w = min * sr h = min / sr anchors.append([cx, cy, w, h]) # anchors = np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 4) anchors = np.array(anchors).reshape(1, 1, feature_size[0], feature_size[1], -1) print(anchors.shape) print(anchors[:8]) # Feature1: 38*38,每个像素点4个anchor,总共5776个anchor(步长为8) # 每个像素点4个anchor, (0,0)位置对应anchor如下: # w/h=1: [4, 4, 30, 30] # [4, 4, 42.42640687, 42.42640687] # w/h=2: [4, 4, 42.42640687, 21.21320344] # w/h=0.5: [4, 4, 21.21320344, 42.42640687]
一张训练图片上可能只有几个gt_box,因此需要确定选择那些anchor来负责预测这几个gt_box
ssd论文中的匹配策略有两个:
-
所有的gt_box选择与它iou最大的anchor进行匹配
-
对剩下的anchor,选择与其iou最大的gt_box进行匹配,而且这个iou必须大于设定阈值(0.5)时才算匹配上
这样匹配完成后,一个gt_box可以匹配多个anchor,且最少匹配到一个anchor;而一个anchor最多匹配一个gt_box,如果没有匹配上gt_box则作为负样本。具体的匹配逻辑看代码比较清晰和容易理解,下面是示例代码:

class SSDTargetGenerator(mx.gluon.Block): def __init__(self, iou_thresh=0.5, neg_thresh=0.5, negative_mining_ratio=3, stds=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2], **kwargs): super(SSDTargetGenerator, self).__init__() self.iou_thresh = iou_thresh self.stds = mx.nd.array(stds) def forward(self, anchors, cls_preds, gt_boxes, gt_ids): ''' Parameters ---------- anchors: num_anchor*4 cls_preds:None gt_boxes: 1*num_gt*4 gt_ids: 1*num_gt*1 Returns ------- cls_targets: 1*num_anchor box_targets: 1*num_anchor*4 ''' # print(1, anchors.shape, gt_boxes.shape, gt_ids.shape) anchors_cornors = self._center_to_corner(anchors) ious = self.box_iou(gt_boxes, anchors_cornors) #[num_gt, num_anchor] # [num_gt,] best_prior_overlap, best_prior_idx = ious.max(axis=1), ious.argmax(axis=1) #[num_anchor,] best_truth_overlap, best_truth_idx = ious.max(axis=0), ious.argmax(axis=0) #每一个anchor与它IOU最大的gt_box匹配 best_truth_overlap[best_prior_idx] = 2 # ensure best prior #与gt_box的IOU最大的anchor,将其IOU设置为2,保证每个gt_box与其IOU最大的anchor匹配 # ensure every gt matches with its prior of max overlap for j in range(best_prior_idx.shape[0]): #与gt_box的IOU最大的anchor,将best_truth_idx中该anchor的匹配索引设置为对应gt_box best_truth_idx[best_prior_idx[j]] = j matches = gt_boxes[0, best_truth_idx] cls_targets = gt_ids[0, best_truth_idx] + 1 #num_anchor*1 cls_targets[best_truth_overlap < self.iou_thresh] = 0 #num_anchor*4, 若anchor与gt_box的IOU小于阈值,设置为不匹配 box_targets = self.encode(matches, anchors, self.stds) # print(3, cls_targets.shape, box_targets.shape) return cls_targets.reshape(1,-1), box_targets.reshape(1, -1, 4) def _center_to_corner(self, anchors): boxes = mx.nd.concat(anchors[:, :2] - anchors[:, 2:]/2, anchors[:, :2] + anchors[:, 2:]/2, dim=1) return boxes def box_iou(self, box_a, box_b): assert box_a.shape[0] == 1 box_a = box_a[0] A = box_a.shape[0] B = box_b.shape[0] # s1 = box_b[:, 2:].repeat(repeats=A, axis=0).reshape(B, A, 2).transpose(axes=(1, 0, 2)) # print(s1.shape) max_xy = mx.nd.minimum(box_a[:, 2:].repeat(repeats=B, axis=0).reshape(A, B, 2), box_b[:, 2:].repeat(repeats=A, axis=0).reshape(B, A, 2).transpose(axes=(1, 0, 2))) min_xy = mx.nd.maximum(box_a[:, :2].repeat(repeats=B, axis=0).reshape(A, B, 2), box_b[:, :2].repeat(repeats=A, axis=0).reshape(B, A, 2).transpose(axes=(1, 0, 2))) diff = (max_xy-min_xy) inter = mx.nd.clip(diff, a_min=0, a_max=mx.nd.max(diff).asscalar()) inter_area = inter[:, :, 0] * inter[:, :, 1] area_a = (box_a[:, 2] - box_a[:, 0])*(box_a[:, 3] - box_a[:, 1]) area_a = area_a.repeat(repeats=B, axis=0).reshape(A, B) area_b = (box_b[:, 2] - box_b[:, 0])*(box_b[:, 3] - box_b[:, 1]) area_b = area_b.repeat(repeats=A, axis=0).reshape(B, A).transpose(axes=(1, 0)) # print(inter_area.shape, area_a.shape, area_b.shape) return inter_area/(area_a+area_b-inter_area) def encode(self, matches, priors, stds): # encode variance # print(2, matches.shape, priors.shape) g_cxcy = (matches[:, :2] + matches[:, 2:])/2 - priors[:, :2] g_cxcy = g_cxcy/stds[:2] g_wh = (matches[:, 2:]-matches[:, :2])/priors[:, 2:] g_wh = mx.nd.log(g_wh)/stds[2:] return mx.nd.concat(g_cxcy, g_wh, dim=1)
参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/53182444
https://blog.csdn.net/yuanlunxi/article/details/84746729
1.3 SSD损失函数Multibox_loss
SSD的loss函数包括分类损失cls_losses和坐标损失box_losses,cls_losses采用的交叉熵损失函数,box_losses采用的是smooth_L1损失函数。有两点值得注意:
-
box_losses只计算正样本的losses,而且预测值为相对于anchor的偏移值,不是最后的box
-
由于负样本远多于正样本,为了保证正负样本的均衡,SSD采用了hard negative mining策略,只选择损失值最大的负样本
这里的hard negative mining指,在计算cls_closses时,只选择正样本和部分loss值最大的负样本参与计算。例如一张图片中有100个样本,其中10个正样本,90个负样本,实际计算loss值时,将90个负样本的loss值排序,选择30个loss值最大的负样本,再加上10个正样本,这样总共40个样本参与最终loss的反向传递。(保证正负样本比例为1:3,同时是比较难的负样本)
Multibox_loss 参考代码如下:

class SSDMultiBoxLoss(gluon.Block): r"""Single-Shot Multibox Object Detection Loss. .. note:: Since cross device synchronization is required to compute batch-wise statistics, it is slightly sub-optimal compared with non-sync version. However, we find this is better for converged model performance. Parameters ---------- negative_mining_ratio : float, default is 3 Ratio of negative vs. positive samples. rho : float, default is 1.0 Threshold for trimmed mean estimator. This is the smooth parameter for the L1-L2 transition. lambd : float, default is 1.0 Relative weight between classification and box regression loss. The overall loss is computed as :math:`L = loss_{class} + lambda imes loss_{loc}`. min_hard_negatives : int, default is 0 Minimum number of negatives samples. """ def __init__(self, negative_mining_ratio=3, rho=1.0, lambd=1.0, min_hard_negatives=0, **kwargs): super(SSDMultiBoxLoss, self).__init__(**kwargs) self._negative_mining_ratio = max(0, negative_mining_ratio) self._rho = rho self._lambd = lambd self._min_hard_negatives = max(0, min_hard_negatives) def forward(self, cls_pred, box_pred, cls_target, box_target): """Compute loss in entire batch across devices.""" # require results across different devices at this time cls_pred, box_pred, cls_target, box_target = [_as_list(x) for x in (cls_pred, box_pred, cls_target, box_target)] # cross device reduction to obtain positive samples in entire batch num_pos = [] for cp, bp, ct, bt in zip(*[cls_pred, box_pred, cls_target, box_target]): pos_samples = (ct > 0) num_pos.append(pos_samples.sum()) num_pos_all = sum([p.asscalar() for p in num_pos]) if num_pos_all < 1 and self._min_hard_negatives < 1: # no positive samples and no hard negatives, return dummy losses cls_losses = [nd.sum(cp * 0) for cp in cls_pred] box_losses = [nd.sum(bp * 0) for bp in box_pred] sum_losses = [nd.sum(cp * 0) + nd.sum(bp * 0) for cp, bp in zip(cls_pred, box_pred)] return sum_losses, cls_losses, box_losses # compute element-wise cross entropy loss and sort, then perform negative mining cls_losses = [] box_losses = [] sum_losses = [] for cp, bp, ct, bt in zip(*[cls_pred, box_pred, cls_target, box_target]): pred = nd.log_softmax(cp, axis=-1) pos = ct > 0 cls_loss = -nd.pick(pred, ct, axis=-1, keepdims=False) rank = (cls_loss * (pos - 1)).argsort(axis=1).argsort(axis=1) # loss进行排序 hard_negative = rank < nd.maximum(self._min_hard_negatives, pos.sum(axis=1) * self._negative_mining_ratio).expand_dims(-1) #选择多少个负样本,作为比较难的负样本 # mask out if not positive or negative cls_loss = nd.where((pos + hard_negative) > 0, cls_loss, nd.zeros_like(cls_loss)) #正样本+选择的负样本,参与loss计算 cls_losses.append(nd.sum(cls_loss, axis=0, exclude=True) / max(1., num_pos_all)) bp = _reshape_like(nd, bp, bt) box_loss = nd.abs(bp - bt) box_loss = nd.where(box_loss > self._rho, box_loss - 0.5 * self._rho, (0.5 / self._rho) * nd.square(box_loss)) # box loss only apply to positive samples box_loss = box_loss * pos.expand_dims(axis=-1) #只有正样本有box_loss, 负样本的box_loss置0 box_losses.append(nd.sum(box_loss, axis=0, exclude=True) / max(1., num_pos_all)) sum_losses.append(cls_losses[-1] + self._lambd * box_losses[-1]) return sum_losses, cls_losses, box_losses
2. SSD512_Vgg16
SSD300输入的图片分辨率为300x300,ssd512输入的图片分辨率尺寸为 512x512,相比于ssd300,ssd512网络最大的区别是:extra_layer多增加了一个特征提取层,这样ssd512总共有7个尺度的feature,比ssd300多一个feature。ssd512的整体网络结构如下所示:
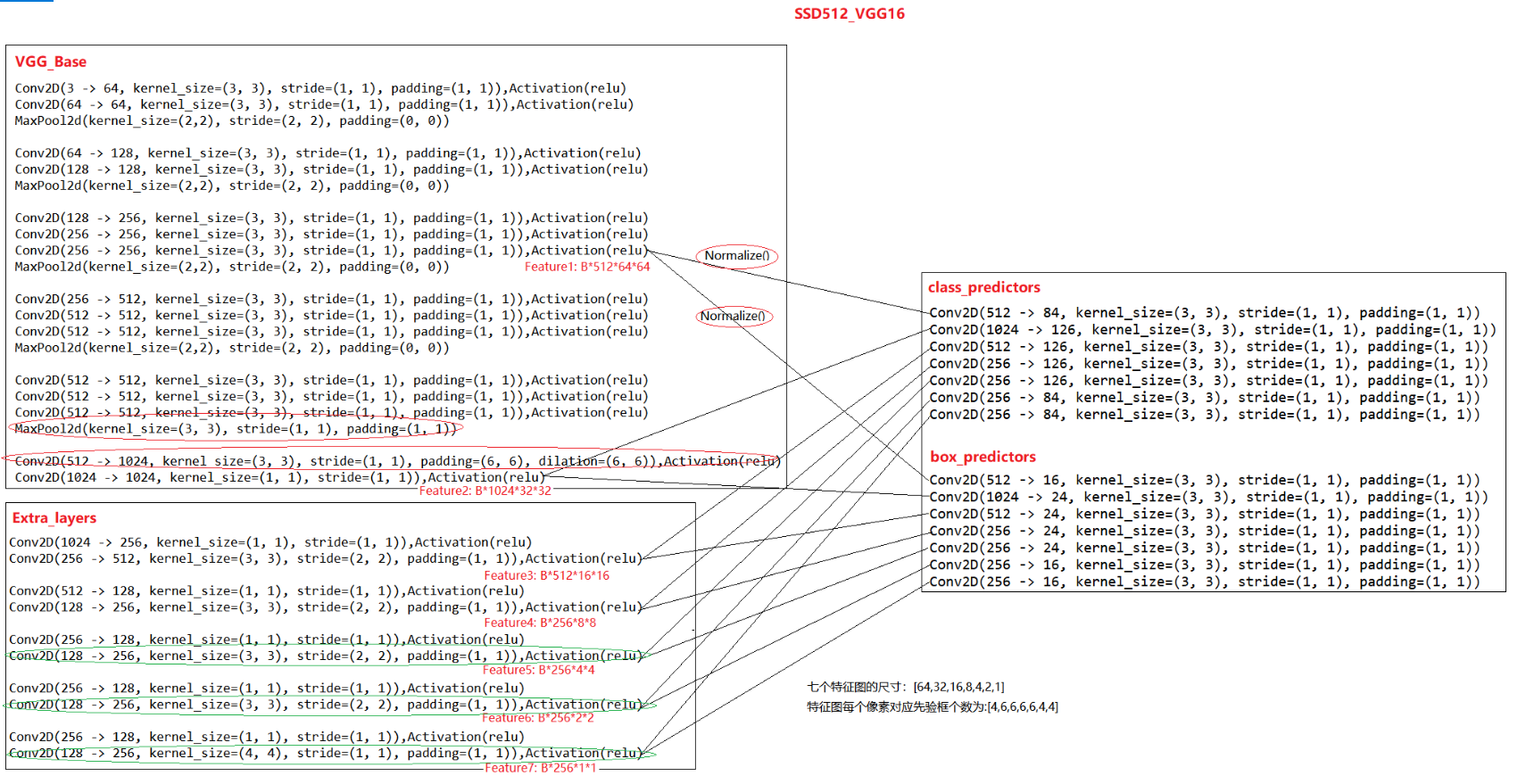
3. SSD的改进
在实际项目使用过程中,可以根据自身需要对SSD进行改进,比较简单的改进主要有两个方面,一是对网络结构的调整,如将backbone由vgg16替换成resnet50,引入注意力机制等;二是对于anchor的尺寸和比例进行调整,如检测信号塔时,其宽高比都小,而默认的anchor比例为[1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 2:1, 3:1], 可以改为[1:2, 1:4, 1:6, 1:8, 1:10]
