简单来说,Beautiful Soup是python的一个库,最主要的功能是从网页抓取数据。官方解释如下:
''' Beautiful Soup提供一些简单的、python式的函数用来处理导航、搜索、修改分析树等功能。 它是一个工具箱,通过解析文档为用户提供需要抓取的数据,因为简单,所以不需要多少代码就可以写出一个完整的应用程序。 '''
安装
#安装 Beautiful Soup pip install beautifulsoup4 #安装解析器 Beautiful Soup支持Python标准库中的HTML解析器,还支持一些第三方的解析器,其中一个是 lxml .根据操作系统不同,可以选择下列方法来安装lxml: $ apt-get install Python-lxml $ easy_install lxml $ pip install lxml 另一个可供选择的解析器是纯Python实现的 html5lib , html5lib的解析方式与浏览器相同,可以选择下列方法来安装html5lib: $ apt-get install Python-html5lib $ easy_install html5lib $ pip install html5lib
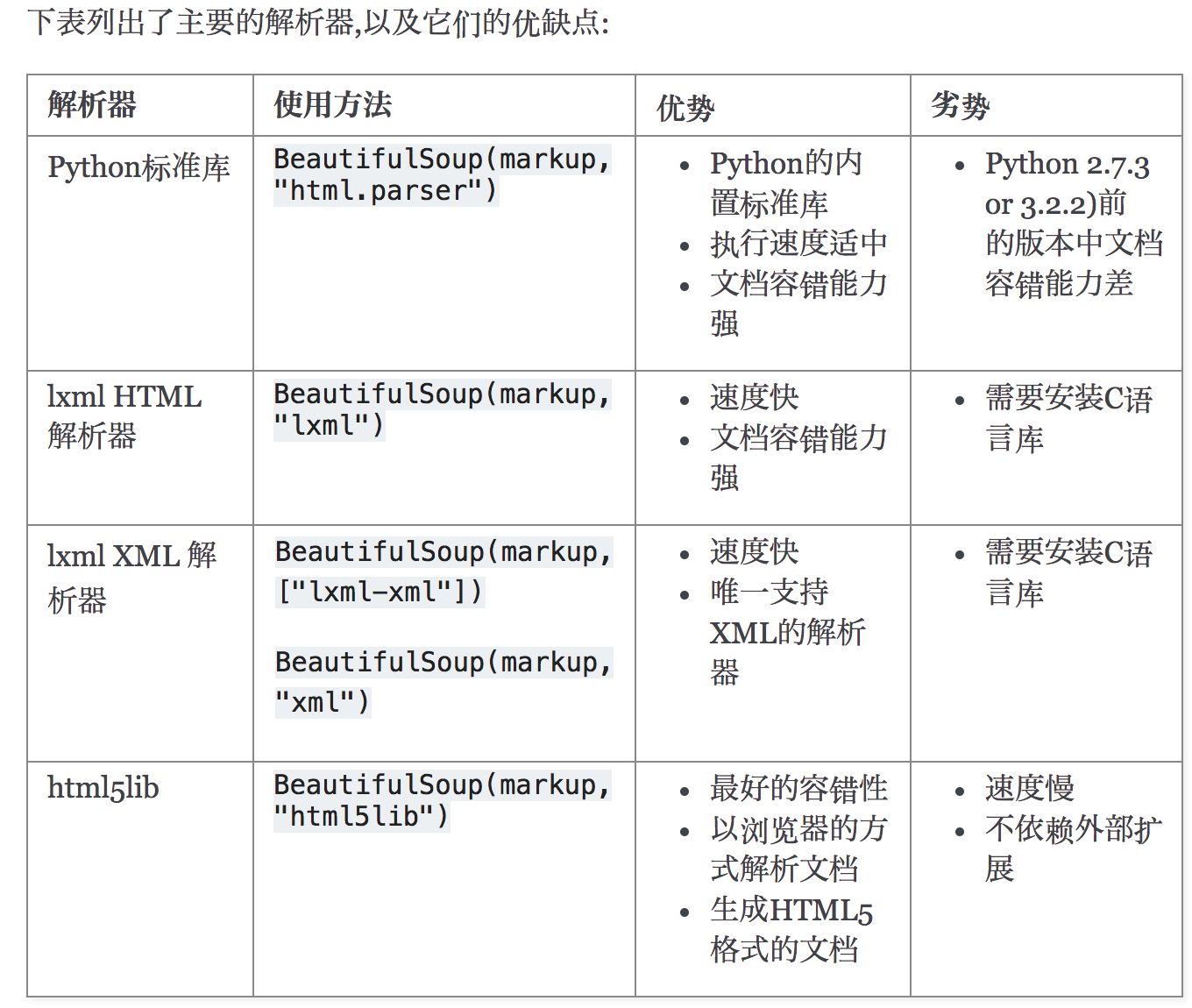
解析器
简单使用
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html_doc = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="sister"><b>$37</b></p> <p class="story" id="p">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" >Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ # 方式一: # soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, "lxml") # print(soup) # 方式二: # soup = BeautifulSoup(open('a.html'), "lxml") # print(soup) soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, "lxml") # print(soup) # 自动补全 soup.prettify() print(soup.p) # 获取p标签下的b标签 print(soup.p.b) # 获取p标签下的b标签下的文本 print(soup.p.b.text) # 找body内的所有标签 print(soup.body.contents) # 获取p标签属性 print(soup.p.attrs) # 获取p标签的孩子, 返回一个iter对象 print(list(soup.p.children)) # 获取p标签的子子孙孙 print(list(soup.p.descendants)) # 获取p标签的爸爸 print(soup.p.parent) # 获取p标签的爸爸, 获取p标签的爸爸的爸爸, 获取p标签的爸爸的爸爸的爸爸 print(list(soup.p.parents)) # 获取a标签内的href属性 print(soup.a.attrs['href'])
搜索文档树
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html_doc =""" <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="sister"><b>$37</b></p> <p class="story" id="p">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" >Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ # 搜索文档树 # 1.文本查找 # 通过文本查找p标签 soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, "lxml") # print(soup) # 自动补全 soup.prettify() print(soup.find_all(name='p')) # 通过文本查找文本为$37的p标签 print(soup.find_all(name='p', text='$37')) # 通过文本查找id为link3的a标签 print(soup.find_all(name='a', attrs={"id": "link3"})) import re # 2.正则查找 # 通过正则查找所有p标签 print(soup.find_all(name=re.compile("^p"))) # 通过正则查找所有a标签 print(soup.find_all(name=re.compile("^a"))) # 通过正则查找所有id为link的p标签 print(soup.find_all(name="p", attrs={"id": re.compile("^link")})) # 通过正则查找所有id为link的a标签 print(soup.find_all(name="a", attrs={"id": re.compile("^link")})) # 通过正则查找所有class为story的p标签 print(soup.find_all(name="p", attrs={"class": re.compile("story")})) # 3.列表 # 通过列表查找所有的a、p标签 print(soup.find_all(name=['p', 'a'])) # 通过列表查找所有的正则匹配有Elsie的文本 print(soup.find_all(text=[re.compile("Elsie")])) # 通过列表查找所有的正则匹配有Elsie的文本的a标签 print(soup.find_all(name=['a'], text=[re.compile("Elsie")])) # 4.True # 获取所有标签 print(soup.find_all(name=True)) # 获取所有有id的a标签 print(soup.find_all(name="a", attrs={"id": True})) # # 获取所有有class的a标签 print(soup.find_all(name="a", attrs={"class": True})) # 5.方法 def have_id_not_class(a): # if tag.has_attr('id') and not tag.has_attr('class'): # return tag if a.has_attr('class') and not a.has_attr('id'): return a # 通过方法查找所有有class没id的标签 print(soup.find_all(have_id_not_class))
给新热抽屉网1-100页所有用户点赞
import requests # 一: 访问主页获取cookies index_res = requests.get('https://dig.chouti.com/', headers={ 'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/71.0.3578.98 Safari/537.36' }) # print(index_res.cookies.get_dict()) index_cookies = index_res.cookies.get_dict() ''' url: https://dig.chouti.com/login method: POST headers: user-agent: referer: cookie form_data: phone: 8615622792660 password: k46709394 oneMonth: 1 ''' # 二 携带主页的cookies进行登陆 login_url = 'https://dig.chouti.com/login' headers = { 'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/71.0.3578.98 Safari/537.36', 'referer': 'https://dig.chouti.com/', } form_data = { 'phone': '8615622792660', 'password': 'k46709394', 'oneMonth': '1' } # 往登陆连接发送post请求进行登陆 login_res = requests.post(login_url, cookies=index_cookies, headers=headers, data=form_data) print(login_res) # 登陆成功返回文本 print(login_res.text) # 对Id=25068561的用户进行点赞 # vote_res = requests.post('https://dig.chouti.com/link/vote?linksId=25068561', headers=headers, cookies=index_cookies) # print(vote_res.text) ''' url: https://dig.chouti.com/all/hot/recent/1 headers: ''' from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # 循环拼接1-100页的 特推 页面 for line in range(1, 100): hot_url = 'https://dig.chouti.com/all/hot/recent/%s' % line # 往特推页面发送get请求获取当前页所有用户 hot_res = requests.get(hot_url, headers=headers, ) # print(hot_res.text) soup = BeautifulSoup(hot_res.text, 'lxml') # 通过bs4获取到所有id为content-list用户特推的div标签 div_1 = soup.find(name='div', attrs={"id": "content-list"}) # print(div_1) # # 通过bs4获取到所有class为item的用户特推的div标签 div_s = soup.find_all(name='div', attrs={"class": "item"}) for div in div_s: # 获取所有用户的id # 通过bs4查找到class为part2的div,然后获取属性中的share-linkid进而获取id值 id = div.find(name='div', attrs={"class": "part2"}).get("share-linkid") # print(id) # 对所有用户进行点赞 vote_res = requests.post('https://dig.chouti.com/link/vote?linksId=%s' % id, headers=headers, cookies=index_cookies) print(vote_res.text) ''' {"result":{"code":"9999", "message":"推荐成功", "data":{"jid":"cdu_53191784515","likedTime":"1552034126796000","lvCount":"6","nick":"人生苦短灬及时行乐","uvCount":"430","voteTime":"小于1分钟前"}}}