A permutation — is a sequence of length nn integers from 11 to nn, in which all the numbers occur exactly once. For example, [1][1], [3,5,2,1,4][3,5,2,1,4], [1,3,2][1,3,2] — permutations, and [2,3,2][2,3,2], [4,3,1][4,3,1], [0][0] — no.
Polycarp was recently gifted a permutation a[1…n]a[1…n] of length nn. Polycarp likes trees more than permutations, so he wants to transform permutation aa into a rooted binary tree. He transforms an array of different integers into a tree as follows:
- the maximum element of the array becomes the root of the tree;
- all elements to the left of the maximum — form a left subtree (which is built according to the same rules but applied to the left part of the array), but if there are no elements to the left of the maximum, then the root has no left child;
- all elements to the right of the maximum — form a right subtree (which is built according to the same rules but applied to the right side of the array), but if there are no elements to the right of the maximum, then the root has no right child.
For example, if he builds a tree by permutation a=[3,5,2,1,4]a=[3,5,2,1,4], then the root will be the element a2=5a2=5, and the left subtree will be the tree that will be built for the subarray a[1…1]=[3]a[1…1]=[3], and the right one — for the subarray a[3…5]=[2,1,4]a[3…5]=[2,1,4]. As a result, the following tree will be built:
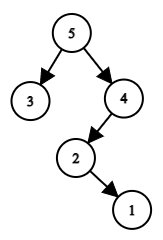 The tree corresponding to the permutation a=[3,5,2,1,4]a=[3,5,2,1,4].
The tree corresponding to the permutation a=[3,5,2,1,4]a=[3,5,2,1,4].Another example: let the permutation be a=[1,3,2,7,5,6,4]a=[1,3,2,7,5,6,4]. In this case, the tree looks like this:
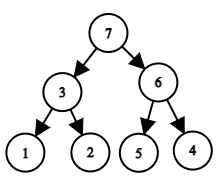 The tree corresponding to the permutation a=[1,3,2,7,5,6,4]a=[1,3,2,7,5,6,4].
The tree corresponding to the permutation a=[1,3,2,7,5,6,4]a=[1,3,2,7,5,6,4].Let us denote by dvdv the depth of the vertex avav, that is, the number of edges on the path from the root to the vertex numbered avav. Note that the root depth is zero. Given the permutation aa, for each vertex, find the value of dvdv.
The first line contains one integer tt (1≤t≤1001≤t≤100) — the number of test cases. Then tt test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains an integer nn (1≤n≤1001≤n≤100) — the length of the permutation.
This is followed by nn numbers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an — permutation aa.
For each test case, output nn values — d1,d2,…,dnd1,d2,…,dn.
3 5 3 5 2 1 4 1 1 4 4 3 1 2
1 0 2 3 1 0 0 1 3 2
1 //2021-03-15 08:50:02 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 #define scanf scanf_s 8 9 const int N = 1001; 10 const int M = 1001; 11 12 struct node { 13 int to, nxt; 14 }e[M]; 15 int edge_num; 16 int fir[N], d[N], a[N]; 17 18 void addEdge(int u, int v) { 19 e[++edge_num].to = v; 20 e[edge_num].nxt = fir[u]; 21 fir[u] = edge_num; 22 } 23 24 int T, n; 25 26 int solve(int l, int r) { 27 if (l == r) return r; 28 if (l > r) return -1; 29 int root; 30 for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) { 31 if (a[i] == *max_element(a + l, a + r + 1)) { 32 root = i; 33 break; 34 } 35 } 36 int ls = solve(l, root - 1); 37 int rs = solve(root + 1, r); 38 39 if (ls != -1) addEdge(root, ls); 40 if (rs != -1) addEdge(root, rs); 41 return root; 42 } 43 44 void dfs(int u, int deg) { 45 d[u] = deg; 46 for (int i = fir[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt) { 47 int to = e[i].to; 48 dfs(to, deg + 1); 49 } 50 } 51 52 int main() { 53 scanf("%d", &T); 54 while (T--) { 55 memset(fir, 0, sizeof(fir)); 56 memset(d, 0, sizeof(d)); 57 memset(e, 0, sizeof(e)); 58 edge_num = 0; 59 scanf("%d", &n); 60 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 61 scanf("%d", &a[i]); 62 } 63 solve(1, n); 64 int root; 65 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 66 if (a[i] == n) root = i; 67 dfs(root, 0); 68 69 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 70 printf("%d ", d[i]); 71 printf(" "); 72 } 73 74 return 0; 75 }