一、简介
在安卓中,View代表视图,是安卓中十分重要的一个概念,重要程度不亚于四大组件,用户每时每刻都在与View打交道,包括展示数据、事件传递等。因此,熟练掌握View的应用以及原理是Android进阶的必经之路。最近笔者在学习任玉刚著的《Android 开发艺术探索》中的View的相关知识,便把学习心得及总结记录下来,与大家交流学习。
二、View的定义
引用官方文档的描述:A View occupies a rectangular area on the screen and is responsible for drawing and event handling. 一个View占据一个矩形区域,负责绘制以及事件处理。所以一个View代表一个控件,我们平时接触的TextView,EditView,Button,ListView都是继承自View的。此外,除了View,还有一个ViewGroup,所谓ViewGroup是“控件组”,表示ViewGroup里面还有别的View,而且ViewGroup也是继承自View的。总的来说,View可以是单一的控件,也可是是许多控件组成的一组控件。
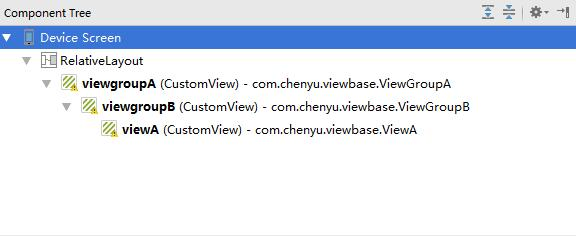
为了说明View的层级关系,笔者创建了一个Demo,其层级关系如下图所示:笔者自定义了3个View,首先viewGroupA继承自ViewGroup,内部包含了一个viewGroupB;viewGroupB继承自ViewGroup,内部包含了一个viewA,而viewA继承自View。
三、View的几个重要参数
对于一个View来说,最重要的莫过于位置参数了,因为这能标识一个View在哪,以及这个View的宽高,这对于一个View的绘制来说也很重要。一个View的位置的确定,取决于它的四个顶点,top(左上角纵坐标)、left(左上角横坐标)、bottom(右下角纵坐标)、right(右下角横坐标)。注意:以上坐标都是相对坐标,表示View相对于父布局的坐标。另外,在Android中,x轴和y轴的正方向分别为右和下。
那么怎么获取这些参数呢?我们看看View的源码:
public class View implements Drawable.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,AccessibilityEventSource {
...
protected int mLeft;
protected int mRight;
protected int mTop;
protected int mBottom;
...
}
可以看出,View内有四个成员变量,分表代表了Top、Left、Right、Bottm的值,所以我们可以利用View的get方法获取这些值,比如说这样:
int left = MyView.getLeft();
int top = MyView.getTop();
int right = MyView.getRight();
int bottom = MyView.getBottom()
除了以上四个基本参数之外,还有x、y、translationX、translationY,类似地,安卓也提供了相应的get/set方法。接下来以一幅图来说明一下,这些参数的区别:
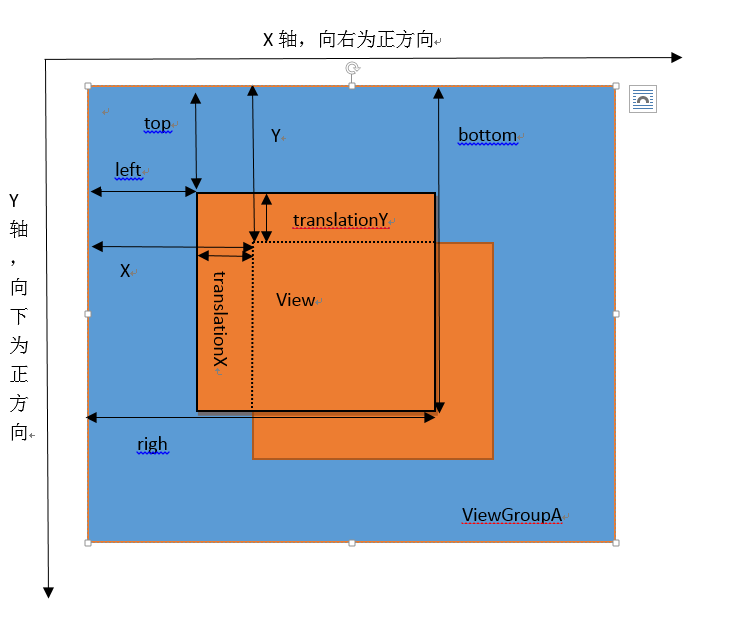
由上图可总结如下:
①top、left、right、bottom代表View的初始坐标,在绘制完毕后就不会再改变
②translationX、translationY代表View左上角的偏移量(相对于父容器),比如上图是View进行了平移,那么translation代表水平平移的像素值,translationY代表竖直平移的像素值。
③x、y代表当前View左上角相对于父容器的坐标,即实时相对坐标。
④以上参数的关系可以用这两个公式表示:x = left + translationX 和y = top+ translationY。
四、注意事项
在使用View.getTop()、View.getX()等这些函数获取以上说到的参数时,有一个容易出错的地方,那就是不应该在onCreate()方法中直接获取,因为此时view还没还是绘制,所以得到的所有参数都会是0。以下结合一个Demo来说明这个问题:
(1)先看布局以及布局文件:
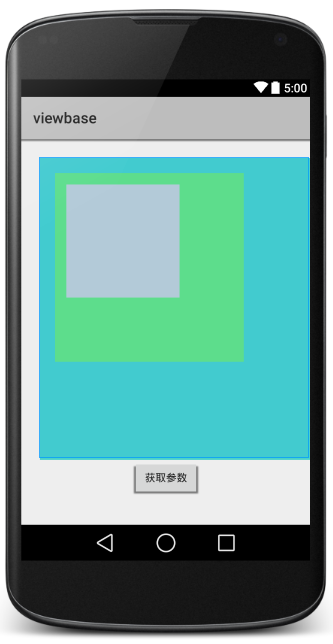
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<com.chenyu.viewbase.ViewGroupA
android:layout_width="400dp"
android:layout_height="400dp"
android:background="#4bd2c8"
android:layout_marginTop="50px"
android:layout_marginLeft="50px"
android:id="@+id/viewgroupA">
<com.chenyu.viewbase.ViewGroupB
android:id="@+id/viewgroupB"
android:layout_width="250dp"
android:layout_height="250dp"
android:background="#a07cf44e"
android:layout_marginTop="40px"
android:layout_marginLeft="40px">
<com.chenyu.viewbase.ViewA android:id="@+id/viewA"
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#cdd1d2"
android:layout_marginTop="30px"
android:layout_marginLeft="30px"/>
</com.chenyu.viewbase.ViewGroupB>
</com.chenyu.viewbase.ViewGroupA>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="获取参数"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_below="@+id/viewgroupA"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
</RelativeLayout>
(2)ViewGroupA、ViewGroupB、ViewA的代码基本相同,只不过ViewGroupA和ViewGroupB继承的是LinearLayout而ViewA继承的是View,所以只给出ViewGroupA的代码如下:
public class ViewGroupA extends LinearLayout {
public ViewGroupA(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public ViewGroupA(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public ViewGroupA(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
}
(3)MainActivity:我们在onCreate()方法内先获取了ViewGroupA的坐标,然后在监听事件中再获取全部的坐标:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private LinearLayout viewGroupA;
private LinearLayout viewGroupB;
private View viewA;
private Button button;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
viewGroupA = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.viewgroupA);
viewGroupB = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.viewgroupB);
viewA = findViewById(R.id.viewA);
button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int viewGroupA_top = viewGroupA.getTop();
int viewGroupA_left = viewGroupA.getLeft();
Log.d("cylog", "viewGroupA的左上角坐标是:("+viewGroupA_left+","+viewGroupA_top+")");
int viewGroupB_top = viewGroupB.getTop();
int viewGroupB_left = viewGroupB.getLeft();
Log.d("cylog", "viewGroupB的左上角坐标是:("+viewGroupB_left+","+viewGroupB_top+")");
int viewA_top = viewA.getTop();
int viewA_left = viewA.getLeft();
Log.d("cylog", "viewA的左上角坐标是:("+viewA_left+","+viewA_top+")");
}
});
int viewGroupA_top = viewGroupA.getTop();
int viewGroupA_left = viewGroupA.getLeft();
Log.d("cylog", "viewGroupA的左上角坐标是:("+viewGroupA_left+","+viewGroupA_top+")");
}
}
运行程序,并点击Button按钮,查看log日志:
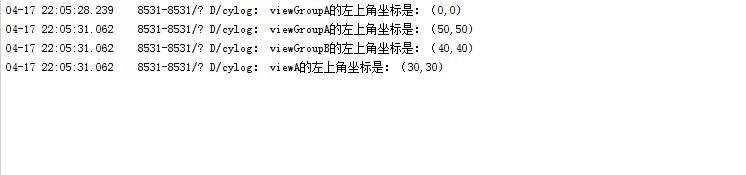
根据运行结果可知,在onCreate()方法内,是获取不到View的坐标参数的,因为此时View还未开始绘制,所以全部坐标参数都是0,由于在监听按钮事件的时候,View已经绘制完毕,此时才能获取参数。这是尤其需要注意的一点。同时可以看出,所打印的坐标都是相对于父布局的坐标。比如我们在布局文件中,设置了viewGroupA的margin_Top和margin_Left分别为50px和50px,此时viewGroupA的左上角坐标是(50,50),符合预期结果,同样地,viewGroupB(40,40)和viewA(30,30)都符合预期。
作者:丶蓝天白云梦
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/86431650a5f6
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。