-------------------siwuxie095
选择排序法
它的工作原理如下:
首先在未排序序列中找到最小(大)元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置,
然后,再从剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小(大)元素,然后放到已排
序序列的末尾。以此类推,直到所有元素均排序完毕
参考链接:
程序 1:使用模板编写算法
Student.h:
#ifndef STUDENT_H #define STUDENT_H
//.h文件是不对外隐藏的,而.cpp文件在编译之后对外界进行了源代码的隐藏 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;
struct Student { string name; int score;
//小于号的重载 bool operator<(const Student &otherStudent) { //当前学生的学分和其它学生(传入进来的学生)的学分进行比较 return score < otherStudent.score;
////在分数相同时,字母小的排在前面(即 字典序更靠前) //return score != otherStudent.score ? // score < otherStudent.score : name < otherStudent.name; }
//输出运算符的重载 friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const Student &student) { os << "Student:" << student.name << " " << student.score << endl; return os; } };
#endif |
SelectionSort.h:
#ifndef SELECTIONSORT_H #define SELECTIONSORT_H
//选择排序:从小到大进行排序 template<typename T> void selectionSort(T arr[], int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { //寻找[i,n]区间里的最小值 int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) { minIndex = j; } } //swap()函数:交换两个值,对于swap()函数来说: //在C++ 11标准中,它就在std标准命名空间中,即 标准库中,不用包含其它 //如果是比较老的标准,它在algorithm库中,需要include <algorithm> swap(arr[i], arr[minIndex]); } }
#endif |
main.cpp:
#include "Student.h" #include "SelectionSort.h"
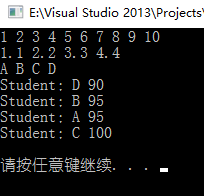
int main() { int a[] = { 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 }; selectionSort(a,10); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << a[i] << " "; } cout << endl;
float b[] = { 4.4, 3.3, 2.2, 1.1 }; selectionSort(b, 4); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { cout << b[i] << " "; } cout << endl;
string c[] = { "D", "C", "B", "A" }; selectionSort(c, 4); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { cout << c[i] << " "; } cout << endl;
Student d[] = { { "D", 90 }, { "C", 100 }, { "B", 95 }, { "A", 95 } }; selectionSort(d, 4); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { cout << d[i]; } cout << endl;
system("pause"); return 0; } |
运行一览:
程序 2:随机生成算法测试用例,并测试算法的性能
SortTestHelper.h:
#ifndef SORTTESTHELPER_H #define SORTTESTHELPER_H
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <ctime> #include <cassert> using namespace std;
//辅助排序测试 namespace SortTestHelper {
//生成测试数据(测试用例),返回一个随机生成的数组: //生成有n个元素的随机数组,每个元素的随机范围为[rangeL,rangeR] int *generateRandomArray(int n, int rangeL, int rangeR) { //默认rangeL要小于等于rangeR assert(rangeL <= rangeR);
int *arr = new int[n];
//对于数组中的每一个元素,将之随机成为rangeL和rangeR之间的随机数 //先设置随机种子:这里将当前的时间作为种子来进行随机数的设置 srand(time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { //rand()函数+百分号+数的范围,即 取中间的一个随机整数,再加上rangeL即可 arr[i] = rand() % (rangeR - rangeL + 1) + rangeL; } return arr; }
//生成一个近乎有序的数组 int *generateNearlyOrderedArray(int n, int swapTimes) { //先生成完全有序的数组 int *arr = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { arr[i] = i; }
//以当前时间为随机种子 srand(time(NULL));
//再随机挑选几对元素进行交换,就是一个近乎有序的数组了 for (int i = 0; i < swapTimes; i++) { int posx = rand() % n; int posy = rand() % n; swap(arr[posx], arr[posy]); }
return arr; }
template<typename T> void printArray(T arr[], int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cout << arr[i] << " "; } cout << endl; }
//经过排序算法排序后,再次确认是否已经完全排序 template<typename T> bool isSorted(T arr[], int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { if (arr[i]>arr[i + 1]) { return false; } } return true; }
//衡量一个算法的性能如何,最简单的方式就是看这个算法在特定数据集上的执行时间 //(1)传入排序算法的名字,方便打印输出 //(2)传入排序算法本身,即函数指针 //(3)传入测试用例:数组和元素个数 template<typename T> void testSort(string sortName, void(*sort)(T[], int), T arr[], int n) { //在排序前后分别调用clock()函数 //时间差就是该排序算法执行的时钟周期的个数 clock_t startTime = clock(); sort(arr, n); clock_t endTime = clock();
assert(isSorted(arr, n));
//endTime 减去 startTime 转为double类型,除以 CLOCKS_PER_SEC,其中: // //CLOCKS_PER_SEC 是标准库中定义的一个宏,表示每一秒钟所运行的时钟周期 //的个数,而(endTime-startTime)返回的是运行了几个时钟周期 // //这样,最终的结果就是在这段时间中程序执行了多少秒 cout << sortName << ":" << double(endTime - startTime) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl; }
//复制数组 int *copyIntArray(int a[], int n) { int *arr = new int[n]; //copy()函数在std中: //第一个参数是原数组的头指针, //第二个参数是原数组的尾指针, //第三个参数是目的数组的头指针 // //注意:copy()函数运行时会报错,需要在: //项目->属性->配置属性->C/C++->预处理器->预处理器定义 //在其中添加:_SCL_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS copy(a, a + n, arr); return arr; } }
#endif |
SelectionSort.h:
#ifndef SELECTIONSORT_H #define SELECTIONSORT_H
//选择排序:从小到大进行排序 template<typename T> void selectionSort(T arr[], int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { //寻找[i,n]区间里的最小值 int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) { minIndex = j; } } //swap()函数:交换两个值,对于swap()函数来说: //在C++ 11标准中,它就在std标准命名空间中,即 标准库中,不用包含其它 //如果是比较老的标准,它在algorithm库中,需要include <algorithm> swap(arr[i], arr[minIndex]); } }
#endif |
main.cpp:
#include "SortTestHelper.h" #include "SelectionSort.h"
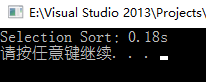
int main() { //当n扩大10倍时,排序用时就会扩大100倍 //即选择排序的时间复杂度是O(n^2)级别的 //(所消耗的时间和数据之间是成平方关系的) int n = 10000; int *arr = SortTestHelper::generateRandomArray(n, 0, n);
SortTestHelper::testSort("Selection Sort", selectionSort, arr, n); //SortTestHelper::printArray(arr, n); delete[]arr; arr = NULL;
system("pause"); return 0; } |
运行一览:
【made by siwuxie095】