-->Curling 2.0
直接上中文
Descriptions:
今年的奥运会之后,在行星mm-21上冰壶越来越受欢迎。但是规则和我们的有点不同。这个游戏是在一个冰游戏板上玩的,上面有一个正方形网格。他们只用一块石头。游戏的目的是让石子从起点到终点,并且移动的次数最小
图1显示了一个游戏板的例子。一些正方形格子可能被砖块占据。有两个特殊的格子,起始点和目标点,这是不占用块。(这两个方块是不同的)一旦石头开始移动就不会停下,除非它击中砖块块。为了使石头到达终点,你可以通过让石块击中墙壁或者砖块来停下。
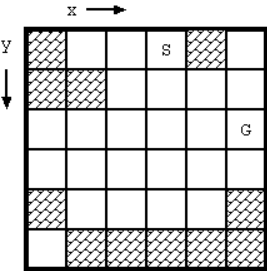
图1:例子(S:开始,G:目标)
石头的运动遵循以下规则:
- 开始时,石头静止起点广场上。
- 石头的运动仅限于x和y方向。禁止对角线移动。
- 当石头静止时,你可以让他向任意方向移动,除非它移动的方向上有砖块(图2(a))。
- 一旦抛出,石头不断向同一方向移动,直到下列事件之一发生:
- 石头击中砖块(图2(b),(c))。.
- 石头停在他击中的砖块之前
- 被击中的砖块消失
- 石块飞出游戏板之外。
- 游戏结束的条件
- 到达目标点
- 石头停在目标点游戏成功
- 石头击中砖块(图2(b),(c))。.
- 不能在十步之内到达目标点则返回失败。
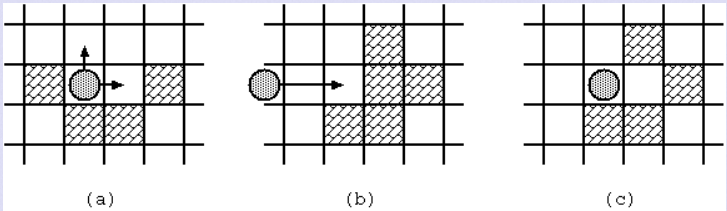
Fig. 2: Stone movements
通过这些规则我们想知道,石头是否能够到达目标点和最少移动次数
初始配置如图1所示,石头从开始到目标需要4次移动。路线如图3所示(a)。注意当石头到达目标时,游戏版的配置如图3(b)改变。
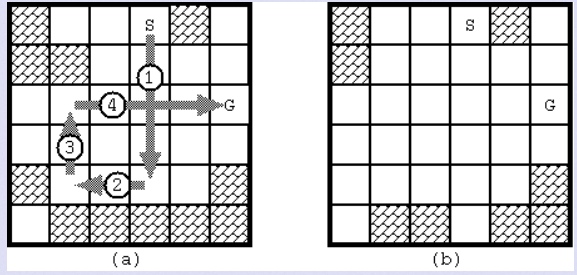
图3:图1的解决方案和解决之后的结果。
Input
输入是一组数据。输入结束标志为两个0。数据组的数量不超过100。
每个数据集如下展示
板的宽度(w)和高度(h)
游戏版的第一行
...
游戏版的h-th行
版的宽和高满足: 2 <= w <= 20, 1 <= h <= 20.
每行由一个空格分隔的十进制数字组成。该数字描述相应的格子的状态。
1 砖块
2 开始点
3 目标点
图. D-1数据如下:
6 6
1 0 0 2 1 0
1 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 3
0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 1
0 1 1 1 1 1
Output
对于每个数据,打印一个十进制整数的行,表示从开始到目标的路径的最小移动次数。如果没有这样的路线,打印- 1。每个行不应该有这个数字以外的任何字符。
Sample Input
2 1 3 2 6 6 1 0 0 2 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 6 1 1 1 2 1 1 3 6 1 1 0 2 1 1 3 12 1 2 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 13 1 2 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 0 0
Sample Output
1 4 -1 4 10 -1
题目连接:
https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-3009
dfs+回溯的变形 把每次走一步变成每次走一大行即可
具体看代码
AC代码:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <fstream> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <deque> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <map> #include <stack> #include <set> #include <sstream> #define mod 1000000007 #define eps 1e-6 #define ll long long #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define MEM(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x)) #define Maxn 25 using namespace std; int h,w;//横纵坐标 int sx,sy,ex,ey;//起点 终点坐标 int ans; int mp[Maxn][Maxn]; int dt[][2]= {{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};//4个方向 void dfs(int x,int y,int step) //在(x, y)位置上的步数step { if(x==ex&&y==ey)//到达终点 { if(step<ans)//若有更小值 ans=step; return; } if(step==10||step>=ans)//若超过10步,或超过当前最短步数 return; for(int i=0; i<4; i++)//四个方向搜索 { int tx=dt[i][0]+x; int ty=dt[i][1]+y; while(tx>=0&&tx<h&&ty>=0&&ty<w&&mp[tx][ty]!=1)//若此方向能走,则走到尽头,直至出场或撞墙 { if(tx==ex&&ty==ey)//若在过程中到达目标点 { step++; if(step<ans) ans=step; return; } tx+=dt[i][0]; ty+=dt[i][1]; } if((tx==x+dt[i][0]&&ty==y+dt[i][1])||tx<0||tx>=h||ty<0||ty>=w)//此方向不能走,或出场 continue; mp[tx][ty]=0;//撞墙 step++; dfs(tx-dt[i][0],ty-dt[i][1],step); step--;//回溯 mp[tx][ty]=1; } } int main() { while(cin>>w>>h,w+h) { ans=11;//初始化 MEM(mp,0); for(int i=0; i<h; i++) for(int j=0; j<w; j++) { cin>>mp[i][j]; if(mp[i][j]==2) { sx=i; sy=j; mp[sx][sy]=0; } if(mp[i][j]==3) { ex=i; ey=j; } } dfs(sx,sy,0);//搜索 if(ans==11) cout<<-1<<endl; else cout<<ans<<endl; } }