1 概述
1. 作用:'正确、高效' 的将 '同一批数据' 插入至 '不同的表' 中 2. 好处 (1) '正确':避免数据差异 (2) '高效':优于写多个 insert into(因为无论插入多少张表,'主表' 只会被读取一次) 3. 场景,若需求:将表 t 中的数据 '同时插入' 至表 t1、t2 若不知晓 insert all 语句,咱可能会使用 insert into 两次 insert into t1 select * from t; insert into t2 select * from t; 问题:在两次 insert 过程中,有可能 t 表的数据发生了改变, 从而导致 t1、t2 '得到的数据不一致'。 解决办法:insert all
2 insert 的两种形式
1. insert first: 仅对 '第一个' 匹配成功项进行插入
2. insert all : 对 '每个' 匹配成功项都进行插入
基础数据准备:
create table stu_info ( sno number(3), sname varchar2(30), sex varchar2(2) ); insert into stu_info(sno, sname, sex) values(1, '瑶瑶', '女'); insert into stu_info(sno, sname, sex) values(2, '优优', '男'); insert into stu_info(sno, sname, sex) values(3, '倩倩', '女'); commit; -- 两张测试表 create table stu_info_1 as select * from stu_info where 1 = 2; create table stu_info_2 as select * from stu_info where 1 = 2;
2.1 insert first
-- 仅对 '第一个' 匹配成功项进行插入 insert first when sno >= 2 then -- 不能用别名哦,如:t.sno into stu_info_1(sno, sname, sex) when sno >= 3 then into stu_info_2(sno, sname, sex) select t.sno, t.sname, t.sex from stu_info t;
查询结果:
select * from stu_info; select * from stu_info_1; select * from stu_info_2;
图示:仅对 ‘第一个’ 匹配成功项进行插入
2.2 insert all
-- 对 '每个' 匹配成功项都进行插入 insert all when sno >= 2 then -- 不能写别名哦,如:t.sno into stu_info_1(sno, sname, sex) when sno >= 3 then into stu_info_2(sno, sname, sex) select t.sno, t.sname, t.sex from stu_info t;
查询结果:对 ‘每个’ 匹配成功项都进行插入
3 数据一致性(同时插入)
3.1 验证:insert into 数据不一致
1. 模拟:将表 stu_info 中的数据同时插入 stu_info_1 和 stu_info_2 2. 分三个窗口模拟 '同时插入(并行)' (1) 窗口1: 将 stu_info 数据插入 stu_info_1(模拟时长 30 s) (2) 窗口2: 将 stu_info 数据插入 stu_info_2(模拟时长 30 s) (3) 窗口3:此时更新 stu_info 记录,使之影响 tu_info_1 和 stu_info_2(上述模拟时长内) 3. 清空表 stu_info_1、stu_info_2 -- 若有数据 truncate table stu_info_1; truncate table stu_info_2; 4. dbms_lock 包权限 -- 若无权限,sys 用户授权 -- conn system/system@orcl as sysdba grant execute on sys.dbms_lock to scott;
图示:
窗口1:插入 stu_info_1,更新 sno = 2 的记录时,等待(模拟执行时长)
declare begin for i in 1 .. 3 loop if i = 2 then dbms_lock.sleep(30); -- 模拟执行时长:30 秒 end if; insert into stu_info_1 (sno, sname, sex) select t.sno, t.sname, t.sex from stu_info t where t.sno = i; commit; end loop; end;
窗口2:插入 stu_info_1,更新 sno = 2 的记录时,等待(模拟执行时长)
declare begin for i in 1 .. 3 loop if i = 3 then dbms_lock.sleep(30); -- 模拟执行时长:30 秒 end if; insert into stu_info_2 (sno, sname, sex) select t.sno, t.sname, t.sex from stu_info t where t.sno = i; commit; end loop; end;
窗口3:更新 stu_info 记录,使之影响 tu_info_1 和 stu_info_2(上述模拟时长内)
update stu_info t set t.sname = 'update_2', t.sex = '22' where t.sno = 2;
commit;
测试结果:stu_info_1 和 stu_info_2 两者记录不一致!

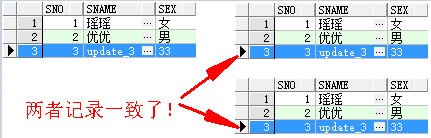
3.2 验证:insert all 数据一致
1. 同理,可分为 两个窗口测试
2. 清空表 stu_info_1、stu_info_2,并还原 stu_info 的数据
窗口1:插入数据至 stu_info_1 和 stu_info_1
declare begin for i in 1 .. 3 loop if i = 2 then dbms_lock.sleep(30); -- 模拟执行时长:30 秒 end if; insert all into stu_info_1(sno, sname, sex) into stu_info_2(sno, sname, sex) select t.sno, t.sname, t.sex from stu_info t where t.sno = i; commit; end loop; end;
窗口2:更新 stu_info 记录,使之影响 tu_info_1 和 stu_info_2(上述模拟时长内)
update stu_info t set t.sname = 'update_3', t.sex = '33' where t.sno = 3;
commit;