顾名思义,Model + Form == ModelForm。model和form的合体,所以有以下功能:
- 验证数据字段(Form的功能)
- 数据库操作(Model的功能)
model有操作数据库的字段,form验证也有那几个字段,虽然耦合度降低,但是代码是有重复的。如果利用model里的字段,那是不是form里的字段就不用写了。
在了解ModelForm模块之前,我们来看看Model+Form原生写法以及Model+Form模块,最后来看看三者的区别及优势。
一、Model+Form(原生写法)
1、models.py文件
class UserType(models.Model):
caption = models.CharField(max_length=32)
class User(models.Model):
username = models.CharField(max_length=32)
email = models.EmailField(max_length=32)
#指定关系一对多,指定和哪张表建立一对多,指定和哪个字段关联
user_type = models.ForeignKey(to='UserType',to_field='id')
2、前端myform.py文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/myform/" method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ msg }}<br/>
<label for="id_username">Username:</label>
<input type="text" id="id_username" name="username"/>
<br/>
<label for="id_email">Email:</label>
<input type="text" id="id_email" name="email"/>
<br/>
<select name="user_type">
{% for t in user_type %}
<option name ="{{ t.caption }}">{{ t.caption }}</option>
{% endfor %}
</select>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<br/>
<table>
<th>
<tr>用户名</tr>
<tr>邮箱</tr>
<tr>角色</tr>
</th>
{% for obj in new_obj %}
<tr>
<td>{{ obj.username }}</td>
<td>{{ obj.email }}</td>
<td>{{ obj.user_type.caption }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</body>
</html>
3、views.py文件
def myform(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
obj = models.User.objects.all()
user_type = models.UserType.objects.all()
return render(request,'myform.html',{'new_obj':obj,'user_type':user_type})
elif request.method == 'POST':
msg = ''
username = request.POST.get('username')
email = request.POST.get('email')
u_type = request.POST.get('user_type')
user_type = models.UserType.objects.all()
obj = models.User.objects.all()
c = models.User.objects.filter(username=username, email=email).count()
ut = models.UserType.objects.filter(caption=u_type).first()
if c>0:
msg = '用户名和邮箱重复!'
return render(request, 'myform.html', {'obj': obj,'msg':msg,'user_type':user_type})
elif not username or not email:
msg = '用户名和邮箱不能为空!'
return render(request, 'myform.html', {'obj': obj, 'msg':msg,'user_type':user_type})
else:
msg = '增加记录成功!'
models.User.objects.create(username=username, email=email, user_type=ut)
return render(request, 'myform.html', {'obj': obj,'msg':msg,'user_type':user_type})
4、效果图
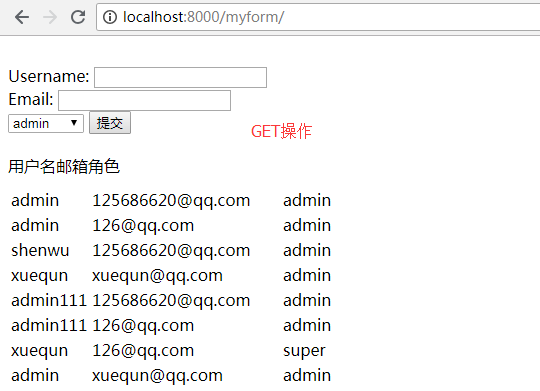
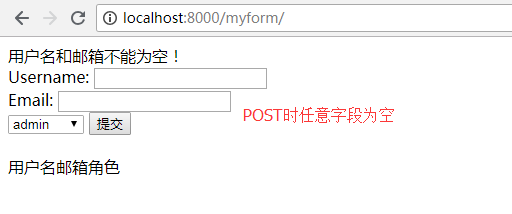
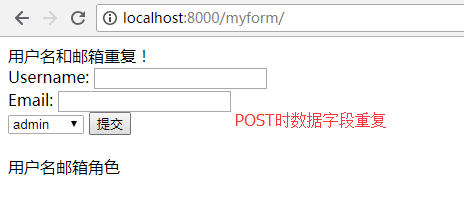
二、Model+Form模块
1、models.py文件
同上面的models.py文件
2、forms.py文件
#coding:utf-8
from django import forms
from django.forms import fields
from app01 import models
from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError
class UserInfoForm(forms.Form):
username = fields.CharField(max_length=32)
email = fields.EmailField(max_length=32)
user_type = fields.ChoiceField(
choices=models.UserType.objects.values_list('id','caption')
)
# 下面的操作是让数据在网页上实时更新:每次刷新时,必先执行父类的初始化函数,再设定下拉列表框选项。
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(UserInfoForm,self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.fields['user_type'].choices = models.UserType.objects.values_list('id','caption')
#自定义清理数据字段操作:1、清理单个字段;2、清理多个字段;
# def clean_username(self):
# #
# value = self.cleaned_data['username']
# if value == 'root':
# return value
# else:
# raise ValidationError('你不是我的...')
# def clean(self):
# username = self.cleaned_data.get('username')
# email = self.cleaned_data.get('email')
# if models.User.objects.filter(username=username, email=email).count() == 1:
# raise ValidationError('用户名和邮箱联合唯一索引重复!!!')
# return self.cleaned_data
#
# def _post_clean(self):
# print 'aaa %s' %self.cleaned_data
# username = self.cleaned_data['username']
# email = self.cleaned_data['email']
# if models.User.objects.filter(username=username,email=email).count()==1:
# self.add_error("__all__", ValidationError('用户名和邮箱联合唯一索引重复!!!'))
3、前端文件index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/index/" method="POST" novalidate="novalidate">
{% csrf_token %}
#作为p标签展示,obj.as_table将内容渲染在tr中;obj.as_p,将内容渲染在p标签中;obj.as_ul将内容渲染在li标签中。
{{ obj.as_p }}
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<table>
<th>
<tr>用户名</tr>
<tr>邮箱</tr>
<tr>角色</tr>
</th>
{% for obj in new_obj %}
<tr>
<td>{{ obj.username }}</td>
<td>{{ obj.email }}</td>
<td>{{ obj.user_type.caption }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</body>
</html>
4、views.py文件
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import unicode_literals
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from app01 import models
from forms import UserInfoForm
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
obj = UserInfoForm()
new_obj = models.User.objects.all()
return render(request,'index.html',{'obj':obj,'new_obj':new_obj})
elif request.method == 'POST':
obj = UserInfoForm(request.POST)
if obj.is_valid():
rt_dic = obj.cleaned_data
username = rt_dic.get('username')
email = rt_dic.get('email')
user_type_id = rt_dic.get('user_type')
ut = models.UserType.objects.filter(id=user_type_id).first()
models.User.objects.create(username=username,email=email,user_type=ut)
return render(request,'index.html',{'obj':obj})
5、效果
POST提交数据:
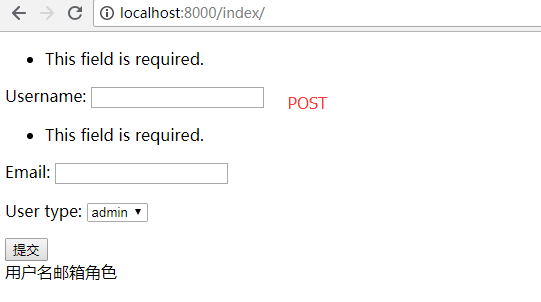
GET方式:
三、ModelForm模块
1、models.py文件
同上面的models.py文件
2、forms.py文件
class UserModelForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
#指定model的哪个表
model = models.User
#指定model的那些字段
fields = "__all__"
3、前端文件index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/mf/" method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ obj.as_p }}
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<table>
<th>
<tr>用户名</tr>
<tr>邮箱</tr>
<tr>角色</tr>
</th>
{% for obj in new_obj %}
<tr>
<td>{{ obj.username }}</td>
<td>{{ obj.email }}</td>
<td>{{ obj.user_type.caption }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</body>
</html>
4、views.py文件
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import unicode_literals
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from app01 import models
from forms import UserInfoForm
from django import forms
# Create your views here.
def mf(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
obj = UserModelForm()
new_obj = models.User.objects.all()
return render(request,'index.html',{'obj':obj,'new_obj':new_obj})
elif request.method == 'POST':
obj = UserModelForm(request.POST)
if obj.is_valid():
obj.save()
return render(request,'index.html',{'obj':obj})
5、效果
四、三种方式比较
共同点:
- models.py,即数据库字段的定义都是一样。
不同点:
1、Model+原生Form
- HTML里面的form表单字段需要用户自己写
- 表单里面字段的格式错误需要用户自己判断,考虑的情况比较多【必选】
- 保存方式为create()
2、Model+Form模块
- 需要用户定义forms(表单字段以及字段验证方法【可选】)
- HTML里面的form表单字段不需要用户写,直接使用obj.as_p就行
- 保存方式为create()
- 继承方式:UserForm -> Form -> BaseForm
3、纯ModelForm模块
- 继承ModelForm,不需要自定义forms文件
- 直接可以指定models的对象以及对象的字段
- HTML里面的form表单字段不需要用户写,直接使用obj.as_p就行
- 保存方式为save()
- 继承方式:UserModelForm (ModelForm名称)-> ModelForm -> BaseModelForm【里面会有save方法】 -> BaseForm
- is_valid() ===>full_clean()=====>【self._clean_fields() 清洗单个字段 self._clean_form()清洗整个表单,调用clean()方法,自定义错误的钩子 self._post_clean()用户自定义错误的钩子】