一.Stack栈
栈是一种先进后出的数据结构,例如在文本编辑器上都存在撤销功能,每次使用的时候都会发现最后一次的编辑操作永远是最先撤销,这个功能就是利用栈来实现的,
--栈的基本操作形式: 在java程序之中使用Stack来描述栈的操作,这个类的定义如下: public class Stack<E>extends Vector<E>,可以发现Stack是Vector的子类,但是他使用的并不是Vector类之中所提供的方法,而是使用了如下两个方法来实现功能:
入栈: public E push(E item)
出栈: public E pop()
--范例:实现栈的操作
1 public class MyStackDemo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 Stack<String> all = new Stack<>();
4 all.push("A");
5 all.push("B");
6 all.push("C");
7 System.out.println(all.pop());
8 System.out.println(all.pop());
9 System.out.println(all.pop());
10 System.out.println(all.pop());
11 }
12 }
--运行结果
Exception in thread "main" java.util.EmptyStackException
at java.util.Stack.peek(Stack.java:102)
at java.util.Stack.pop(Stack.java:84)
at 类集合框架.集合工具类.MyStackDemo.main(MyStackDemo.java:18)
C
B
A
Process finished with exit code 1
--由于多执行了一次出栈操作,因此出现了空栈异常.所有的数据保存之后,将按照倒叙的形式进行弹出,如果栈已经空了,则会抛出空栈异常.
二.Queue队列
Queue描述的是一个队列,而队列的主要特点是实现先进先出的操作形式,其基本的操作形式如下:
--在队列之中存在队尾和对首,所有的操作数据都是通过对首一个个的进入(就想我们排队买票的场景),在进行的队列操作的情况下,往往会有两种操作形式:在对首进行数据的接收处理(消费者),在队尾进行数据的生产(生产者).使用队列进行操作,我们可以发现生产者不必再等待消费者处理数据.生产者可以一直处于生产状态(多线程生产者与消费者处理模型).队列的实现可以使用LinkedList子类来完成.
--队列的使用主要依靠Queue接口之中提供的方法来处理:
向队列之中追加数据:boolean offer(E e) 也可以直接使用boolean add(E e)
通过队列获取数据: E poll() 弹出后删除数据
--范例:实现队列操作
1 public class MyQueueDemo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
4 queue.offer("X"); //追加数据,通过队尾增加
5 queue.offer("A"); //追加数据,通过队尾增加
6 queue.offer("Z"); //追加数据,通过队尾增加
7 System.out.println(queue.poll()); //弹出数据X
8 System.out.println(queue.poll()); //弹出数据A
9 System.out.println(queue.poll()); //弹出数据Z
10 }
11 }
--运行结果
X
A
Z
Process finished with exit code 0
--除了LinkedList的子类之外,还有优先级队列的概念,可以使用PriorityQueue实现优先级队列(带有比较功能):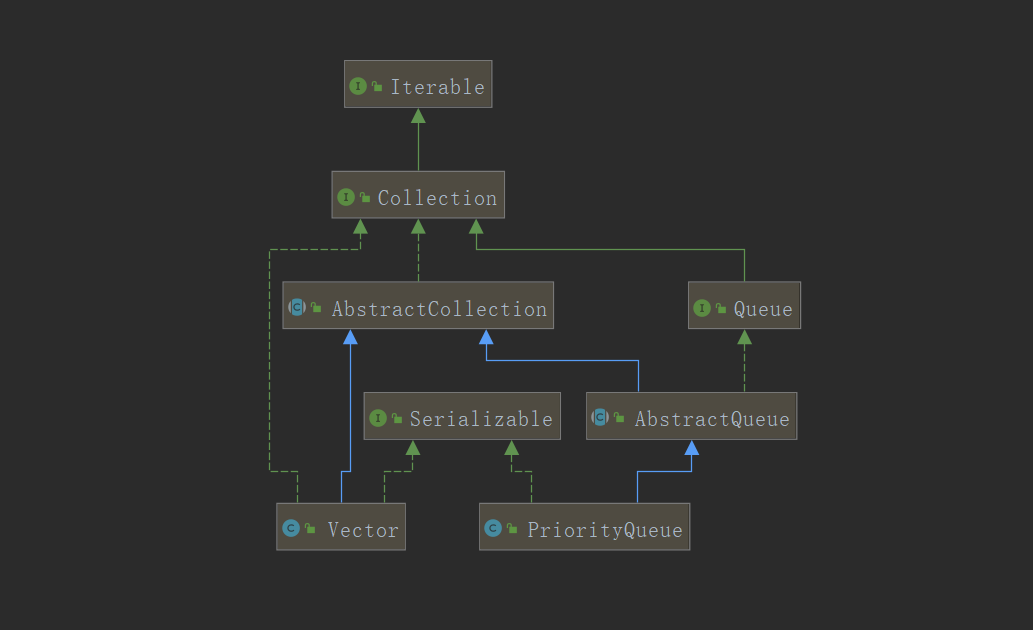
1 public class MyQueueDemo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 Queue<String> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
4 queue.offer("X"); //追加数据,通过队尾增加
5 queue.offer("A"); //追加数据,通过队尾增加
6 queue.offer("Z"); //追加数据,通过队尾增加
7 System.out.println(queue.poll()); //弹出数据X
8 System.out.println(queue.poll()); //弹出数据A
9 System.out.println(queue.poll()); //弹出数据Z
10 }
11 }
--运行结果
A
X
Z
Process finished with exit code 0
--可以发下程序之中带有排序功能,那么可以肯定的是与Comparable接口有直接的对应关系.对于队列的选用原则也是需要根据实际的项目环境来决定的.
三.Properties操作类
做国际化编程之中(点击查看文章),了解过资源文件(*.properties),这类文件的存储结构是按照"key = value "的形式保存的,这种形式和Map集合很相似,但是唯一的区别在于其所能保存的内容只有字符串,所以为了能够更好的描述属性的定义,在java.util包中提供有Properties类型,此类型时Hashtable的子类
可以发现在继承HashTable时,为HashTable定义的泛型为Object:public class Properties extends Hashtable<Object,Object>,实际上是因为Properties是不需要操作泛型的,因为它能够操作的类型只能是String类型.在Properties中要想实现属性的操作,性需要使用如下方法来实现:
设置属性:public Object setProperty(String key,String value)
获取属性: public String getProperty(String key) key不存在返回空
获得属性(不存在返回默认值defaultValue):public String getProperty(String key,String defaultValue)
输出属性内容: public void store(Writer writer,String comments)throws IOException
通过输入流读取属性内容: public void load(InputStream inStream)throws IOException
--范例:观察属性的设置和取得
1 public class MyPropertiesDemo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 Properties properties = new Properties();
4 //只允许设置字符串
5 properties.setProperty("test", "java_test");
6 properties.setProperty("love", "code java");
7 System.out.println(properties.getProperty("test"));
8 System.out.println(properties.getProperty("love"));
9 System.out.println(properties.getProperty("what"));
10 }
11 }
--运行结果
java_test
code java
null
Process finished with exit code 0
--在获取时设置默认值
1 public class MyPropertiesDemo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 Properties properties = new Properties();
4 //只允许设置字符串
5 properties.setProperty("test", "java_test");
6 properties.setProperty("love", "code java");
7 System.out.println(properties.getProperty("test"));
8 System.out.println(properties.getProperty("love","不知道你在说什么"));
9 System.out.println(properties.getProperty("what","不知道你在说什么"));
10 }
11 }
--运行结果
java_test
code java
不知道你在说什么
Process finished with exit code 0
--通过代码可以发现Properties里面可以像Map集合那样进行内容的设置与获取,但是唯一的差别是他只能操作String类型,另外需要注意的是:之所以会提供有Properties类,还有一个最重要的内容是他可以根据输出流输出属性,也可以使用输入流读取属性内容:
--范例:将属性内容保存在文件之中
1 public class MyPropertiesDemo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
3 Properties properties = new Properties();
4 //只允许设置字符串
5 properties.setProperty("test", "java_test");
6 properties.setProperty("love", "code java");
7 properties.setProperty("BeiJing", "北京");
8 properties.store(new FileOutputStream(new File("D:" + File.separator + "java_test" + File.separator
9 + "test.properties")),"中文的注释看不见的_English");
10
11 }
12 }
--查看输出结果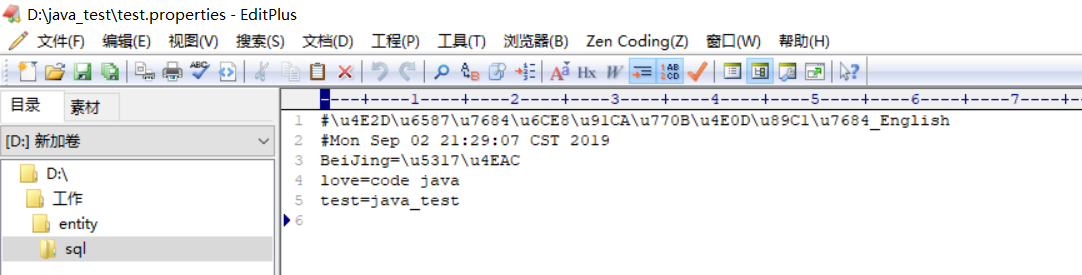
--可以发现所有的中文都转变为了Unicode编码.可以发现资源文件的输出处理确实可以实现,如果输出的是中文,则自动帮助用户进行转码处理.
--范例:读取资源文件(使用Properties)
1 public class MyPropertiesDemo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
3 Properties properties = new Properties();
4 properties.load(new FileInputStream(new File("D:" + File.separator + "java_test" + File.separator
5 + "test.properties")));
6 System.out.println(properties);
7 }
8 }
--运行结果
{love=code java, BeiJing=北京, test=java_test}
Process finished with exit code 0
--使用properties类型的最大特点是可以实现资源内容的输入与输出操作,但是在实际的开发之中Properties往往用于读取配置资源的信息.这一点主要是在标准设计之中做做程序初始化准备的时候使用的.
四.Collections工具类
Collections是java提供的一组集合数据的操作工具类,利用他可以实现各个集合的操作.
--范例:使用Collections操作LIst集合
1 public class MyCollectionsDemo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 List<String> all = new ArrayList<>();
4 //追加元素
5 Collections.addAll(all,"hello","world","java");
6 System.out.println(all);
7 //数据的反转
8 Collections.reverse(all);
9 System.out.println(all);
10 //使用二分查找
11 int content = Collections.binarySearch(all, "java");
12 System.out.println(all.get(content));
13 }
14 }
--大部分情况下对于集合的使用没有过多复杂的要求,更多的情况下就是利用集合保存数据,要么进行输出,要么进行查询.
--解释Collections与Collection的区别:
1.Collection是集合的接口,允许保存单值对象;
2.Collections是集合操作的工具类,两者没有本质联系;