Flexbox早有耳闻,但是决定切实尝试一番,还是因为看了这条围脖:

我觉得用flexbox可以实现,但是发觉无从下手,属性特性都不了解。趁此机会,学习下。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---->flex container的属性
---->flex item的属性
---->练习一:子元素的完美居中问题
---->练习二:不使用媒体查询多块元素根据分辨率自动排列
---->练习三:添加媒体查询,基本页面布局伸缩
上面demo要用现代浏览器打开,并且要记得不断改变浏览器窗口的大小,来查看效果。
flex container的属性
display:
首先,对于container应用下面代码,针对它的直接子元素创建一个flex的上下文。
.container { display: flex; /* or inline-flex */ }
flex-direction:

它建立一个主轴,用来确定flex items在flex container中的放置方向。
.container { flex-direction: row | row-reverse | column | column-reverse; }
**row(default) :flex item从左向右排列(如果你定义了direction属性的话,这里会有影响);
**row-reverse : flex item从右向左排列;
**column : 跟row相同,但是是从上向下排列;
**column-reverse : 跟row-reverse相同,但是是从下向上排列;
flex-wrap:

默认的情况下,flex items会尝试在一行中显示,通过制定这个属性相关的值,你可以定义是否换行。direction属性的值 会影响到flex-wrap的值的作用。
.container{ flex-wrap: nowrap | wrap | wrap-reverse; }
**nowrap:单行,flex item从左向右显示(direction:ltr);
**wrap: 多行,flex item从左向右显示;
**wrap-reverse:多行,flex item显示方向与direction定义的方向相反。
flex-flow:
flex-flow: <‘flex-direction’> || <‘flex-wrap’>
这个属性是flex-direction和flex-wrap属性的简写,默认值是 row nowrap。
justify-content:

它定义了相对主轴的对齐方式。它定义了水平方向上剩余空间的分配方式。
.container { justify-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around; }
可以根据上面的示意图寻找合适的属性。
align-items:

这个属性定义flex item在十字轴(垂直于主轴)的当前行上的默认行为。
.container { align-items: flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch; }
align-content:

这个属性定义了在垂直方向上剩下的空间的分配方式。
.container { align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | stretch; }
flex item的属性

order:

一般情况下,flex items会按照他们在文档中的顺序来排列。order属性可以控制他们在flex container中的显示顺序。
.item { order: <integer>; }
flex-grow:

给flex items设置flex-grow的数值可以让flex items根据数值比例自适应分配空间。就像上面图中一样的。(不要用负值)
.item { flex-grow: <number>; /* default 0 */ }
flex-shrink:
这个属性定义flex items的伸缩能力。(不要用负值)
.item { flex-shrink: <number>; /* default 1 */ }
flex-basis:
这个属性定义了在有剩余的空间可分布时一个元素的默认大小。
.item { flex-basis: <length> | auto; /* default auto */ }
flex:
这个属性是 flex-grow, flex-shrink和flex-basis的缩写。默认值是 0 1 auto
.item { flex: none | [ <'flex-grow'> <'flex-shrink'>? || <'flex-basis'> ] }
align-self:

这个元素与flex items自己的对齐方式有关
.item { align-self: auto | flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch; }
了解了之后接着跟着练习写demo(源代码都放在github上面):
总结:
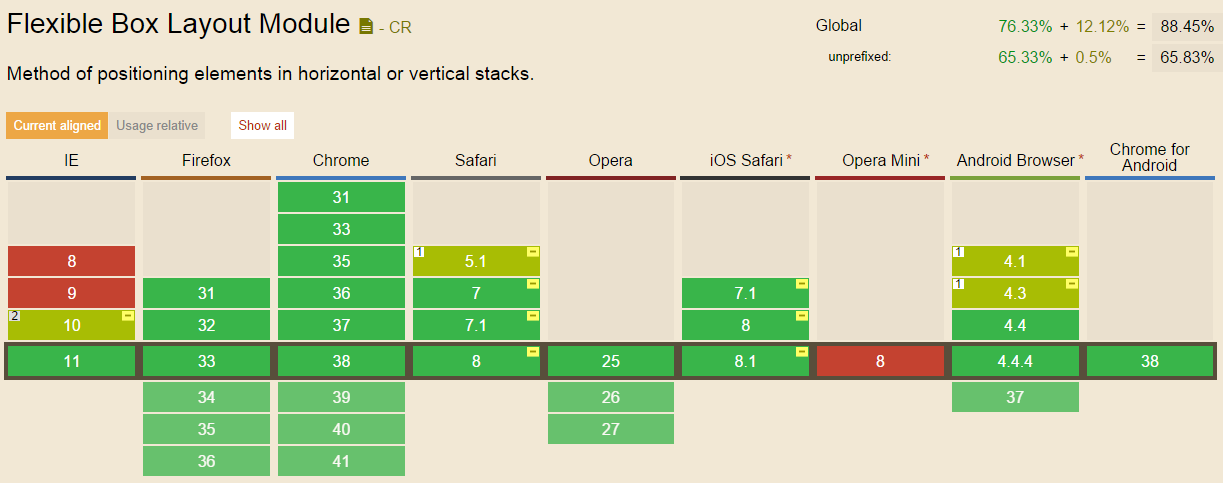
虽然它很强大,但是如果需要考虑浏览器的兼容性的话,可能就需要另寻它法了。这里是它的浏览器兼容性一览表:
关于最前面微博那道题目的解法,那个微博下面已经有贴了代码啦,贴过来看看:
http://ajccom.sinaapp.com/demo/test.html
http://codepen.io/airen/pen/PwoNrQ
上面两个代码都值得学习呢。
不过我觉得喔,第一个demo就符合要求了啦。