一旦你对程序进行了改动,就要对改动的部分进行测试!不管改动多么简单,一定要对它进行测试!
不要试图在写代码的过程中设计程序,把需要做的东西写在纸上。
不要依靠编译器来保证代码的正确性,要理解所写的每一行代码
字节:计算机内存的基本单元。比特,也叫位,拥有两种状态的数据单元,比如0或1,开或关。
1byte=8bit
前缀和后缀自增和自减运算符:注意:i值 是6,

c++中数据显示位数的控制:

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double f = 333233.1415926535;
float aa = 12.25678;
float bb = 0.123456789;
cout << f << endl;
cout << aa << endl;
cout << bb << endl;
cout.setf(ios::fixed | ios::showpoint);
cout.precision(3);
//
cout << f << endl; //输出3位小数,3.142
cout << aa << endl;
cin.get();
return 0;
}
显示结果:
333233
12.2568
0.123457
333233.142
12.257
c++控制语句:
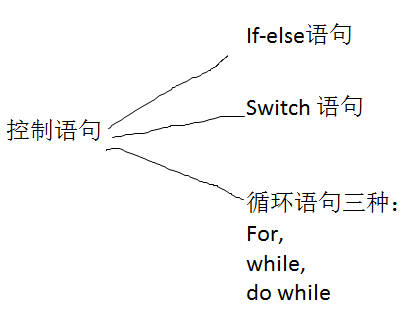
c++中if语句:(4种)
1.if-else语句
if (condition)
{
//条件为真时执行
}
else
{
//条件为假时执行
}
2.if-else if-else语句
if (condition1)
{
//属于条件1的语句
}
else if(condition 2)
{
//属于条件2的语句
}
else
{
//属于条件3的语句
}
注意,else语句不一定是必须的,也就是说:if或if--else if或者if-else if -else if....-else也是允许的;但是只能有一个else语句。
3.嵌套if-else语句
示例如下:
if (condition) //第一个条件
{
if (another condition) //这里是嵌套的if 语句
{
//语句
}
//更多的语句
}
4.条件运算符
int windspeed;
bool bHurricane;
if (winspeed>75)
bHurricane=true;
else
bHurricane=false;
通过条件 运算符“?”只通过一行代码就能完成上述检查与操作赋值:
int windspeed;
bool bHurricane;
bHurricane = windspeed>75? true : false
注意,运算符“?”回影响代码的 易读性,初学者不建议使用
c++中switch语句;
switch(此处是变量)
{
case value1:
//语句块1
break; //break不要忘记加上
case value2: case value3:(表示2或者3情况下)
//语句块2
break;
default: //缺省情况下
//语句n
}
c++中的循环有三种:
for 循环:当清楚循环体需重复执行的次数时,多使用之
示例:输出字母表
结果:
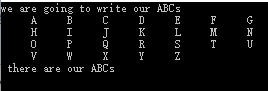
#include<iostream> #include<iomanip> //为了使用setw using namespace std; int main() { int letter_ctr, i; cout << "we are going to write our ABCs" << endl; letter_ctr = 0; for (i = 65; i < 91; ++i) //A=65,z=90 { //将整数转化为字符 cout << setw(6) << static_cast<char>(i); letter_ctr ++; if (letter_ctr == 7) { cout << endl; letter_ctr = 0; } } cout << " there are our ABCs"; cin.get(); return 0; }
while循环:可用于在不能事先确定循环次数的情况下对循环进行控制。
while(condition)
{
//这些语句在条件为真时被执行
}
do while循环:与while循环类似,但是在循环体执行结束检查循环的条件
do
{
//循环语句体
} while (condition);
cin.ignore()函数:
用于回车符的删除,
有时在cin>>后面跟有getline(),cin会将回车符留在输入队列中,需要将回车符移除才能正确赋值给变量
int aa; string bb; cout << "how many do you have?" << endl; cin >> aa; cout << aa << endl;; cin.ignore(); // 加上这个getlIne才能正确赋值,遇到回车符会停止 cout << "the color is ???" << endl; getline(cin,bb); cout << bb;
