Find a path
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2116 Accepted Submission(s): 909
Problem Description
Frog fell into a maze. This maze is a rectangle containing N rows and M columns. Each grid in this maze contains a number, which is called the magic value. Frog now stays at grid (1, 1), and he wants to go to grid (N, M). For each step, he can go to either the grid right to his current location or the grid below his location. Formally, he can move from grid (x, y) to (x + 1, y) or (x, y +1), if the grid he wants to go exists.
Frog is a perfectionist, so he'd like to find the most beautiful path. He defines the beauty of a path in the following way. Let’s denote the magic values along a path from (1, 1) to (n, m) as A1,A2,…AN+M−1, and Aavg is the average value of all Ai. The beauty of the path is (N+M–1) multiplies the variance of the values:(N+M−1)∑N+M−1i=1(Ai−Aavg)2
In Frog's opinion, the smaller, the better. A path with smaller beauty value is more beautiful. He asks you to help him find the most beautiful path.
Frog is a perfectionist, so he'd like to find the most beautiful path. He defines the beauty of a path in the following way. Let’s denote the magic values along a path from (1, 1) to (n, m) as A1,A2,…AN+M−1, and Aavg is the average value of all Ai. The beauty of the path is (N+M–1) multiplies the variance of the values:(N+M−1)∑N+M−1i=1(Ai−Aavg)2
In Frog's opinion, the smaller, the better. A path with smaller beauty value is more beautiful. He asks you to help him find the most beautiful path.
Input
The first line of input contains a number T indicating the number of test cases (T≤50).
Each test case starts with a line containing two integers N and M (1≤N,M≤30). Each of the next N lines contains M non-negative integers, indicating the magic values. The magic values are no greater than 30.
Each test case starts with a line containing two integers N and M (1≤N,M≤30). Each of the next N lines contains M non-negative integers, indicating the magic values. The magic values are no greater than 30.
Output
For each test case, output a single line consisting of “Case #X: Y”. X is the test case number starting from 1. Y is the minimum beauty value.
Sample Input
1
2 2
1 2
3 4
Sample Output
Case #1: 14
Source
Recommend
wange2014
题意:
给出一个n*m的地图,要求从左上角(0, 0)走到右下角(n-1, m-1)。
地图中每个格子中有一个值。然后根据这些值求出一个最小值。
这个最小值要这么求——
这是我们从起点走到终点的路径,其中N是地图的长,M是地图的宽,Ai表示路径中第i个点的值,Aavg表示路径中所有的点的值的平均值。要求这个式子的值最小。
我们可以将它转化为
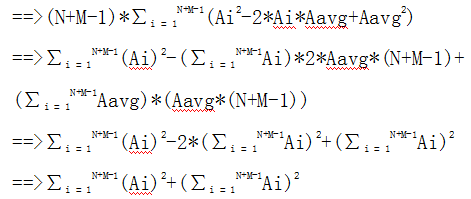
好了,推到这里,我们需要的数学知识就结束了(实际上以我的数学知识也只能做到这里了……)。然后dp就好了——
Dp[i][j][k],i表示第i行,j表示第j列,k表示所有Ai的和,这个里面保存的是所有  的值。
的值。
然后dp下去就好了.
dp[i][j][k] = min(dp[i][j][k], dp[i-1][j][k-mp[i-1][j]]+mp[i][j]*mp[i][j], dp[i][j][k-mp[i][j-1]]+mp[i][j]*mp[i][j]);
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<cstdlib> #include<queue> #include<set> #include<vector> using namespace std; #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define eps 1e-10 #define PI acos(-1.0) #define _e exp(1.0) #define ll long long const int maxn=35; int t,n,m; int dp[maxn][maxn][1800],map[maxn][maxn]; int ans; int minn(int x,int y) { if(x==-1) return y; return x<y?x:y; } void solve() { memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp)); dp[0][0][map[0][0]]=map[0][0]*map[0][0]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) { if(i-1>=0) for(int k=map[i][j];k<1800;k++) if(dp[i-1][j][k-map[i][j]]!=-1) dp[i][j][k]=minn(dp[i][j][k],dp[i-1][j][k-map[i][j]]+map[i][j]*map[i][j]); if(j-1>=0) for(int k=map[i][j];k<1800;k++) if(dp[i][j-1][k-map[i][j]]!=-1) dp[i][j][k]=minn(dp[i][j][k],dp[i][j-1][k-map[i][j]]+map[i][j]*map[i][j]); } } int main() { scanf("%d",&t); int ca=1; while(t--) { scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) scanf("%d",&map[i][j]); solve(); ans=-1; for(int i=0;i<1800;i++) if(dp[n-1][m-1][i]!=-1) { int mid=(n+m-1)*dp[n-1][m-1][i]-i*i; //把化简后的公式里的剩余部分补齐 if(ans==-1) ans=mid; else ans=ans<mid?ans:mid; } printf("Case #%d: %d ",ca++,ans); } return 0; }