一、MTV模型
Django的MTV分别代表:
Model(模型):负责业务对象与数据库的对象(ORM)
Template(模版):负责如何把页面展示给用户
View(视图):负责业务逻辑,并在适当的时候调用Model和Template
此外,Django还有一个urls分发器,它的作用是将一个个URL的页面请求分发给不同的view处理,view再调用相应的Model和Template

二、django基本命令
-
下载安装django
pip3 install django
-
创建一个django project
django-admin.py startproject mysite
当前目录下会生成mysite的工程,目录结构如下:
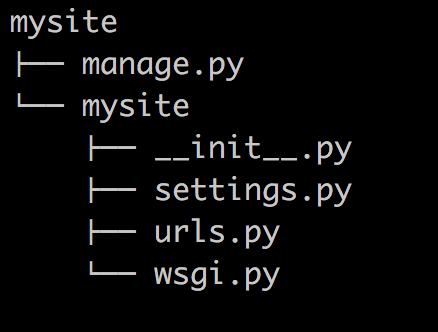
- manage.py ----- Django项目里面的工具,通过它可以调用django shell和数据库等。
- settings.py ---- 包含了项目的默认设置,包括数据库信息,调试标志以及其他一些工作的变量。
- urls.py ----- 负责把URL模式映射到应用程序。
-
在mysite目录下创建应用
python manage.py startapp blog
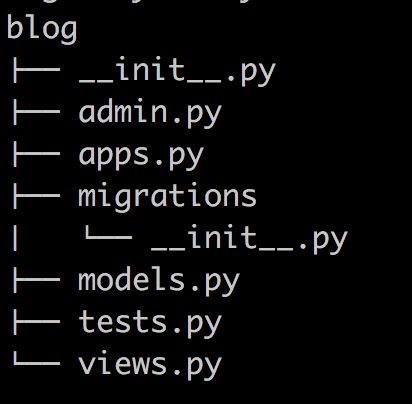
-
启动django项目
python manage.py runserver 8080
三、请求的生命周期
网站的本质是socket
服务端(网站)
1. 先启动并监听:80端口 3. 获取请求信息: 获取请求中的URL 根据URL在已经写好的路由关系中进行匹配: [ /login/ login /index/ index ]
def login(request): 请求头 请求体 处理请求 return 响应内容: 响应头 <!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-cn">。。。</html> 断开
客户端(浏览器)
2. 发送请求 - 连接:www.cnblogs.com:80 - 发送数据: GET: GET /news/?page=1&xx=11 http1.1 host:www.cnblogs.com Accept-Encoding:gzip, deflate, br User-Agent:Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36 POST: POST /news/?page=1&xx=11 http1.1 host:www.cnblogs.com Accept-Encoding:gzip, deflate, br User-Agent:Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36 name=alex&pwd=123 4. 接收响应内容 响应头写到浏览器 响应体在浏览器上展示 断开
四、主机管理案例
1、创建project及app
django-admin.py startproject mysite #创建project
python manage.py startapp app01 #创建app
python manage.py runserver #启动
2、修改配置文件
- settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'app01.apps.App01Config', #添加app01
]
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
# 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', #注释此行
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
]
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')] #添加模板路径
,
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]#数据库
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'db.sqlite3'),
}
}
补充

DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME':'dbname',
'USER': 'root',
'PASSWORD': 'xxx',
'HOST': '',
'PORT': '',
}
}
# 由于Django内部连接MySQL时使用的是MySQLdb模块,而python3中还无此模块,所以需要使用pymysql来代替
# 如下设置放置的与project同名的配置的 __init__.py文件中
import pymysql
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
#静态文件目录
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS = (
os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static'),
)
- 代码详情
文件路径

""" Django settings for day16 project. Generated by 'django-admin startproject' using Django 1.11.4. For more information on this file, see https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/topics/settings/ For the full list of settings and their values, see https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/ref/settings/ """ import os # Build paths inside the project like this: os.path.join(BASE_DIR, ...) BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) # Quick-start development settings - unsuitable for production # See https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/howto/deployment/checklist/ # SECURITY WARNING: keep the secret key used in production secret! SECRET_KEY = 'l))&0*l6$aja*lcq8=0-s9u4byl2%alzfsgdxs_&3_qre&=mvw' # SECURITY WARNING: don't run with debug turned on in production! DEBUG = True ALLOWED_HOSTS = [] # Application definition INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'django.contrib.admin', 'django.contrib.auth', 'django.contrib.contenttypes', 'django.contrib.sessions', 'django.contrib.messages', 'django.contrib.staticfiles', 'app01.apps.App01Config', ] MIDDLEWARE = [ 'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware', 'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware', 'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware', # 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware', 'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware', 'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware', ] ROOT_URLCONF = 'day16.urls' TEMPLATES = [ { 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates', 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')] , 'APP_DIRS': True, 'OPTIONS': { 'context_processors': [ 'django.template.context_processors.debug', 'django.template.context_processors.request', 'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth', 'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages', ], }, }, ] WSGI_APPLICATION = 'day16.wsgi.application' # Database # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/ref/settings/#databases DATABASES = { 'default': { 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3', 'NAME': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'db.sqlite3'), } } # Password validation # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/ref/settings/#auth-password-validators AUTH_PASSWORD_VALIDATORS = [ { 'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.UserAttributeSimilarityValidator', }, { 'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.MinimumLengthValidator', }, { 'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.CommonPasswordValidator', }, { 'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.NumericPasswordValidator', }, ] # Internationalization # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/topics/i18n/ LANGUAGE_CODE = 'en-us' TIME_ZONE = 'UTC' USE_I18N = True USE_L10N = True USE_TZ = True # Static files (CSS, JavaScript, Images) # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/howto/static-files/ STATIC_URL = '/static/' STATICFILES_DIRS = ( os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static'), )

from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^login/',views.login), url(r'^index/',views.index), url(r'^parts/',views.parts), url(r'^part_add/',views.part_add), url(r'^part_del/',views.part_del), url(r'^part_edit/',views.part_edit), ]

from django.db import models # Create your models here. from django.db import models class UserInfo(models.Model): id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) user = models.CharField(max_length=32) pwd = models.CharField(max_length=64) age = models.IntegerField() class Department(models.Model): id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
#创建数据库表 python3 manage.py makemigrations python3 manage.py migrate

from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect # Create your views here. from app01 import models # def test(request): # # #查询所有用户信息 # # user_list = models.UserInfo.objects.all() # # for obj in user_list: # # print(obj,obj.id,obj.user,obj.pwd) # # # # return HttpResponse('123') # # # # user_list = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(user='alex',pwd='123').all # # print(user_list) # # # # user = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(user='alex',pwd='123').first() # # print(user,user.id,user.user,user.pwd) # return HttpResponse('123') def login(request): if request.method == "GET": #打开login.html文件 #找到特殊标记{{msg}} #并将第三个参数中字典总的对应值替换 #将替换完毕的字符串发送给用户浏览器 return render(request,"login.html",{'msg':''}) else: #去请求体中获取数据 username1 = request.POST.get("username") password1 = request.POST.get("password") print(username1,password1) userinfo = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(user=username1,pwd=password1).first() print(userinfo) if userinfo: # return redirect('http://www.baidu.com') return redirect('/index/') else: return render(request,'login.html',{'msg':'用户名或密码错误'}) # if user == "alex" and pwd == "123": # #在响应头中设置,location:http://www.baidu.com,无响应体 # return redirect('http://www.baidu.com') # #return redirect('/index/') # else: # return render(request,'login.html',{'msg':'用户名或密码错误'}) def index(request): return render(request,'index.html') def parts(request): depart_list = models.Department.objects.all() return render(request,'parts.html',{'depart_list':depart_list}) def part_add(request): if request.method == 'GET': return render(request,'part_add.html') else: ti = request.POST.get('title') models.Department.objects.create(title=ti) return redirect('/parts/') def part_del(request): nid = request.GET.get('nid') models.Department.objects.filter(id=nid).delete() return redirect('/parts/') def part_edit(request): if request.method == 'GET': nid = request.GET.get('nid') obj = models.Department.objects.filter(id=nid).first() if not obj: return HttpResponse('写错了,返回吧') return render(request,'part_edit.html',{'obj':obj}) else: nid = request.GET.get('nid') title = request.POST.get('title') models.Department.objects.filter(id=nid).update(title=title) return redirect('/parts')
创建如下目录,并将bootstrap导入到plugins下

templates文件夹下创建html文件

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>欢迎登录</h1> <ul> <li><a href="/parts/">业务线管理</a></li> </ul> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/plugins/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.css"> </head> <body> <div style=" 500px;margin: 0 auto;margin-top: 80px;"> <form class="form-horizontal" action="/login/" method="post"> <div class="form-group"> <label for="n1" class="col-sm-2 control-label">用户名</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <input id="n1" type="text" name="username" class="form-control" placeholder="用户名"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="n2" class="col-sm-2 control-label">密码</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <input id="n2" type="password" name="password" class="form-control" placeholder="密码"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10"> <input type="submit" value="登 录" class="btn btn-primary">{{ msg }} </div> </div> </form> </div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/plugins/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.css"> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <h1>添加部门</h1> <form action="" method="POST"> <input type="text" name="title"> <input type="submit" vlaue="添加"> </form> </div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/plugins/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.css"> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <h1>编辑部门</h1> <form action="" method="post"> <div class="form-group"> <label for="t1">部门名称</label> <input type="text" id="'t1" class="form-control" name="title" vlaue="{{ obj.title }}"> </div> <input type="submit" value="修改" class="btn btn-default"> </form> </div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/plugins/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.css"> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <h1>部门列表</h1> <div style="margin: 5px 0"> <a href="/part_add/" class="btn btn-success"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-plus" aria-hidden="true"></span>添加</a> </div> <table class="table table-bordered"> <thead> <tr> <th>ID</th> <th>部门</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for obj in depart_list %} <tr> <td>{{ obj.id }}</td> <td>{{ obj.title }}</td> <td> <a href="/part_edit/?nid={{ obj.id }}" class="btn btn-info"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-cog" aria-hidden="true"></span>编辑</a> <a href="/part_del/?nid={{ obj.id }}" class="btn btn-danger"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-remove" aria-hidden="true"></span>删除</a> </td> </tr> {% endfor %} </tbody> </table> </div> </body> </html>
- 数据库截图如下
department表
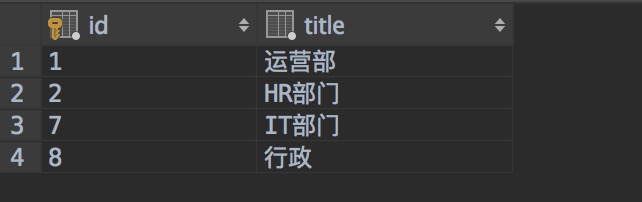
userinfo表

- 项目截图
登录界面
登录成功跳转index

parts界面

五、知识补充
1、数据库相关
执行命令:创建数据库表
python3 manage.py makemigrations
python3 manage.py migrate
对应关系
类 -> 表
对象 -> 行
数据库操作
表级别: from django.db import models # 类对象数据库的表 class UserInfo(models.Model): # 字段对应数据库中列 id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) # 创建id列,自增,int,主键 user = models.CharField(max_length=32,null=False) # varchar(32) pwd = models.CharField(max_length=64) age = models.IntegerField() # int类型 class Department(models.Model): """ 部门表 """ id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) title = models.CharField(max_length=32) python manage.py makemigrations python manage.py migrate 行: 增加: models.UserInfo.objects.create(user="alex",pwd='123',age=18) dic = {'user':'alex','pwd':'123',"age":18 } models.UserInfo.objects.create(**dic) 删除: models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id=12,name='alex').delete() dic = {'user':'alex','pwd':'123',"age":18 } models.UserInfo.objects.filter(**dic).delete() 修改: models.UserInfo.objects.filter(id=12,name='alex').update(user='11111',pwd='xxxx') models.UserInfo.objects.filter(**{...}).update(**{...}) 查看: # [obj,obj,obj,....] v = models.UserInfo.objects.all() # [obj,obj,obj,....] v = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(....) # obj models.UserInfo.objects.filter(....).first() # 获取一个对象;无、多都会报错 models.UserInfo.objects.get(id=1,name='alex')
2、路由系统
1. 路由系统 a. url添加起始和终止符 url(r'^example/$', views.example), url(r'^example/add/$', views.example_add), b. 传参,推荐使用二和三 # 方式一 # http://127.0.0.1:8000/example_edit/?nid=11&xid=1 url(r'^example_edit/$', views.example_edit) def example_edit(request): nid = request.GET.get('nid') xid = request.GET.get('xid') print(nid,xid) return HttpResponse('编辑') # 方式二: # /example_edit/123/111/ url(r'^example_edit/(d+)/(d+)/$', views.example_edit), def example_edit(request,nid,xid): print(nid,xid) return HttpResponse('编辑') # 方式三: # /example_edit/123/111/ url(r'^example_edit/(?P<xid>d+)/(?P<nid>d+)/$', views.example_edit), def example_edit(request,nid,xid): print(nid,xid) return HttpResponse('编辑') c. 路由分发
from django.conf.urls import url,include
s19day17/urls.py url(r'^cmdb/', include('cmdb.urls')) url(r'^openstack/', include('openstack.urls')) cmdb/urls.py from django.conf.urls import url,include from cmdb import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^host/$', views.host), ] openstack/urls.py from django.conf.urls import url,include from openstack import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^host/$', views.host), ]
3、视图函数
def example_edit(request,nid,xid): request.method request.GET request.POST return HttpResponse('文本') return redirect('url') # 打开模板,读取数据到内存 # {'k1':'v1'},对模板中的特殊字符进行“渲染” # 生成不含特殊标签(已经被替换完毕)的字符串 return render(request,'模板路径',{'k1':'v1'})
def keng(request):
return render(request,'keng.html',{'k1':123,'k2':"alex"})
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>{{ k1 }}</h1> <script> alert("{{ k2 }}"); </script> </body> </html>
4、模板语言
tpl.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>{{ "asdfasdf"|upper }}</h1> <h1>{{ k1 }}</h1> #单值 <h1>{{ k2.2 }}</h1> #索引 {% for item in k2 %} #循环 <a href="#">{{ item }}</a> {% endfor %} <h1>{{ k3.age }}</h1> {% for k,v in k3.items %} <a href="#">{{ k }} {{ v }}</a> {% endfor %} {% if k1 == 123 %} #if判断 <h1>下课</h1> {% else %} <h1>放学</h1> {% endif %} </body> </html>
views.py
def tpl(request):
data_dict = {
'k1': 123123,
'k2':[11,22,33,'alex'],
'k3':{'name':'李杰','age':18}
}
return render(request, 'tpl.html', data_dict)
母版
{% block css %} 程序块{% endblock %} 其余地方为母版内容,继承
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/plugins/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.css"> <style> body{ margin: 0; } </style> {% block css %} {% endblock %} </head> <body> <div style="height: 48px;background-color: #1b6d85"> 头部菜单 </div> <div> <div style="float: left; 20%;background-color: #dddddd;height: 500px;"> 菜单 </div> <div style="float: left; 80%"> {% block content %} {% endblock %} </div> </div> {% block js %} {% endblock %} </body> </html>
