一、 实验要求
-
1、按照https://github.com/mengning/mykernel 的说明配置mykernel 2.0,熟悉Linux内核的编译;
-
2、基于mykernel 2.0编写一个操作系统内核,参照https://github.com/mengning/mykernel 提供的范例代码
-
3、简要分析操作系统内核核心功能及运行工作机制
二、实验流程
1、配置mykernel 2.0
wget https://raw.github.com/mengning/mykernel/master/mykernel-2.0_for_linux-5.4.34.patch
sudo apt install axel
axel -n 20 https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v5.x/linux-5.4.34.tar.xz
xz -d linux-5.4.34.tar.xz
tar -xvf linux-5.4.34.tar
cd linux-5.4.34
patch -p1 < ../mykernel-2.0_for_linux-5.4.34.patch
sudo apt install build-essential libncurses-dev bison flex libssl-dev libelf-dev
make defconfig
make -j$(nproc)
sudo apt install qemu
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage
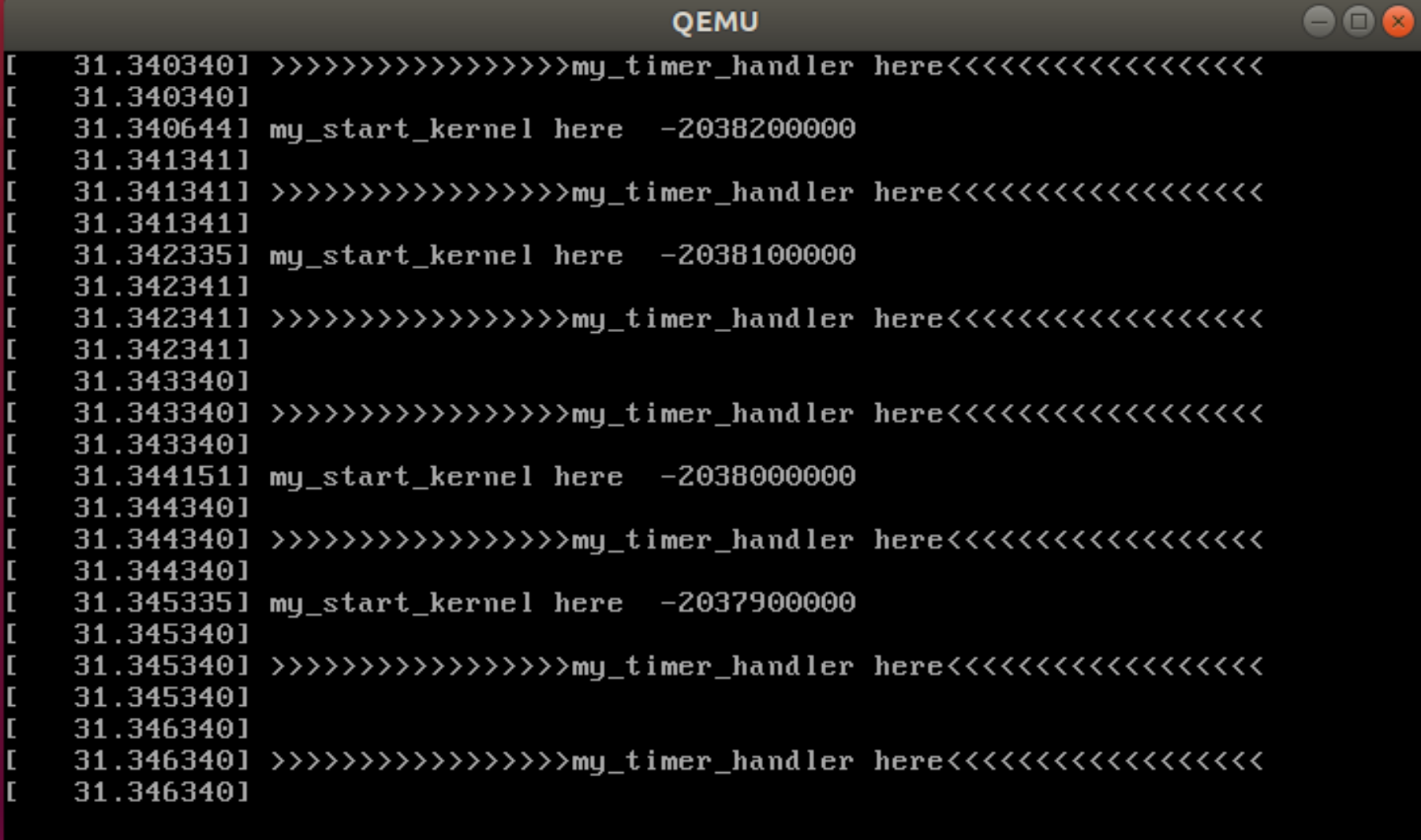
查看linux-5.4.34/mykernel目录存在 mymain.c和myinterrupt.c:
mymain.c: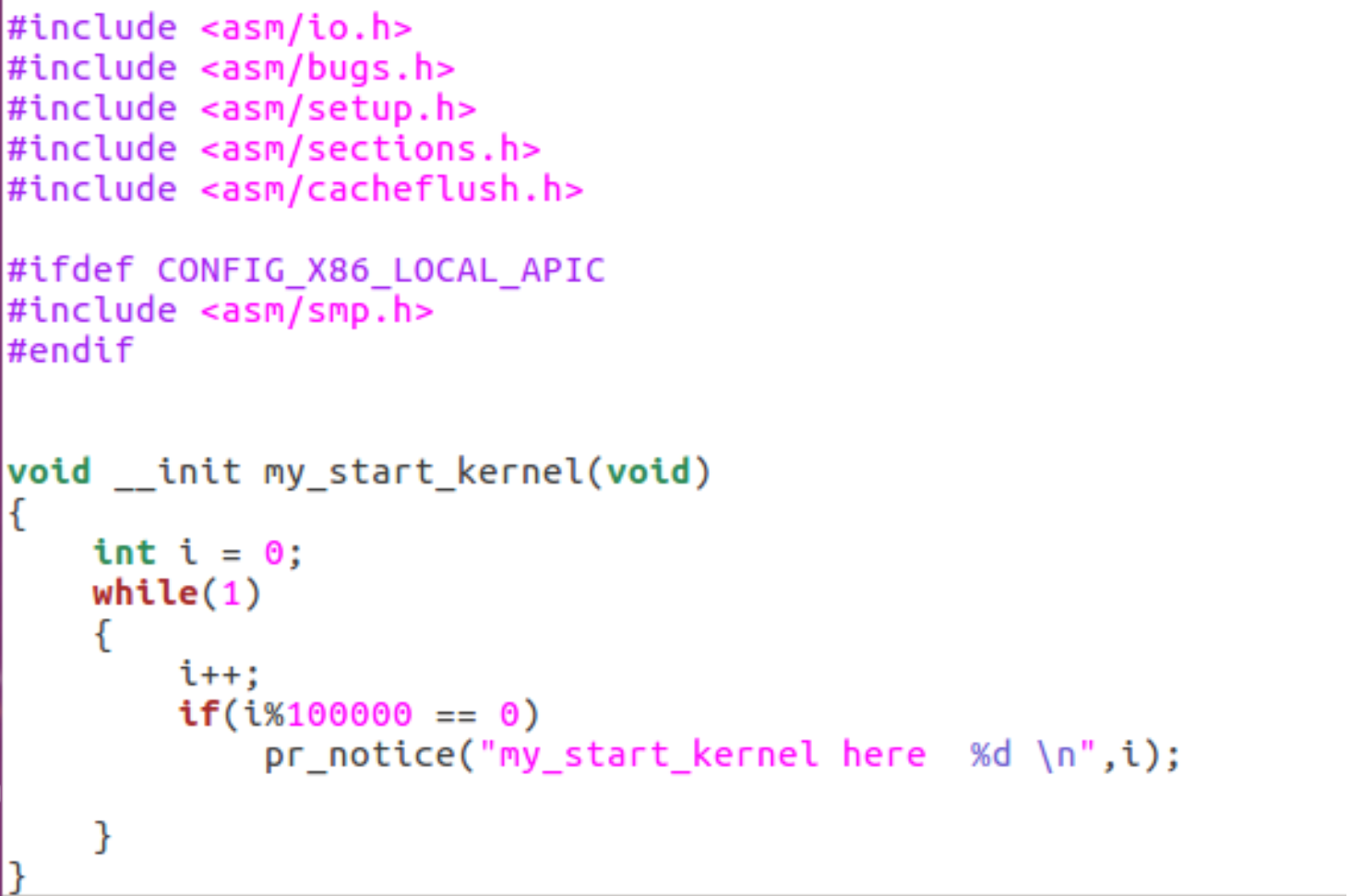
myinterrupt.c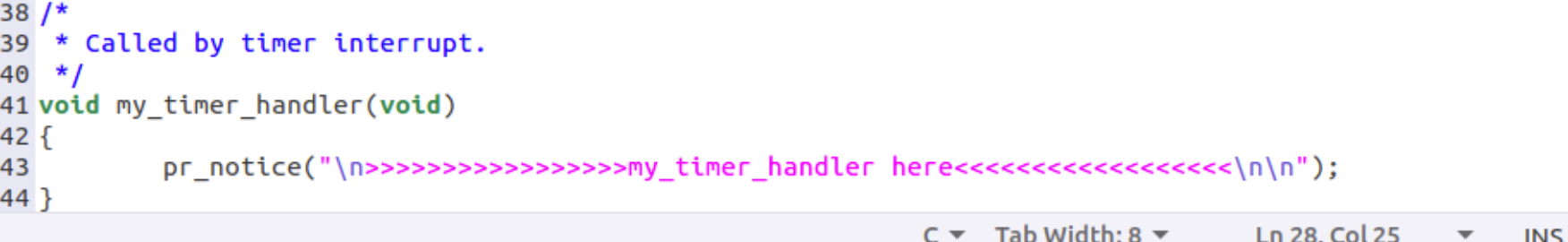
2、基于mykernel 2.0编写一个操作系统内核
首先编写mypcb.h文件,代码如下:
#define MAX_TASK_NUM 4
#define KERNEL_STACK_SIZE 1024*2
/* CPU-specific state of this task */
struct Thread {
unsigned long ip;
unsigned long sp;
};
typedef struct PCB{
int pid;
volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
unsigned long stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE];
/* CPU-specific state of this task */
struct Thread thread;
unsigned long task_entry;
struct PCB *next;
}tPCB;
void my_schedule(void);
接下来修改myinterrupt.c文件:
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include "mypcb.h"
extern tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
extern tPCB * my_current_task;
extern volatile int my_need_sched;
volatile int time_count = 0;
/*
* Called by timer interrupt.
* it runs in the name of current running process,
* so it use kernel stack of current running process
*/
void my_timer_handler(void)
{
if(time_count%1000 == 0 && my_need_sched != 1)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_timer_handler here<<<
");
my_need_sched = 1;
}
time_count ++ ;
return;
}
void my_schedule(void)
{
tPCB * next;
tPCB * prev;
if(my_current_task == NULL
|| my_current_task->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_schedule<<<
");
/* schedule */
next = my_current_task->next;
prev = my_current_task;
if(next->state == 0)/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
{
my_current_task = next;
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>switch %d to %d<<<
",prev->pid,next->pid);
/* switch to next process */
asm volatile(
"pushq %%rbp
" /* save rbp of prev */
"movq %%rsp,%0
" /* save rsp of prev */
"movq %2,%%rsp
" /* restore rsp of next */
"movq $1f,%1
" /* save rip of prev */
"pushq %3
"
"ret
" /* restore rip of next */
"1: " /* next process start here */
"popq %%rbp
"
: "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip)
: "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip)
);
}
return;
然后修改mymain.c文件:
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include "mypcb.h"
tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
tPCB * my_current_task = NULL;
volatile int my_need_sched = 0;
void my_process(void);
void __init my_start_kernel(void)
{
int pid = 0;
int i;
/* Initialize process 0*/
task[pid].pid = pid;
task[pid].state = 0;/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
task[pid].task_entry = task[pid].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process;
task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];
task[pid].next = &task[pid];
/*fork more process */
for(i=1;i<MAX_TASK_NUM;i++)
{
memcpy(&task[i],&task[0],sizeof(tPCB));
task[i].pid = i;
task[i].thread.sp = (unsigned long)(&task[i].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1]);
task[i].next = task[i-1].next;
task[i-1].next = &task[i];
}
/* start process 0 by task[0] */
pid = 0;
my_current_task = &task[pid];
asm volatile(
"movq %1,%%rsp
" /* set task[pid].thread.sp to rsp */
"pushq %1
" /* push rbp */
"pushq %0
" /* push task[pid].thread.ip */
"ret
" /* pop task[pid].thread.ip to rip */
:
: "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp) /* input c or d mean %ecx/%edx*/
);
}
int i = 0;
void my_process(void)
{
while(1)
{
i++;
if(i%10000000 == 0)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d -
",my_current_task->pid);
if(my_need_sched == 1)
{
my_need_sched = 0;
my_schedule();
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d +
",my_current_task->pid);
}
}
}
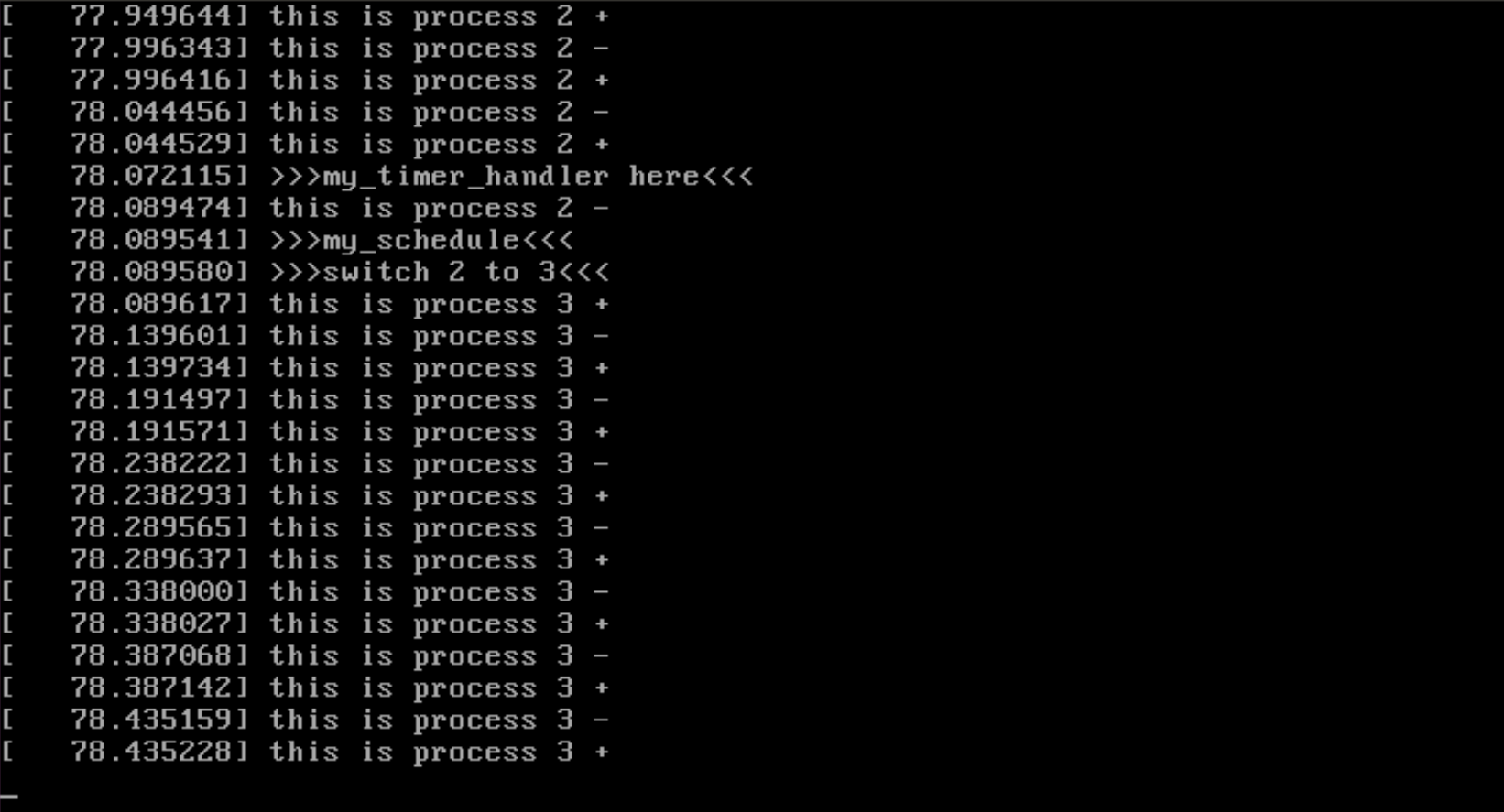
重新进行编译,并运行,如下:
make -j$(nproc)
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage
3. 简要分析操作系统内核核心功能及运行工作机制
asm volatile(
"movq %1,%%rsp
"
"pushq %1
"
"pushq %0
"
"ret
"
:
: "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp)
);
RSP寄存器指向原堆栈的栈顶,%1指后面的task[pid].thread.sp
压栈当前进程RBP寄存器
压栈当前进程RIP寄存器,%0指task[pid]. thread.ip
ret命令正好可以让压栈的进程RIP保存到RIP寄存器中
asm volatile(
"pushq %%rbp
"
"movq %%rsp,%0
"
"movq %2,%%rsp
"
"movq $1f,%1
"
"pushq %3
"
"ret
"
"1: "
"popq %%rbp
"
: "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip)
: "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip)
);
movq %%rsp,%0 保存prev进程(进程0)当前RSP寄存器的值到prev->thread.sp(%0)
movq %2,%%rsp 将next进程的栈顶地址next->thread.sp放⼊RSP寄存器,完成了进程0和进程1的堆栈切换
movq $1f,%1 保存prev进程当前RIP寄存器值到prev->thread.ip(%1),这⾥$1f是指标号1
pushq %3 把即将执⾏的next进程的指令地址next->thread.ip(%3)⼊栈
ret 将压⼊栈中的next->thread.ip放⼊RIP寄存器,程序jianjie直接使用RIP寄存器,通过ret间接改变
popq %%rbp 将next进程堆栈基地址从堆栈中恢复到RBP寄存器中