要了解程序的运行原理,就要先知道程序的进入点及生命周期。以往ASP.NET MVC的启动方式,是继承 HttpApplication 作为网站开始的进入点,而ASP.NET Core 改变了网站的启动方式,变得比较像是 Console Application。
本篇将介绍ASP.NET Core 的程序生命周期 (Application Lifetime) 及捕捉 Application 停止启动事件。
程序进入点
.NET Core 把 Web 及 Console 项目都处理成一样的启动方式,默认以 Program.cs 的 Program.Main 作为程序入口,再从程序入口把 ASP.NET Core 网站实例化。个人觉得比ASP.NET MVC 继承 HttpApplication 的方式简洁许多。
通过 .NET Core CLI 创建的 Program.cs 內容大致如下:
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
namespace MyWebsite
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BuildWebHost(args).Run();
}
public static IWebHost BuildWebHost(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.Build();
}
}
Program.Main 通过 BuildWebHost 方法取得 WebHost 后,再运行 WebHost;WebHost 就是 ASP.NET Core 的网站实例。
- WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder
通过此方法建立 WebHost Builder。WebHost Builder 是用來生成 WebHost 的对象。
可以在 WebHost 生成之前设置一些前置动作,当 WebHost 建立完成时,就可以使用已准备好的物件等。 - UseStartup
设置该 Builder 生成的 WebHost 启动后,要执行的类。 - Build
当前置准备都设置完成后,就可以调用 WebHost Builder 方法实例化 WebHost,并得到该实例。 - Run
启动 WebHost。
Startup.cs
当网站启动后,WebHost会实例化 UseStartup 设置的Startup类,并且调用以下两个方法:
- ConfigureServices
- Configure
通过 .NET Core CLI生成的Startup.cs 内容大致如下:
Startup.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace MyWebsite
{
public class Startup
{
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
// For more information on how to configure your application, visit https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=398940
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.Run(async (context) =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World!");
});
}
}
}
- ConfigureServices
ConfigureServices 是用来将服务注册到 DI 容器用的。这个方法可不实现,并不是必要的方法。 - Configure
这个是必要的方法,一定要实现。但Configure方法的参数并不固定,参数的实例都是从 WebHost 注入进来,可依需求增减需要的参数。 - IApplicationBuilder 是最重要的参数也是必要的参数,Request 进出的 Pipeline 都是通过 ApplicationBuilder 来设置。
对 WebHost 来说 Startup.cs 并不是必要存在的功能。
可以试着把 Startup.cs 中的两个方法,都改成在 WebHost Builder 设置,变成启动的前置准备。如下:
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace MyWebsite
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BuildWebHost(args).Run();
}
public static IWebHost BuildWebHost(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureServices(services =>
{
// ...
})
.Configure(app =>
{
app.Run(async (context) =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World!");
});
})
.Build();
}
}
把 ConfigureServices 及 Configure 都改到 WebHost Builder 注册,网站的执行结果是一样的。
两者之间最大的不同就是调用的时间点不同。
- 在 WebHost Builder 注册,是在 WebHost 实例化之前就调用。
- 在 Startup.cs 注册,是在 WebHost 实例化之后调用。
但
Configure无法使用除了IApplicationBuilder以外的参数。
因为在 WebHost 实例化前,自己都还没被实例化,怎么可能会有有对象能注入给Configure。
Application Lifetime
除了程序进入点外,WebHost的启动和停止也是网站事件很重要一环,ASP.NET Core不像ASP.NET MVC用继承的方式捕捉启动及停止事件,而是透过Startup.Configure注入IApplicationLifetime来补捉Application启动停止事件。
IApplicationLifetime有三个注册监听事件及终止网站事件可以触发。如下:
public interface IApplicationLifetime
{
CancellationToken ApplicationStarted { get; }
CancellationToken ApplicationStopping { get; }
CancellationToken ApplicationStopped { get; }
void StopApplication();
}
- ApplicationStarted
当WebHost启动完成后,会执行的启动完成事件。 - ApplicationStopping
当WebHost触发停止时,会执行的准备停止事件。 - ApplicationStopped
当WebHost停止事件完成时,会执行的停止完成事件。 - StopApplication
可以通过此方法主动触发终止网站。
示例
通过Console输出执行的过程,示例如下:
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace MyWebsite
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Output("Application - Start");
var webHost = BuildWebHost(args);
Output("Run WebHost");
webHost.Run();
Output("Application - End");
}
public static IWebHost BuildWebHost(string[] args)
{
Output("Create WebHost Builder");
var webHostBuilder = WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureServices(services =>
{
Output("webHostBuilder.ConfigureServices - Called");
})
.Configure(app =>
{
Output("webHostBuilder.Configure - Called");
})
.UseStartup<Startup>();
Output("Build WebHost");
var webHost = webHostBuilder.Build();
return webHost;
}
public static void Output(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine($"[{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss")}] {message}");
}
}
}
Startup.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace MyWebsite
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup()
{
Program.Output("Startup Constructor - Called");
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
// For more information on how to configure your application, visit https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=398940
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
Program.Output("Startup.ConfigureServices - Called");
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IApplicationLifetime appLifetime)
{
appLifetime.ApplicationStarted.Register(() =>
{
Program.Output("ApplicationLifetime - Started");
});
appLifetime.ApplicationStopping.Register(() =>
{
Program.Output("ApplicationLifetime - Stopping");
});
appLifetime.ApplicationStopped.Register(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(5 * 1000);
Program.Output("ApplicationLifetime - Stopped");
});
app.Run(async (context) =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World!");
});
// For trigger stop WebHost
var thread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(5 * 1000);
Program.Output("Trigger stop WebHost");
appLifetime.StopApplication();
}));
thread.Start();
Program.Output("Startup.Configure - Called");
}
}
}
执行结果
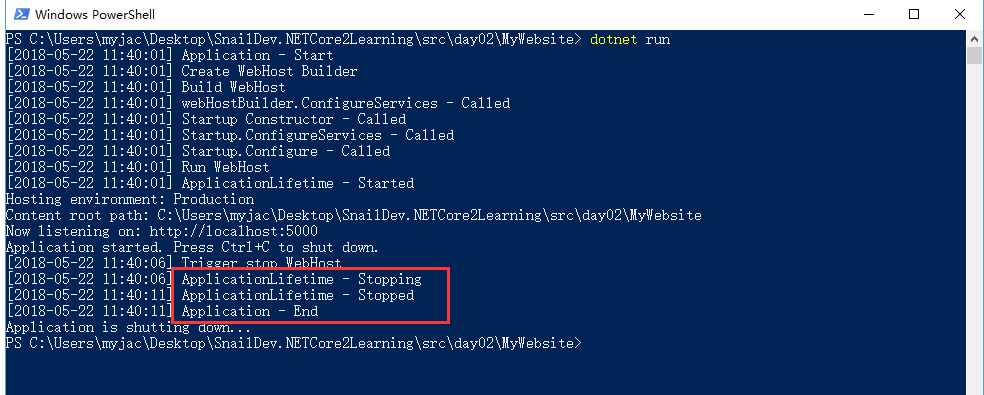
输出内容少了webHostBuilder.Configure - Called,因为Configure只能有一个,后注册的Configure会把之前注册的覆盖掉。
程序执行流程如下:
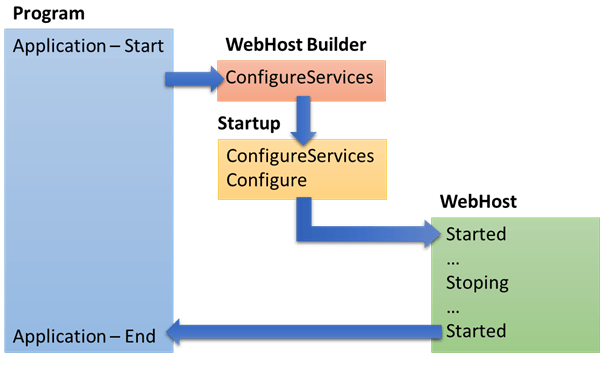
参考
Application startup in ASP.NET Core
Hosting in ASP.NET Core
老司机发车啦:https://github.com/SnailDev/SnailDev.NETCore2Learning