简介
一个节点最多有两颗子树的数据结构,通常称为左子树、右子树
分类
1、满二叉树
除了最后一层没有子节点之外,其余所有节点均有左右子树
2、完全二叉树
假设树的深度为K,前K-1层的节点数均达到最大值,并且第K层的所有节点均连续集中在左侧,这一类称为完全二叉树

3、二叉搜索树/二叉排序树
如果一颗二叉树所有左节点的值均小于根节点,并且所有右节点的值均不小于根节点,那么此类树称为二叉搜索树/二叉排序树;
中序遍历的时候,遍历的顺序为节点取值由小到大
4、平衡二叉树/AVL树
一颗空树或者左子树和右子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右子树均为AVL树
5、普通二叉树
二叉树的遍历
前序遍历:根节点->左子树->右子树
中序遍历:左子树->根节点->右子树
后序遍历:左子树->右子树->根节点
层次遍历:BFS --- 广度优先遍历
其中最重要的、应用最多的是中序遍历。
二叉树结构图:
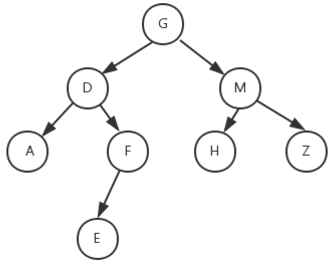
前序遍历(根->左->右)
重要的是:前序遍历要求根节点的遍历优先于左子树、左子树的遍历优先于右子树;
网上的各种总结五花八门,思想就是:对于每一个树结构,优先访问根节点,然后访问整个左子树,最后右子树
代码:
private static List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return resultList; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode curNode = stack.pop(); if (curNode != null) { resultList.add(curNode.val); if (curNode.right != null) { stack.push(curNode.right); } if (curNode.left != null) { stack.push(curNode.left); } } } return resultList; }
中序遍历
步骤:
1、遍历节点的左子树
2、判断该节点是否有左子树,如果有,执行第一步;否则打印该节点。
3、判断该节点是否有右子树,如果有,则执行第一步;否则返回到上一级节点。
代码:
private static List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); TreeNode cur = root; while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { if (cur != null) { stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; } else { cur = stack.pop(); resultList.add(cur.val); cur = cur.right; } } return resultList; }
后序遍历
private static List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return resultList; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode curNode = stack.pop(); if (curNode != null) { resultList.add(curNode.val); if (curNode.left != null) { stack.push(curNode.left); } if (curNode.right != null) { stack.push(curNode.right); } } } Collections.reverse(resultList); return resultList; }