一、java.util.HashSet
1.1 HashSet集成结构
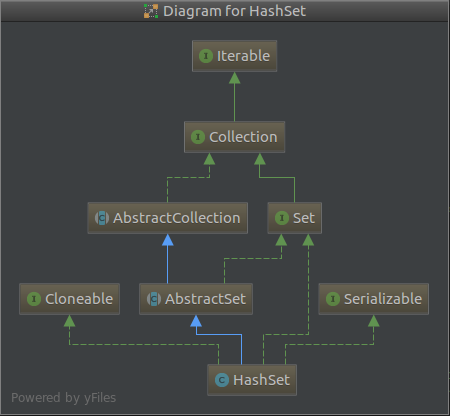
1.2 java.util.HashSet属性
1 private transient HashMap<E,Object> map; 2 3 // Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map 4 private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
HashSet的本质其实就是一个HashMap。Set集合一个重要的特性就是元素不重复,而HashMap本身就是符合这一特性的。
1 public Iterator<E> iterator() { 2 return map.keySet().iterator(); 3 }
集合的迭代器就是HashMap中keySet()的迭代器。
HashSet类需要理解的不多,看懂了HashMap这个类就没什么问题了。HashMap源码解析请参考:java.util.HashMap和java.util.HashTable (JDK1.8)
二、java.util.LinkedHashMap
2.1 LinkedHashMap继承结构
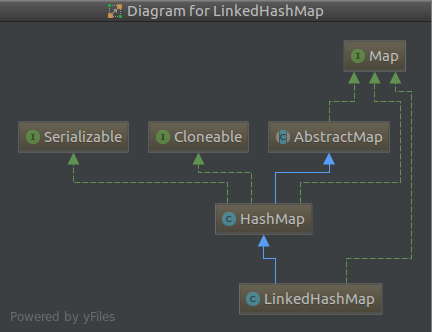
图中蓝色的为继承extend,虚线为implements
HashMap的本质是一个Node的数组,本质是个数组,数组可以根据下标去访问数组内容。HashMap的Map.Entry是无序的。
LinkedHashMap继承自HashMap,因此LinkedHashMap首先它是一个HashMap,其次它具备Node链表的属性。这个Node链表维护了Node插入顺序或者访问顺序。
2.2 LinkedHashMap属性
1 static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> { 2 // 包含前一节点和后一节点的引用,是个双向链表 3 Entry<K,V> before, after; 4 Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { 5 super(hash, key, value, next); 6 } 7 } 8 // 链表头节点,也是最老的节点 9 transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head; 10 // 链表尾节点,也是最年轻的节点 11 transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail; 12 // 访问顺序,true为访问顺序,false为插入顺序 13 final boolean accessOrder;
accessOrder默认为false,如果需要设置成true,LinkedhashMap提供了如下构造函数:
1 public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, 2 float loadFactor, 3 boolean accessOrder) { 4 super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); 5 this.accessOrder = accessOrder; 6 }
设置为false,则整个双向链表按照插入顺序进行排列;为true则按照访问顺序进行排列,当某个节点被get访问,则将该节点放置到链表最结尾(最结尾是最年轻的节点)。
访问顺序则是采用了LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法,其核心思想是“如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高”。
2.3 LinkedHashMap方法
1 // 将src的相关引用全部复制给dst节点 2 private void transferLinks(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> src, 3 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> dst) { 4 // 修改节点自身的before和after引用 5 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> b = dst.before = src.before; 6 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> a = dst.after = src.after; 7 // 修改前后节点的引用 8 if (b == null) 9 head = dst; 10 else 11 b.after = dst; 12 if (a == null) 13 tail = dst; 14 else 15 a.before = dst; 16 }
这个方法是替换节点的核心,新的节点接替旧的节点的所有引用关系,旧的节点无法被引用最终会被GC回收。
1 // 删除节点操作 2 void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e) { // unlink 3 // 保存当前节点及其前后节点 4 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = 5 (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after; 6 // 从链表中去除掉该节点,主要是去除对该节点的引用 7 // 将该节点对链表其它节点的引用也去掉 8 p.before = p.after = null; 9 if (b == null) 10 head = a; 11 else 12 b.after = a; 13 if (a == null) 14 tail = b; 15 else 16 a.before = b; 17 } 18 19 void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last 20 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last; 21 // 如果按照访问顺序,则需要将被访问节点至于链表最结尾处 22 if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) { 23 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = 24 (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after; 25 p.after = null; 26 if (b == null) 27 head = a; 28 else 29 b.after = a; 30 if (a != null) 31 a.before = b; 32 else 33 last = b; 34 if (last == null) 35 head = p; 36 else { 37 p.before = last; 38 last.after = p; 39 } 40 tail = p; 41 ++modCount; 42 } 43 } 44 45 void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest 46 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first; 47 // removeEldestEntry(first) 默认返回false,如果需要可以继承LinkedHashMap,覆盖该函数。 48 // removeEldestEntry(first) 如果返回true,则在put的时候会删除链表头结点 49 if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) { 50 K key = first.key; 51 removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true); 52 } 53 }
上面三个方法在HashMap中也是存在的,不过方法体为空,LinkedHashMap覆盖了该方法。在HashMap的put、get、remove方法中
LinkedHashMap并没有重新实现put、get、remove、clear方法,仍然是采用HashMap的实现方式,不同的是afterNodeRemoval、afterNodeAccess、afterNodeInsertion已经不再是空的方法体了。
在LinkedHashMap, LinkedKeySet, LinkedValueSet, LinkedEntrySet类中的forEach方法以及都是遍历链表的,因此可以按照插入顺序(或访问顺序)去遍历LinkedHashMap,从而解决了HashMap无序问题。
三、java.util.IndentifyHashMap
3.1 IndentifyHashMap继承结构
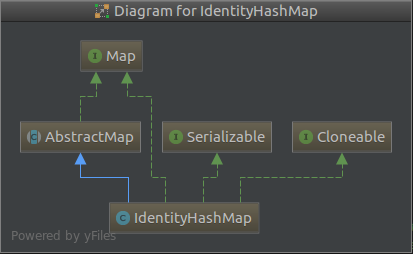
IdentityHashMap虽然冠以HashMap之名,却不是HashMap的子类,它是继承自AbstractHashMap。
IdentityHashMap比较两个key是否相等,并不是采用内容比较,而是直接进行==比较,比较两个key是否为同一个对象。
3.2 IdentityHashMap属性
1 transient Object[] table; // non-private to simplify nested class access 2 int size; 3 transient int modCount; 4 static final Object NULL_KEY = new Object();
identityHashMap是一个Object数组,size表示当前Map存入的数据总数,modCount表示修改次数。
IdentityHashMap允许使用NULL作为key,如下代码所示,如果key为null,则存入预先定义的NULL_KEY对象。
1 private static Object maskNull(Object key) { 2 return (key == null ? NULL_KEY : key); 3 } 4 5 static final Object unmaskNull(Object key) { 6 return (key == NULL_KEY ? null : key); 7 }
3.3 IdentityHashMap方法
1 private static int nextKeyIndex(int i, int len) { 2 return (i + 2 < len ? i + 2 : 0); 3 }
这个方法在IdentityHashMap中频繁用到,作用是寻找下一个index以解决hash碰撞问题,下一个index获取也是按照非常简单的(i+2 < len ? i+2 : 0)。
HashMap采用链表和红黑树避免hash碰撞问题,而在IdentityHashMap中则是采用开放定址法,而且采用的是最简单的线性探测法。
我们先来看下最hash算法
1 private static int hash(Object x, int length) { 2 int h = System.identityHashCode(x); 3 // Multiply by -127, and left-shift to use least bit as part of hash 4 return ((h << 1) - (h << 8)) & (length - 1); 5 }
无论x对象所属的类是否重新实现了hashCode()方法,System.identityHashCode(x) 都将返回默认的hashCode()结果,所谓默认的hashCode()就是指Object类中的hashCode()方法。Object类中的hashCode()可以为不同的对象返回不同的结果,根据Java doc中的描述,这是根据对象的内存地址来计算hash结果的。System.identityHashCode(x) 在x为null时返回0。
hash方法在通过System.identityHashCode方法获得hash code之后,再通过移位和与运算计算index。因为采用System.identityHashCode方法获取hash code,因此不同的对象hash code是不同的。
1 public V put(K key, V value) { 2 final Object k = maskNull(key); 3 4 retryAfterResize: for (;;) { 5 final Object[] tab = table; 6 final int len = tab.length; 7 // 计算下标 8 int i = hash(k, len); 9 10 // 遍历所有可能的位置,直到找到一个空位 11 for (Object item; (item = tab[i]) != null; 12 i = nextKeyIndex(i, len)) { 13 // 待插入的key已经存在,替换value 14 if (item == k) { 15 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 16 V oldValue = (V) tab[i + 1]; 17 tab[i + 1] = value; 18 return oldValue; 19 } 20 } 21 22 // 新加一个节点如果size > len/3则需要扩容 23 final int s = size + 1; 24 // Use optimized form of 3 * s. 25 // Next capacity is len, 2 * current capacity. 26 if (s + (s << 1) > len && resize(len)) 27 // 扩容后待插入的节点需要重新查找位置 28 continue retryAfterResize; 29 30 // 修改次数加一 31 modCount++; 32 // 在下标i存放key,在i+1下标存放value 33 tab[i] = k; 34 tab[i + 1] = value; 35 size = s; 36 return null; 37 } 38 }
在put方法中,判断两个key是否相等,是直接使用“==”的,也就是说不同对象就会被当做不同的key处理。
其次在存放的时候i存放key,i+1存放value,这也就能解释查找下一个空位方法nextKeyIndex中使用i+2的原因了。
从put方法中还能看出扩容条件为size > len/3,也就是说IdentityHashMap最多只能使用总capacity的1/3。相对于HashMap默认的loadFactor=0.75,IdentityHashMap的使用率还是非常低的。
接下来看下resize方法
1 private boolean resize(int newCapacity) { 2 // assert (newCapacity & -newCapacity) == newCapacity; // power of 2 3 // 直接扩容为之前的2倍 4 int newLength = newCapacity * 2; 5 6 Object[] oldTable = table; 7 int oldLength = oldTable.length; 8 if (oldLength == 2 * MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { // can't expand any further 9 if (size == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY - 1) 10 throw new IllegalStateException("Capacity exhausted."); 11 return false; 12 } 13 if (oldLength >= newLength) 14 return false; 15 // 重新new一个新的数组出来,简单粗暴! 16 Object[] newTable = new Object[newLength]; 17 18 for (int j = 0; j < oldLength; j += 2) { 19 Object key = oldTable[j]; 20 if (key != null) { 21 Object value = oldTable[j+1]; 22 // 将原数组上的key value清空,不清空将会导致内存无法被释放 23 oldTable[j] = null; 24 oldTable[j+1] = null; 25 // key重新hash 26 int i = hash(key, newLength); 27 while (newTable[i] != null) 28 // hash冲突了就查找下一个位置 29 i = nextKeyIndex(i, newLength); 30 newTable[i] = key; 31 newTable[i + 1] = value; 32 } 33 } 34 table = newTable; 35 return true; 36 }
resize方法真的是简单粗暴,直接double capacity,然后将旧的table中的数据hash到新的table中。
1 public V get(Object key) { 2 Object k = maskNull(key); 3 Object[] tab = table; 4 int len = tab.length; 5 // 根据key计算下标 6 int i = hash(k, len); 7 while (true) { 8 Object item = tab[i]; 9 if (item == k) 10 return (V) tab[i + 1]; 11 if (item == null) 12 return null; 13 // 查找下一个位置 14 i = nextKeyIndex(i, len); 15 } 16 }
get方法和containsKey方法方法体相同,其实现思路也就是遍历数组,如果插到一个空位置,则说明不存在该key。
1 public V remove(Object key) { 2 Object k = maskNull(key); 3 Object[] tab = table; 4 int len = tab.length; 5 int i = hash(k, len); 6 7 while (true) { 8 Object item = tab[i]; 9 // 查找到该key 10 if (item == k) { 11 modCount++; 12 size--; 13 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 14 V oldValue = (V) tab[i + 1]; 15 // 相应位置置空 16 tab[i + 1] = null; 17 tab[i] = null; 18 // 直接置空会导致查找出现问题 19 closeDeletion(i); 20 return oldValue; 21 } 22 // 没有找到该key 23 if (item == null) 24 return null; 25 i = nextKeyIndex(i, len); 26 } 27 }
因为IdentityHashMap是以开放定址法解决hash冲突的,直接将数组某个地方设置为null,势必会导致查找出问题。为此需要调用closeDeletion方法来解决这一问题。
1 private void closeDeletion(int d) { 2 // Adapted from Knuth Section 6.4 Algorithm R 3 Object[] tab = table; 4 int len = tab.length; 5 6 Object item; 7 for (int i = nextKeyIndex(d, len); (item = tab[i]) != null; 8 i = nextKeyIndex(i, len) ) { 9 int r = hash(item, len); 10 // 将后面的因为hash碰撞而存放的元素往前移 11 if ((i < r && (r <= d || d <= i)) || (r <= d && d <= i)) { 12 // 将后面的元素往前移位 13 tab[d] = item; 14 tab[d + 1] = tab[i + 1]; 15 tab[i] = null; 16 tab[i + 1] = null; 17 d = i; 18 } 19 } 20 }
closeDeletion方法其思路就是对空置出来的位置d后面的元素进行hash判断,如果之前是因为hash碰撞存放在d后面的,则直接往前移,将这个空置的d位置给覆盖掉。在这个过程中要注意table数组是个环形的。
整体感觉IdentityHashMap实现非常的简单粗暴,优化较少,可能是因为使用较少的原因。