单位IM改版了
用户聊天内容要存放在数据库.
一般JAVA Insert MySQL有如下几种方式
1.自动提交Insert
2.事务提交Insert
3.批量提交
4.使用Load File接口
模拟表结构如下
- create table chat_message(
- id bigint primary key auto_increment,
- src_userid bigint not null,
- target_userid bigint not null,
- message varchar(200),
- ts timestamp not null default current_timestamp,
- s1 int,
- s2 int,
- s3 int,
- s4 int
- );
下面代码,分别使用四种方式,Insert 2w记录.记录执行时间.
依赖
commons-lang3-3.3.2.jar
mysql-connector-java-5.1.31-bin.jar(低版本驱动有性能影响)
- import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
- import java.io.InputStream;
- import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
- import java.sql.Connection;
- import java.sql.DriverManager;
- import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
- import java.sql.SQLException;
- import org.apache.commons.lang3.RandomStringUtils;
- public class Main {
- private static String URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mvbox";
- private static String USERNAME = "xx";
- private static String PWD = "xx";
- private static int MAX = 20000;
- private static String SQL = "insert into chat_message(src_userid,target_userid,message,s1,s2,s3,s4) values(?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
- public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
- long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
- testLoadFile(100);
- long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
- System.out.println((end - start));
- System.out.println(MAX / ((end - start) / 1000));
- }
- private static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
- Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
- Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PWD);
- return con;
- }
- private static void testInsert() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
- Connection con = getConnection();
- con.setAutoCommit(false);
- PreparedStatement pt = con.prepareStatement(SQL);
- int i = 0;
- while (i < MAX) {
- pt.setLong(1, 1 + (int) (Math.random() * 100000000));
- pt.setLong(2, 1 + (int) (Math.random() * 100000000));
- pt.setString(3, RandomStringUtils.randomAscii(200));
- pt.setInt(4, 1);
- pt.setInt(5, 1);
- pt.setInt(6, 1);
- pt.setInt(7, 1);
- pt.executeUpdate();
- con.commit();
- i++;
- }
- con.close();
- }
- private static void testInsertAutoCommit() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
- Connection con = getConnection();
- con.setAutoCommit(true);
- PreparedStatement pt = con.prepareStatement(SQL);
- int i = 0;
- while (i < MAX) {
- pt.setLong(1, 1 + (int) (Math.random() * 100000000));
- pt.setLong(2, 1 + (int) (Math.random() * 100000000));
- pt.setString(3, RandomStringUtils.randomAscii(200));
- pt.setInt(4, 1);
- pt.setInt(5, 1);
- pt.setInt(6, 1);
- pt.setInt(7, 1);
- pt.executeUpdate();
- i++;
- }
- con.close();
- }
- private static void testBatchInsert(int batchSize) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
- Connection con = getConnection();
- con.setAutoCommit(false);
- PreparedStatement pt = con.prepareStatement(SQL);
- int i = 0;
- while (i < MAX) {
- pt.setLong(1, 1 + (int) (Math.random() * 100000000));
- pt.setLong(2, 1 + (int) (Math.random() * 100000000));
- pt.setString(3, RandomStringUtils.randomAscii(200));
- pt.setInt(4, 1);
- pt.setInt(5, 1);
- pt.setInt(6, 1);
- pt.setInt(7, 1);
- pt.addBatch();
- if (i % batchSize == 1) {
- pt.executeBatch();
- con.commit();
- }
- i++;
- }
- pt.executeBatch();
- con.commit();
- con.close();
- }
- private static void testLoadFile(int batchSize)
- throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
- String fieldsterminated = " ";
- String linesterminated = " ";
- String loadDataSql = "LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE 'sql.csv' INTO TABLE chat_message FIELDS TERMINATED BY '"
- + fieldsterminated + "' LINES TERMINATED BY '" + linesterminated
- + "' (src_userid,target_userid,message,s1,s2,s3,s4) ";
- Connection con = getConnection();
- con.setAutoCommit(false);
- PreparedStatement pt = con.prepareStatement(loadDataSql);
- com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement mysqlStatement = null;
- if (pt.isWrapperFor(com.mysql.jdbc.Statement.class)) {
- mysqlStatement = pt.unwrap(com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement.class);
- }
- int i = 0;
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(10000);
- while (i < MAX) {
- sb.append(1 + (int) (Math.random() * 100000000));
- sb.append(fieldsterminated);
- sb.append(1 + (int) (Math.random() * 100000000));
- sb.append(fieldsterminated);
- sb.append(RandomStringUtils.randomAscii(200).replaceAll("\\", " "));
- sb.append(fieldsterminated);
- sb.append(1);
- sb.append(fieldsterminated);
- sb.append(1);
- sb.append(fieldsterminated);
- sb.append(1);
- sb.append(fieldsterminated);
- sb.append(1);
- sb.append(linesterminated);
- if (i % batchSize == 1) {
- byte[] bytes = sb.toString().getBytes();
- InputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
- mysqlStatement.setLocalInfileInputStream(in);
- mysqlStatement.executeUpdate();
- con.commit();
- sb = new StringBuilder(10000);
- }
- i++;
- }
- byte[] bytes = sb.toString().getBytes();
- InputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
- mysqlStatement.setLocalInfileInputStream(in);
- mysqlStatement.executeUpdate();
- con.commit();
- con.close();
- }
- }
测试结果:
| 执行方式 | 执行时间(毫秒) | 每秒Insert数量 |
| 自动提交 | 17437 | 1176 |
| 事务提交 | 22990 | 909 |
| batchInsert 每10条提交 | 12646 | 1666 |
| batchInsert 每50条提交 | 13758 | 1538 |
| batchInsert 每100条提交 | 15870 | 1333 |
| loadfile 每10条提交 | 6973 | 3333 |
| loadfile 每50条提交 | 5037 | 4000 |
| loadfile 每100条提交 | 4175 | 5000 |
http://blog.itpub.net/29254281/viewspace-1841299/
一、我们遇到了什么问题
在标准SQL里面,我们通常会写下如下的SQL insert语句。
|
1
|
INSERT INTO TBL_TEST (id) VALUES(1); |
很显然,在MYSQL中,这样的方式也是可行的。但是当我们需要批量插入数据的时候,这样的语句却会出现性能问题。例如说,如果有需要插入100000条数据,那么就需要有100000条insert语句,每一句都需要提交到关系引擎那里去解析,优化,然后才能够到达存储引擎做真的插入工作。
正是由于性能的瓶颈问题,MYSQL官方文档也就提到了使用批量化插入的方式,也就是在一句INSERT语句里面插入多个值。即,
|
1
|
INSERT INTO TBL_TEST (id) VALUES (1), (2), (3) |
这样的做法确实也可以起到加速批量插入的功效,原因也不难理解,由于提交到服务器的INSERT语句少了,网络负载少了,最主要的是解析和优化的时间看似增多,但是实际上作用的数据行却实打实地多了。所以整体性能得以提高。根据网上的一些说法,这种方法可以提高几十倍。
然而,我在网上也看到过另外的几种方法,比如说预处理SQL,比如说批量提交。那么这些方法的性能到底如何?本文就会对这些方法做一个比较。
二、比较环境和方法
我的环境比较苦逼,基本上就是一个落后的虚拟机。只有2核,内存为6G。操作系统是SUSI Linux,MYSQL版本是5.6.15。
可以想见,这个机子的性能导致了我的TPS一定非常低,所以下面的所有数据都是没有意义的,但是趋势却不同,它可以看出整个插入的性能走向。
由于业务特点,我们所使用的表非常大,共有195个字段,且写满(每个字段全部填满,包括varchar)大致会有略小于4KB的大小,而通常来说,一条记录的大小也有3KB。
由于根据我们的实际经验,我们很肯定的是,通过在一个事务中提交大量INSERT语句可以大幅度提高性能。所以下面的所有测试都是建立在每插入5000条记录提交一次的做法之上。
最后需要说明的是,下面所有的测试都是通过使用MYSQL C API进行的,并且使用的是INNODB存储引擎。
三、比较方法
理想型测试(一)——方法比较
目的:找出理想情况下最合适的插入机制
关键方法:
1. 每个进/线程按主键顺序插入
2. 比较不同的插入方法
3. 比较不同进/线程数量对插入的影响
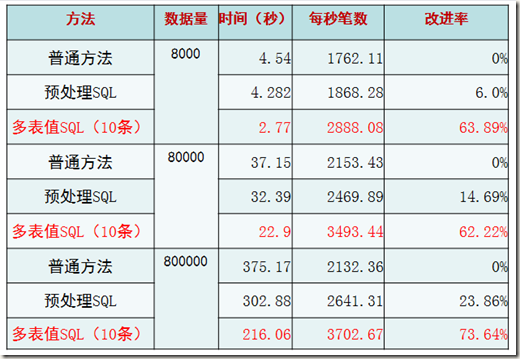
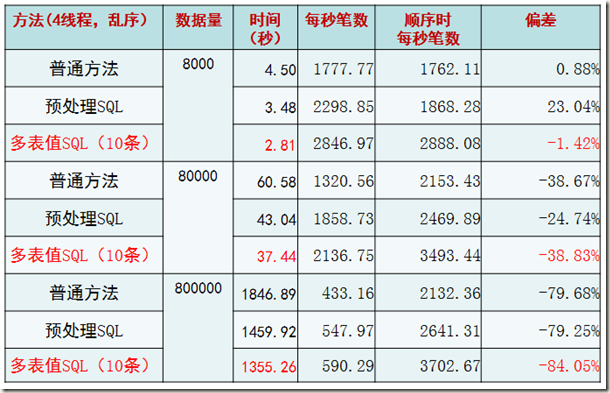
*“普通方法”指的是一句INSERT只插入一个VALUE的情况。
*“预处理SQL”指的是使用预处理MYSQL C API的情况。
* “多表值SQL(10条)”是使用一句INSERT语句插入10条记录的情况。为什么是10条?后面的验证告诉了我们这样做性能最高。
结论,很显然,从三种方法的趋势上来看,多表值SQL(10条)的方式最为高效。
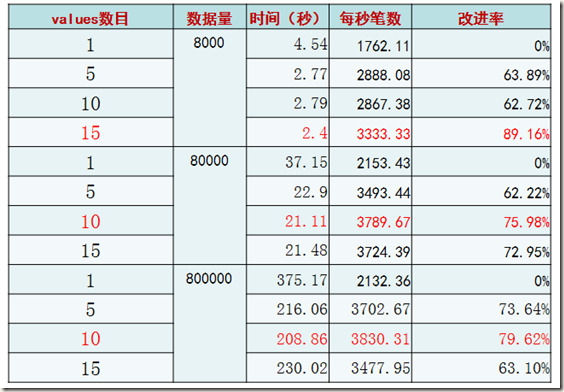
理想型测试(二)——多表值SQL条数比较
很显然,在数据量提高的情况下,每条INSERT语句插入10条记录的做法最为高效。
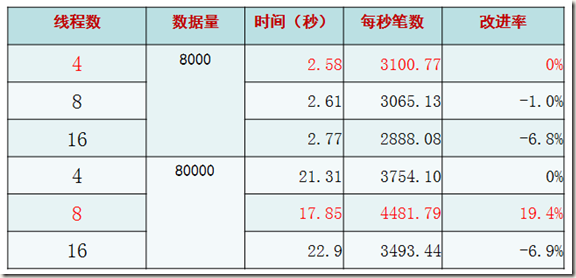
理想型测试(三)——连接数比较
结论:在2倍与CPU核数的连接和操作的时候,性能最高
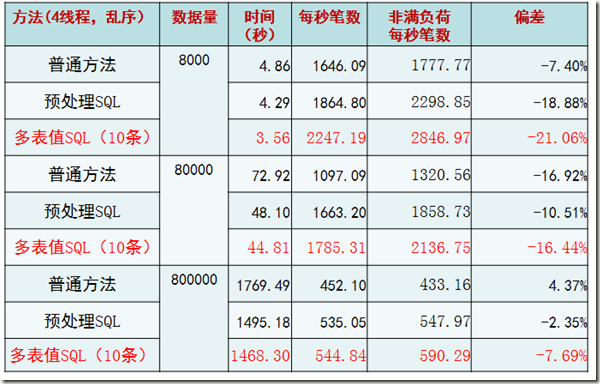
一般性测试—— 根据我们的业务量进行测试
目的:最佳插入机制适合普通交易情况?
关键方法:
1. 模拟生产数据(每条记录约3KB)
2. 每个线程主键乱序插入
很显然,如果是根据主键乱序插入的话,性能会有直线下降的情况。这一点其实和INNODB的内部实现原理所展现出来的现象一致。但是仍然可以肯定的是,多表值SQL(10条)的情况是最佳的。
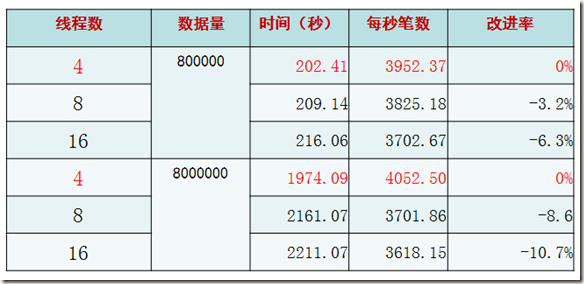
压力测试
目的:最佳插入机制适合极端交易情况?
关键方法:
1. 将数据行的每一个字段填满(每条记录约为4KB)
2. 每个线程主键乱序插入
结果和我们之前的规律类似,性能出现了极端下降。并且这里验证了随着记录的增大(可能已经超过了一个page的大小,毕竟还有slot和page head信息占据空间),会有page split等现象,性能会下降。
四、结论
根据上面的测试,以及我们对INNODB的了解,我们可以得到如下的结论。
•采用顺序主键策略(例如自增主键,或者修改业务逻辑,让插入的记录尽可能顺序主键)
•采用多值表(10条)插入方式最为合适
•将进程/线程数控制在2倍CPU数目相对合适
http://www.cnblogs.com/aicro/p/3851434.html