事务基础:请参看:http://www.cnblogs.com/solverpeng/p/5720306.html
一、Spring 事务管理
1.前提:事务管理器
在使用 Spring 声明式事务管理策略之前,必须配置事务管理器。
Spring 的核心事务管理器的顶级接口是 PlatformTransactionManager。
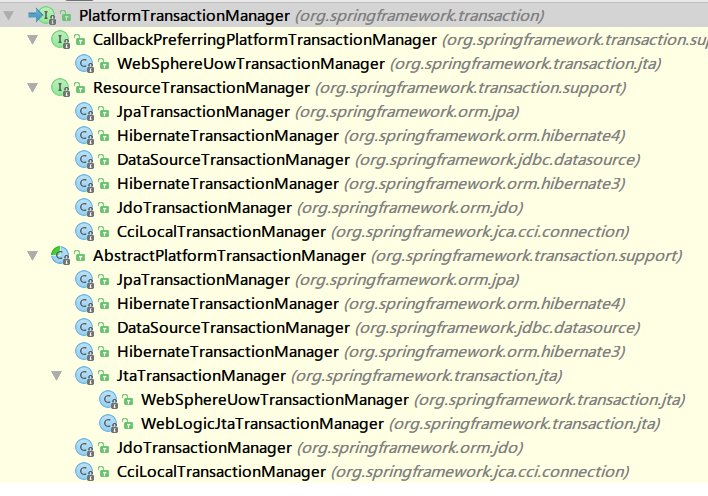
DataSourceTransactionManager:在应用程序中只需要处理一个数据源,而且通过 JDBC 进行存取。
HibernateTransactionManager:用 Hibernate 框架存取数据。
事务管理器以普通 Bean 的形式生命在 Spring IOC 容器中。如:
<context:property-placeholder location="db.properties"/> <bean class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" id="dataSource"> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"/> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.DriverClass}"/> </bean> <bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="transactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean>
2.XML声明式事务管理:Spring 通过 SpringAOP 框架支持声明式事务。
(1)事务管理是一个横切关注点。
(2)具体操作:
<1>在 <beans> 根元素中添加 tx Schema 的约束。可以通过 tx Schema 中定义的 <tx:advice> 元素声明事务增强。
<tx:advice transaction-manager="transactionManager" id="txAdvice"/>
<2>将增强配置到相应的 Spring AOP 切面。
<aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="bookPointcut" expression="execution(* *.BookServiceImpl.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="bookPointcut"/> </aop:config>
需要注意的是:只有公有的方法才可以添加增强。
3.注解声明式的管理事务:Spring 通过 @Transacational 注解声明式地管理事务
(1)Spring 允许使用 @Transacational 注解来标注事务方法。只能标注公有方法。
(2)可以在方法或类级别添加 @Transactional 注解。当添加到类上时,这个类的所有公有方法都会被定义成支持事务处理的。
(3)Spring Config 文件中的配置:
<1>只需要添加 <tx:annotation-driven/> 节点,并为其指定事务管理器就好了。
<2>指定事务管理器:若事务管理器名称是 transacationManager,就可以在 <tx:annotation-driven/> 节点中省略 transaction-manager 属性。
该元素会自动检测该名称的事务管理器。
<context:property-placeholder location="db.properties"/> <bean class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" id="dataSource"> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"/> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.DriverClass}"/> </bean> <bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="transactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <tx:annotation-driven/>
二、Spring 事务传播行为
1.JDBC 提供了事务隔离级别这种解决方案,Spring 对其进行了补充和扩展,就是 事务的传播行为。
2.Spring 提供了七种事务传播行为:
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED、PROPAGATION_REQUIRED_NEW、PROPAGATION_NESTED、PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS、PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED、PROPAGATION_NEVER、PROPAGATION_MANDATORY
我自己理解的 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 和 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED_NEW :
方法 A 调用方法 B:
(1)如果 A 是一个事务方法,B 也是一个事务方法,那么 B 应该使用自己的事务还是 A 的事务?
如果使用 A 的事务 —— PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
如果使用 B 自己的事务 —— PROPAGATION_REQUIRED_NEW
举个例子来说明:
一个事务:A、B两位同学去饭馆吃饭
中午放学后,A 同学去饭馆吃饭,恰巧刚刚认识的 B 同学也在饭馆吃饭,A 同学是该自己吃呢?还是和 B 同学一起吃呢?
如果是和 B 一起 —— PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
如果是 A 自己吃 —— PROPAGATION_REQUIRED_NEW
(2)如果 A 是一个事务方法,B 不是一个事务方法,那么 B 会使用 A 的事务。
提示:PROPAGATION 意思是 传播
*上面是我自己的理解,没有将所有的情况覆盖,可能自己理解的也有偏差,看到此处的时候请小心求证。
(3)Spring 默认的事务传播行为为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
三、Spring 事务其他功能
除了强大的事务传播行为外,Spring 还提供了一些小的附加功能
1.事务超时——为了解决事务时间太长,消耗资源太多的问题,给事务设置一个最大时长,如果超时,则回滚事务。以 秒为单位。
2.只读事务——表示这个事务只读取数据而不更新数据
3.设置事务的回滚属性
默认情况下只检查运行时异常,会导致事务回滚。可以通过 rollbackFor 属性来定义,如果不止一种,可以通过 "," 进行分割。
不论是事务的传播行为还是事务的超时和只读属性,Spring 在 @Transactional 注解中提供了对应的属性。
也可以通过 XML 的方式去配置,如
<tx:advice transaction-manager="transactionManager" id="bookAdvice"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="shop" propagation="REQUIRED"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice>
四、Spring 事务处理时,自我调用事务不生效。
问题描述:
@Service public class PersonService { @Autowired private PersonDao personDao; @Transactional public void outter() { for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { this.inner(i); } } @Transactional(propagation= Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW) public void inner(int index) { personDao.insert(index); if(index==3){ int ii = 0; ii = 1/0; System.out.println(ii); } } }
Spring Config 文件
<context:component-scan base-package="com.nucsoft.spring"/> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/> <bean class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" id="dataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"/> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="transactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <tx:annotation-driven/>
测试:
@Test public void testSupport() { PersonService bean = context.getBean(PersonService.class); bean.outter(); }
结果:不论是将inner() 方法的 propagation 改为 Propagation.REQUIRED 还是 Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW,数据库中都没有插入数据。
分析:
因为 Spring 的事务管理是基于动态代理的,如果 target 中的方法不是被代理对象调用的,那么就不会织入切面代码,即事务不会生效。
对于上面的例子,在 outter() 方法中调用 inner() 方法的 this 是 PersonService 类对象。而不是 PersonService 的代理对象。
解决方案:
使用代理对象调用 inner() 方法。
具体做法:
(1)在 Spring Config 文件中添加如下配置:
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy expose-proxy="true"/>
说明:是否允许暴露代理对象。expose-proxy就是向ThreadLocal中存代理对象。
(2)手动的暴露代理对象。
@Transactional public void outter() { for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { ((PersonService) AopContext.currentProxy()).inner(i); } } @Transactional(propagation= Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW) public void inner(int index) { personDao.insert(index); if(index==3){ int ii = 0; ii = 1/0; System.out.println(ii); } }
说明:AopContext.currentProxy就是从ThreadLocal中取出代理对象。
参考的文章: