对一般小公司来说 可能yarn调度能力足够了 但是对于大规模集群1000 or 2000+的话 yarn的调度性能捉襟见肘
恰好网上看到一篇很好的文章https://tech.meituan.com/2019/08/01/hadoop-yarn-scheduling-performance-optimization-practice.html
参考了YARN-5969 发现hadoop2.9.0已经修正了该issue 实测提高了调度性能
FairScheduler 调度方式有两种
心跳调度:Yarn的NodeManager会通过心跳的方式定期向ResourceManager汇报自身状态 伴随着这次rpc请求 会触发Resourcemanager 触发nodeUpdate()方法 为这个节点进行一次资源调度
持续调度:有一个固定守护线程每隔很短的时间调度 实时的资源分配,与NodeManager的心跳出发的调度相互异步并行进行
- 每次dataNode 发来心跳 时候作为一个event走下面方法
FairScheduler 类
@Override public void handle(SchedulerEvent event) { switch (event.getType()) { case NODE_ADDED: if (!(event instanceof NodeAddedSchedulerEvent)) { throw new RuntimeException("Unexpected event type: " + event); } NodeAddedSchedulerEvent nodeAddedEvent = (NodeAddedSchedulerEvent)event; addNode(nodeAddedEvent.getContainerReports(), nodeAddedEvent.getAddedRMNode()); break; case NODE_REMOVED: if (!(event instanceof NodeRemovedSchedulerEvent)) { throw new RuntimeException("Unexpected event type: " + event); } NodeRemovedSchedulerEvent nodeRemovedEvent = (NodeRemovedSchedulerEvent)event; removeNode(nodeRemovedEvent.getRemovedRMNode()); break; case NODE_UPDATE: if (!(event instanceof NodeUpdateSchedulerEvent)) { throw new RuntimeException("Unexpected event type: " + event); } NodeUpdateSchedulerEvent nodeUpdatedEvent = (NodeUpdateSchedulerEvent)event; nodeUpdate(nodeUpdatedEvent.getRMNode()); break; case APP_ADDED: if (!(event instanceof AppAddedSchedulerEvent)) { throw new RuntimeException("Unexpected event type: " + event); } AppAddedSchedulerEvent appAddedEvent = (AppAddedSchedulerEvent) event;
每次nodeUpdate 走的都是相同的逻辑
attemptScheduling(node) 持续调度跟心跳调度都走该方法
// If the node is decommissioning, send an update to have the total // resource equal to the used resource, so no available resource to // schedule. if (nm.getState() == NodeState.DECOMMISSIONING) { this.rmContext .getDispatcher() .getEventHandler() .handle( new RMNodeResourceUpdateEvent(nm.getNodeID(), ResourceOption .newInstance(getSchedulerNode(nm.getNodeID()) .getUsedResource(), 0))); } if (continuousSchedulingEnabled) { if (!completedContainers.isEmpty()) { //持续调度开启时 attemptScheduling(node); } } else { attemptScheduling(node); //心跳调度 } // Updating node resource utilization node.setAggregatedContainersUtilization( nm.getAggregatedContainersUtilization()); node.setNodeUtilization(nm.getNodeUtilization());
持续调度是一个单独的守护线程
间隔getContinuousSchedulingSleepMs()时间运行一次continuousSchedulingAttempt方法
/**
* Thread which attempts scheduling resources continuously,
* asynchronous to the node heartbeats.
*/
private class ContinuousSchedulingThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
try {
continuousSchedulingAttempt();
Thread.sleep(getContinuousSchedulingSleepMs());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.warn("Continuous scheduling thread interrupted. Exiting.", e);
return;
}
}
}
}
之后进行一次node节点 根据资源宽松情况的排序
void continuousSchedulingAttempt() throws InterruptedException { long start = getClock().getTime(); List<NodeId> nodeIdList = new ArrayList<NodeId>(nodes.keySet()); // Sort the nodes by space available on them, so that we offer // containers on emptier nodes first, facilitating an even spread. This // requires holding the scheduler lock, so that the space available on a // node doesn't change during the sort. synchronized (this) { Collections.sort(nodeIdList, nodeAvailableResourceComparator); } // iterate all nodes for (NodeId nodeId : nodeIdList) { FSSchedulerNode node = getFSSchedulerNode(nodeId); try { if (node != null && Resources.fitsIn(minimumAllocation, node.getAvailableResource())) { attemptScheduling(node); } } catch (Throwable ex) { LOG.error("Error while attempting scheduling for node " + node + ": " + ex.toString(), ex); if ((ex instanceof YarnRuntimeException) && (ex.getCause() instanceof InterruptedException)) { // AsyncDispatcher translates InterruptedException to // YarnRuntimeException with cause InterruptedException. // Need to throw InterruptedException to stop schedulingThread. throw (InterruptedException)ex.getCause(); } } }
依次对node遍历分配Container
queueMgr.getRootQueue().assignContainer(node) 从root遍历树 对抽象的应用资源遍历
boolean validReservation = false; FSAppAttempt reservedAppSchedulable = node.getReservedAppSchedulable(); if (reservedAppSchedulable != null) { validReservation = reservedAppSchedulable.assignReservedContainer(node); } if (!validReservation) { // No reservation, schedule at queue which is farthest below fair share int assignedContainers = 0; Resource assignedResource = Resources.clone(Resources.none()); Resource maxResourcesToAssign = Resources.multiply(node.getAvailableResource(), 0.5f); while (node.getReservedContainer() == null) { boolean assignedContainer = false; Resource assignment = queueMgr.getRootQueue().assignContainer(node); if (!assignment.equals(Resources.none())) { //判断是否分配到container assignedContainers++; assignedContainer = true; Resources.addTo(assignedResource, assignment); } if (!assignedContainer) { break; } if (!shouldContinueAssigning(assignedContainers, maxResourcesToAssign, assignedResource)) { break; } }
接下来在assignContainer 方法中对子队列使用特定的比较器排序这里是fairSchduler
@Override public Resource assignContainer(FSSchedulerNode node) { 对于每一个服务器,对资源树进行一次递归搜索 Resource assigned = Resources.none(); // If this queue is over its limit, reject if (!assignContainerPreCheck(node)) { return assigned; } // Hold the write lock when sorting childQueues writeLock.lock(); try { Collections.sort(childQueues, policy.getComparator()); } finally { writeLock.unlock(); }
对队列下的app排序
/* * We are releasing the lock between the sort and iteration of the * "sorted" list. There could be changes to the list here: * 1. Add a child queue to the end of the list, this doesn't affect * container assignment. * 2. Remove a child queue, this is probably good to take care of so we * don't assign to a queue that is going to be removed shortly. */ readLock.lock(); try { for (FSQueue child : childQueues) { assigned = child.assignContainer(node); if (!Resources.equals(assigned, Resources.none())) { break; } } } finally { readLock.unlock(); } return assigned;
assignContainer 可能传入的是app 可能传入的是一个队列 是队列的话 进行递归 直到找到app为止(root(FSParentQueue)节点递归调用assignContainer(),最终将到达最终叶子节点的assignContainer()方法,才真正开始进行分配)

优化一 : 优化队列比较器
我们在这里 关注的就是排序
hadoop2.8.4 排序类 FairSharePolicy中的 根据权重 需求的资源大小 和内存占比 进行排序 多次获取
getResourceUsage() 产生了大量重复计算 这个方法是一个动态获取的过程(耗时)
@Override
public int compare(Schedulable s1, Schedulable s2) {
double minShareRatio1, minShareRatio2;
double useToWeightRatio1, useToWeightRatio2;
Resource minShare1 = Resources.min(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null,
s1.getMinShare(), s1.getDemand());
Resource minShare2 = Resources.min(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null,
s2.getMinShare(), s2.getDemand());
boolean s1Needy = Resources.lessThan(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null,
s1.getResourceUsage(), minShare1);
boolean s2Needy = Resources.lessThan(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null,
s2.getResourceUsage(), minShare2);
minShareRatio1 = (double) s1.getResourceUsage().getMemorySize()
/ Resources.max(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null, minShare1, ONE).getMemorySize();
minShareRatio2 = (double) s2.getResourceUsage().getMemorySize()
/ Resources.max(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null, minShare2, ONE).getMemorySize();
useToWeightRatio1 = s1.getResourceUsage().getMemorySize() /
s1.getWeights().getWeight(ResourceType.MEMORY);
useToWeightRatio2 = s2.getResourceUsage().getMemorySize() /
s2.getWeights().getWeight(ResourceType.MEMORY);
int res = 0;
if (s1Needy && !s2Needy)
res = -1;
else if (s2Needy && !s1Needy)
res = 1;
else if (s1Needy && s2Needy)
res = (int) Math.signum(minShareRatio1 - minShareRatio2);
else
// Neither schedulable is needy
res = (int) Math.signum(useToWeightRatio1 - useToWeightRatio2);
if (res == 0) {
// Apps are tied in fairness ratio. Break the tie by submit time and job
// name to get a deterministic ordering, which is useful for unit tests.
res = (int) Math.signum(s1.getStartTime() - s2.getStartTime());
if (res == 0)
res = s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName());
}
return res;
}
}
新版优化后如下
@Override public int compare(Schedulable s1, Schedulable s2) { int res = compareDemand(s1, s2); // Pre-compute resource usages to avoid duplicate calculation Resource resourceUsage1 = s1.getResourceUsage(); Resource resourceUsage2 = s2.getResourceUsage(); if (res == 0) { res = compareMinShareUsage(s1, s2, resourceUsage1, resourceUsage2); } if (res == 0) { res = compareFairShareUsage(s1, s2, resourceUsage1, resourceUsage2); } // Break the tie by submit time if (res == 0) { res = (int) Math.signum(s1.getStartTime() - s2.getStartTime()); } // Break the tie by job name if (res == 0) { res = s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()); } return res; } private int compareDemand(Schedulable s1, Schedulable s2) { int res = 0; Resource demand1 = s1.getDemand(); Resource demand2 = s2.getDemand(); if (demand1.equals(Resources.none()) && Resources.greaterThan( RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null, demand2, Resources.none())) { res = 1; } else if (demand2.equals(Resources.none()) && Resources.greaterThan( RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null, demand1, Resources.none())) { res = -1; } return res; } private int compareMinShareUsage(Schedulable s1, Schedulable s2, Resource resourceUsage1, Resource resourceUsage2) { int res; Resource minShare1 = Resources.min(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null, s1.getMinShare(), s1.getDemand()); Resource minShare2 = Resources.min(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null, s2.getMinShare(), s2.getDemand()); boolean s1Needy = Resources.lessThan(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null, resourceUsage1, minShare1); boolean s2Needy = Resources.lessThan(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null, resourceUsage2, minShare2); if (s1Needy && !s2Needy) { res = -1; } else if (s2Needy && !s1Needy) { res = 1; } else if (s1Needy && s2Needy) { double minShareRatio1 = (double) resourceUsage1.getMemorySize() / Resources.max(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null, minShare1, ONE) .getMemorySize(); double minShareRatio2 = (double) resourceUsage2.getMemorySize() / Resources.max(RESOURCE_CALCULATOR, null, minShare2, ONE) .getMemorySize(); res = (int) Math.signum(minShareRatio1 - minShareRatio2); } else { res = 0; } return res; } /** * To simplify computation, use weights instead of fair shares to calculate * fair share usage. */ private int compareFairShareUsage(Schedulable s1, Schedulable s2, Resource resourceUsage1, Resource resourceUsage2) { double weight1 = s1.getWeights().getWeight(ResourceType.MEMORY); double weight2 = s2.getWeights().getWeight(ResourceType.MEMORY); double useToWeightRatio1; double useToWeightRatio2; if (weight1 > 0.0 && weight2 > 0.0) { useToWeightRatio1 = resourceUsage1.getMemorySize() / weight1; useToWeightRatio2 = resourceUsage2.getMemorySize() / weight2; } else { // Either weight1 or weight2 equals to 0 if (weight1 == weight2) { // If they have same weight, just compare usage useToWeightRatio1 = resourceUsage1.getMemorySize(); useToWeightRatio2 = resourceUsage2.getMemorySize(); } else { // By setting useToWeightRatios to negative weights, we give the // zero-weight one less priority, so the non-zero weight one will // be given slots. useToWeightRatio1 = -weight1; useToWeightRatio2 = -weight2; } } return (int) Math.signum(useToWeightRatio1 - useToWeightRatio2); } }
用了测试环境集群 比较了修改前后两次队列排序耗时
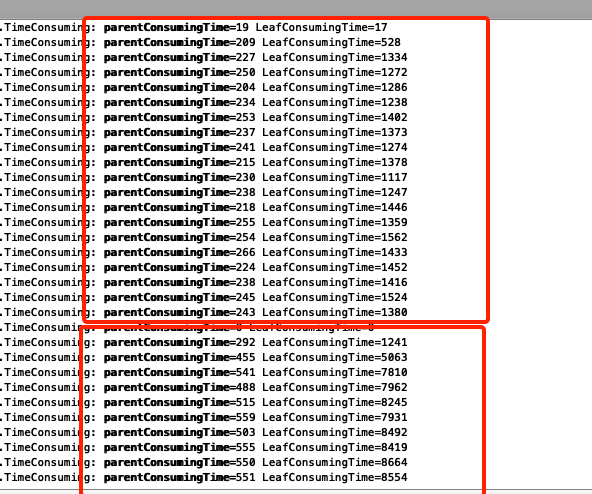
图中使用挫劣的方式比对 请观众凑合看吧^-^
上面红框里为 新版本 下面红框为老版本 虽然没有进行压测 但是在同样的调度任务前提下 是有说服力的 在大集群上每秒调度上千万乃至上亿次该方法时 调度优化变的明显
上线压测时 在1000队列 1500 pending任务600running任务时 调度性能提高了一倍 还是比较明显的提升的
优化二 : 优化yarn调度逻辑
思想:在大规模集群中 资源利用率表现的并不好,为了提高资源利用率,开启持续调度 然而实践发现 资源利用率是上去了但是 集群调度能力很弱 处理跟释放的container并没有提高
排查原因是心跳调度跟持续调度 走相同的synchronized 方法修饰的attemptScheduling 导致竞争锁 分配和释放都变的缓慢 且队列排序分配 在集群pending任务巨多时异常缓慢
优化:1,启用持续调度 禁用心跳调度
2,持续调度按批进行 间接减少队列排序造成的耗时影响
3. 释放不重要的锁 解放性能
说干就干
开启yarn的持续调度 配置如下:
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.fair.continuous-scheduling-enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<discription>是否打开连续调度功能</discription>
</property>
<property>
持续调度 每5ms执行一次上述方法 对node依次迭代执行
void continuousSchedulingAttempt() throws InterruptedException { long start = getClock().getTime(); List<NodeId> nodeIdList = new ArrayList<NodeId>(nodes.keySet()); // Sort the nodes by space available on them, so that we offer // containers on emptier nodes first, facilitating an even spread. This // requires holding the scheduler lock, so that the space available on a // node doesn't change during the sort. synchronized (this) { Collections.sort(nodeIdList, nodeAvailableResourceComparator); //对所有node 根据资源排序 } // iterate all nodes for (NodeId nodeId : nodeIdList) { //遍历所有的node FSSchedulerNode node = getFSSchedulerNode(nodeId); try { if (node != null && Resources.fitsIn(minimumAllocation, node.getAvailableResource())) { //判断该node 上现有的资源是否大于最小配置资源单位 attemptScheduling(node); //执行ttemptScheduling方法
} } catch (Throwable ex) { LOG.error("Error while attempting scheduling for node " + node + ": " + ex.toString(), ex); if ((ex instanceof YarnRuntimeException) && (ex.getCause() instanceof InterruptedException)) { // AsyncDispatcher translates InterruptedException to // YarnRuntimeException with cause InterruptedException. // Need to throw InterruptedException to stop schedulingThread. throw (InterruptedException)ex.getCause(); } } }
下面看下attemptScheduling方法
@VisibleForTesting synchronized void attemptScheduling(FSSchedulerNode node) { if (rmContext.isWorkPreservingRecoveryEnabled() && !rmContext.isSchedulerReadyForAllocatingContainers()) { return; } final NodeId nodeID = node.getNodeID(); if (!nodes.containsKey(nodeID)) { //合法性 // The node might have just been removed while this thread was waiting // on the synchronized lock before it entered this synchronized method LOG.info("Skipping scheduling as the node " + nodeID + " has been removed"); return; } // Assign new containers... // 1. Check for reserved applications // 2. Schedule if there are no reservations boolean validReservation = false; FSAppAttempt reservedAppSchedulable = node.getReservedAppSchedulable(); if (reservedAppSchedulable != null) { validReservation = reservedAppSchedulable.assignReservedContainer(node); } if (!validReservation) { //合法性判断 // No reservation, schedule at queue which is farthest below fair share int assignedContainers = 0; Resource assignedResource = Resources.clone(Resources.none()); Resource maxResourcesToAssign = Resources.multiply(node.getAvailableResource(), 0.5f); //默认使用该node最大50%的资源 while (node.getReservedContainer() == null) { boolean assignedContainer = false; Resource assignment = queueMgr.getRootQueue().assignContainer(node); //主要方法 依次对root树 遍历直到app 对该node上分配container if (!assignment.equals(Resources.none())) { //分配到资源 assignedContainers++; //分配到的container个数增1 assignedContainer = true; Resources.addTo(assignedResource, assignment); } if (!assignedContainer) { break; } //未匹配到 跳出 if (!shouldContinueAssigning(assignedContainers, //根据相关配置判断 现在分配的container个数 是否超出node上配置最大数 或node上的可用资源是否超出最小的配置资源 maxResourcesToAssign, assignedResource)) { break; } } } updateRootQueueMetrics(); }
针对上面源码 修改为如下内容:
持续调度一次分配五个node,减少每个node及分配过程排序的耗时操作。
void continuousSchedulingAttempt() throws InterruptedException { long start = getClock().getTime(); List<NodeId> nodeIdList = new ArrayList<NodeId>(nodes.keySet()); // Sort the nodes by space available on them, so that we offer // containers on emptier nodes first, facilitating an even spread. This // requires holding the scheduler lock, so that the space available on a // node doesn't change during the sort. synchronized (this) { Collections.sort(nodeIdList, nodeAvailableResourceComparator); } ArrayList<ArrayList<NodeId>> newNodeList = inBatchesNodes(nodeIdList, batchNodeAssigon); // 按批次返回node for (ArrayList<NodeId> nodeList : newNodeList) { //每个node进行检查 ArrayList<FSSchedulerNode> fsSchedulerNodeList = new ArrayList<>(); try { for (NodeId nodeId : nodeList) { FSSchedulerNode node = getFSSchedulerNode(nodeId); if (node != null && Resources.fitsIn(minimumAllocation, node.getAvailableResource())) { fsSchedulerNodeList.add(node); } } attemptSchedulings(fsSchedulerNodeList); // 批次进行attemptSchedule }catch (Exception e){ LOG.error("Processing attemptSchedulings error"+fsSchedulerNodeList +":"+fsSchedulerNodeList.toString(),e); fsSchedulerNodeList.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull).forEach(node->{ try { attemptScheduling(node); //有异常仍然走之前的逻辑 } catch (Throwable ex) { LOG.error("Error while attempting scheduling for node " + nodeList + ": " + ex.toString(), ex); } }); } } long duration = getClock().getTime() - start; fsOpDurations.addContinuousSchedulingRunDuration(duration); }
/** * 将传入的list 按size批次 返回 * @param list * @param size * @return */ private ArrayList<ArrayList<NodeId>> inBatchesNodes(List<NodeId> list, int size) { int listSize = list.size(); //表示一共需要取几次 int count = (list.size() % size == 0 ? list.size() / size : list.size() / size + 1); ArrayList<ArrayList<NodeId>> returnList = new ArrayList<>(count); for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i += size) { if (i + size > list.size()) { size = listSize - i; } ArrayList<NodeId> newList = new ArrayList<>(size); for (int j = i; j < i + size; j++) { newList.add(list.get(j)); } returnList.add(newList); } return returnList; }
interface Schedulable 接口新增 方法
/** * Assign list container list this node if possible, and return the amount of * resources assigned. */ public List<Resource> assignContainers(List<FSSchedulerNode> nodes);
@VisibleForTesting protected void attemptSchedulings(ArrayList<FSSchedulerNode> fsSchedulerNodeList) { if (rmContext.isWorkPreservingRecoveryEnabled() && !rmContext.isSchedulerReadyForAllocatingContainers()) { return; } List<FSSchedulerNode> fsSchedulerNodes = new ArrayList(); //定义个新集合 添加通过检查的node 抽象对象 fsSchedulerNodeList.stream().forEach(node -> { final NodeId nodeID = node.getNodeID(); if (nodes.containsKey(nodeID)) { // Assign new containers...// 1. Check for reserved applications // 2. Schedule if there are no reservations boolean validReservation = false; FSAppAttempt reservedAppSchedulable = node.getReservedAppSchedulable(); if (reservedAppSchedulable != null) { validReservation = reservedAppSchedulable.assignReservedContainer(node); } if (!validReservation) { //通过合法检查 if (node.getReservedContainer() == null) { //该node上 没有被某个container预留 fsSchedulerNodes.add(node); } } } else { LOG.info("Skipping scheduling as the node " + nodeID + " has been removed"); } }); if (fsSchedulerNodes.isEmpty()) { LOG.error("Handle fsSchedulerNodes empty and return"); return; } LOG.info("符合条件的nodes:" + fsSchedulerNodeList.size()); List<Resource> resources = queueMgr.getRootQueue().assignContainers(fsSchedulerNodes); //传入node的集合 批量操作 fsOpDurations.addDistributiveContainer(resources.size()); LOG.info("本次分配的container count:" + resources.size()); updateRootQueueMetrics(); }
FSParentQueue 类中 添加实现
@Override public List<Resource> assignContainers(List<FSSchedulerNode> nodes) { List<Resource> assignedsNeed = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<FSSchedulerNode> fsSchedulerNodes = new ArrayList<>(); for (FSSchedulerNode node : nodes) { if (assignContainerPreCheck(node)) { fsSchedulerNodes.add(node); } } if (fsSchedulerNodes.isEmpty()) { LOG.info("Nodes is empty, skip this assign around"); return assignedsNeed; } // Hold the write lock when sorting childQueues writeLock.lock(); try { Collections.sort(childQueues, policy.getComparator()); //排序又见排序 哈哈 } finally { writeLock.unlock(); } /* * We are releasing the lock between the sort and iteration of the * "sorted" list. There could be changes to the list here: * 1. Add a child queue to the end of the list, this doesn't affect * container assignment. * 2. Remove a child queue, this is probably good to take care of so we * don't assign to a queue that is going to be removed shortly. */ readLock.lock(); try { for (FSQueue child : childQueues) { List<Resource> assigneds = child.assignContainers(fsSchedulerNodes); //同样传入node集合 if (!assigneds.isEmpty()) { for (Resource assign : assigneds) { assignedsNeed.add(assign); } break; } } } finally { readLock.unlock(); } return assignedsNeed; }
app最终在FSLeafQueue节点上得到处理(第一版)
@Override public List<Resource> assignContainers(List<FSSchedulerNode> nodes) { Resource assigned = Resources.none(); List<Resource> assigneds = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<FSSchedulerNode> fsSchedulerNodes = new ArrayList<>(); for (FSSchedulerNode node : nodes) { if (assignContainerPreCheck(node)) { fsSchedulerNodes.add(node); } } if (fsSchedulerNodes.isEmpty()) { LOG.info("Nodes is empty, skip this assign around"); return assigneds; } // Apps that have resource demands. TreeSet<FSAppAttempt> pendingForResourceApps = new TreeSet<FSAppAttempt>(policy.getComparator()); readLock.lock(); try { for (FSAppAttempt app : runnableApps) { //所有的app running or pending 队列 进行依次排序 Resource pending = app.getAppAttemptResourceUsage().getPending(); if (!pending.equals(Resources.none())) { //有资源需求的加入排序队列 pendingForResourceApps.add(app); } } } finally { readLock.unlock(); } int count = 0; //每个node 分配container计数 Set<String> repeatApp = new HashSet<>(); //定义去重集合 for (FSSchedulerNode node : fsSchedulerNodes) { //node 遍历 count = 0; for (FSAppAttempt sched : pendingForResourceApps) { //app遍历 // One node just allocate for one app once if (repeatApp.contains(sched.getId())) { //去重 continue; } if (SchedulerAppUtils.isPlaceBlacklisted(sched, node, LOG)) { //判断app有没有在node黑名单里 continue; } if (node.getReservedContainer() == null && Resources.fitsIn(minimumAllocation, node.getAvailableResource())) { //判断node上还有没有资源 assigned = sched.assignContainer(node); //具体分配container方法 if (!assigned.equals(Resources.none())) {//给container 在node上分配到了资源 count++; repeatApp.add(sched.getId()); assigneds.add(assigned); if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("Assigned container in queue:" + getName() + " " + "container:" + assigned); } } } if (count >= maxNodeContainerAssign) { //node 分配的数量 超出最大的配置数 跳出 给下一node 分配 break; } } } return assigneds; }
经过几次修正修改如下(第二版):
@Override public int assignContainers(List<FSSchedulerNode> nodes) { int result = 0; getMetrics().assignCount.incr(); Resource assigned = Resources.none(); ArrayList<FSSchedulerNode> fsSchedulerNodes = new ArrayList<>(); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (FSSchedulerNode node : nodes) { if (assignContainerPreCheck(node)) { fsSchedulerNodes.add(node); } } long preCheckTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); getMetrics().preCheckTime.incr((preCheckTime - start)); if (fsSchedulerNodes.isEmpty()) { LOG.info("Nodes is empty, skip this assign around"); return result; } long runAppSortStart = System.currentTimeMillis(); // Apps that have resource demands. TreeSet<FSAppAttempt> pendingForResourceApps = new TreeSet<FSAppAttempt>(policy.getComparator()); readLock.lock(); try { for (FSAppAttempt app : runnableApps) { Resource pending = app.getAppAttemptResourceUsage().getPending(); if (!pending.equals(Resources.none())) { pendingForResourceApps.add(app); } } } finally { readLock.unlock(); } long runAppSortEnd = System.currentTimeMillis(); getMetrics().runAppSortTime.incr((runAppSortEnd - runAppSortStart)); int count = 0; long appAssignStart, appAssignEnd = 0; Set<Integer> repeatApp = new HashSet<>(); for (FSSchedulerNode node : fsSchedulerNodes) { count = 0; for (FSAppAttempt sched : pendingForResourceApps) { // One node just allocate for one app once if (repeatApp.contains(sched.getApplicationId().hashCode())) { continue; } if (SchedulerAppUtils.isPlaceBlacklisted(sched, node, LOG)) { continue; } appAssignStart = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (node.getReservedContainer() == null && Resources.fitsIn(minimumAllocation, node.getAvailableResource())) { assigned = sched.assignContainer(node); if (!assigned.equals(Resources.none())) { repeatApp.add(sched.getApplicationId().hashCode()); count++; result++; if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("Queue " + getName() + " assigned container in queue:" + getName() + " " + "container:" + assigned); } } else { if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("Queue " + getName() + " app " + sched.getId() + " skip node " + node.getNodeName()); } } } else { if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("Queue " + getName() + " node " + node.getNodeName() + " has resource " + node.getAvailableResource() + " left, node reserved is " + (node.getReservedContainer() == null)); } } appAssignEnd = System.currentTimeMillis(); getMetrics().appContainerAssignTime.incr((appAssignEnd - appAssignStart)); if (appAssignEnd - appAssignStart > 2) { LOG.info("Queue " + getName() + " app assign container use " + (appAssignEnd - appAssignStart) + " ms"); } if (count == maxNodeContainerAssign) { break; } } } return result; }
这轮优化 完毕 对比之前 调度性能提高了四倍样子 线上的积压问题得到有效解决
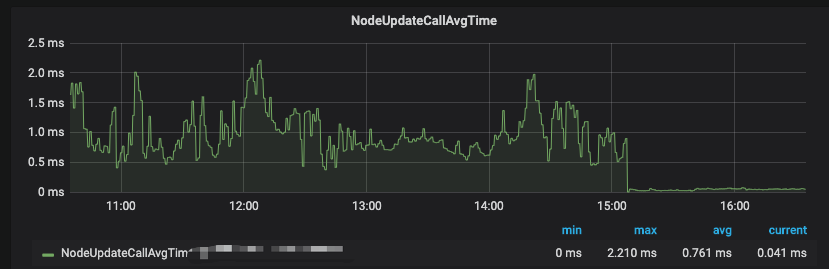
优化后nodeUpdate耗时对比如下