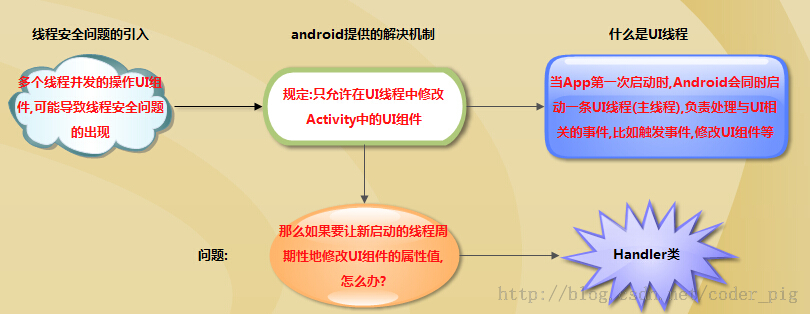
一、android中需要另开线程处理耗时、网络的任务,但是有必须要在UI线程中修改组件。这样做是为了:
①只能在UI线程中修改组件,避免了多线程造成组件显示混乱
②不使用加锁策略是为了提高性能,因为android中经常使用多线程。
handler就是为了解决在多个线程之间的通信问题。
二、基本使用:

1 package com.dqxst.first.multithread; 2 3 import android.app.Activity; 4 import android.os.Bundle; 5 import android.os.Handler; 6 import android.os.Handler.Callback; 7 import android.os.Message; 8 import android.util.Log; 9 import android.view.View; 10 import android.widget.TextView; 11 12 import com.dqxst.first.R; 13 14 public class HandlerActivity extends Activity { 15 private TextView tv,msg_tv; 16 private Handler handler = new Handler(); 17 final Handler msgHandler=new Handler(new Callback() { 18 @Override 19 public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) { 20 //!!!在这里可以进行一些操作,返回true则将msg进行拦截 21 return false; 22 } 23 }){ 24 @Override 25 public void handleMessage(Message msg) { 26 switch(msg.what){ 27 case 200: 28 msg_tv.setText("网络请求成功."); 29 break; 30 case 404: 31 msg_tv.setText("not found!"); 32 break; 33 } 34 super.handleMessage(msg); 35 } 36 37 }; 38 private MyRunnable runnable = new MyRunnable(); 39 40 @Override 41 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 42 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 43 setContentView(R.layout.activity_handler); 44 init(); 45 46 Log.i("main", "主线程=" + Thread.currentThread().toString()); 47 } 48 49 class MyRunnable implements Runnable { 50 @Override 51 public void run() { 52 int time = Integer.parseInt(tv.getText().toString()); 53 int now = time + 1; 54 Log.i("main", "处理UI更新线程=" + Thread.currentThread().toString()); 55 tv.setText(now + ""); 56 //这里是将Runnable间隔1秒重新发送到消息队列中,所以是定时操作的效果 57 handler.postDelayed(runnable, 1000); 58 } 59 60 } 61 62 //下面主要是在子线程中调用post将消息加入到消息队列中 63 public void startCallback(View view) { 64 new Thread() { 65 public void run() { 66 try { 67 Thread.sleep(1000); 68 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 69 e.printStackTrace(); 70 } 71 72 Log.i("main", "新线程=" + Thread.currentThread().toString()); 73 74 handler.post(runnable); 75 } 76 }.start(); 77 } 78 79 //这里是移除消息中的执行体部分,就是那个Runnable 80 public void stopCallback(View view){ 81 handler.removeCallbacks(runnable); 82 } 83 84 public void msgChange(View view){ 85 new Thread(new Runnable() { 86 @Override 87 public void run() { 88 Message message=Message.obtain(); 89 if(Math.random()>0.3){ 90 message.what=200; 91 }else{ 92 message.what=404; 93 } 94 msgHandler.sendMessage(message); 95 } 96 }).start(); 97 } 98 99 private void init() { 100 tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.handler_tv); 101 tv.setText("0"); 102 msg_tv=(TextView) findViewById(R.id.handler_tv_message); 103 } 104 }
由上例可以看到,handler使用有两种形式:
①post/postDelayed:这时传递的是一个Runnable对象,会封装到一个Message对象中发送到消息队列中
②sendMessage:这时需要重写handler的handleMessage或者在构造时传入一个实现Callback接口的对象(该对象的方法也是前面重写的方法名一样,但是先执行,可以用来对消息进行拦截)
三、源码分析:与handler机制有关的类有Looper、MessageQueue、Message以及Handler本身。
1、Looper:主要有两个作用
①创建一个与当前线程相关的Looper实例,通过调用prepare()

1 public static void prepare() { 2 prepare(true); 3 } 4 5 private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) { 6 if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) { 7 throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread"); 8 } 9 sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed)); 10 }
②不断的读取MessageQueue中的消息,通过调用loop(),MessageQueue是和Looper相关的,由其创建和管理。注意:这个过程是阻塞的。

1 public static void loop() { 2 final Looper me = myLooper(); 3 if (me == null) { 4 throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread."); 5 } 6 final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue; 7 8 // Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process, 9 // and keep track of what that identity token actually is. 10 Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); 11 final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); 12 13 //这里是一个死循环,读取message 14 for (;;) { 15 Message msg = queue.next(); // might block 16 //!!!这里注意:通常不会执行这一句,除非使用quit退出Looper 17 if (msg == null) { 18 // No message indicates that the message queue is quitting. 19 return; 20 } 21 22 // This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger 23 Printer logging = me.mLogging; 24 if (logging != null) { 25 logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " + 26 msg.callback + ": " + msg.what); 27 } 28 29 //这里是一个重点,说明了消息的具体执行方法 30 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); 31 32 if (logging != null) { 33 logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback); 34 } 35 36 // Make sure that during the course of dispatching the 37 // identity of the thread wasn't corrupted. 38 final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); 39 if (ident != newIdent) { 40 Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x" 41 + Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x" 42 + Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to " 43 + msg.target.getClass().getName() + " " 44 + msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what); 45 } 46 47 msg.recycleUnchecked(); 48 } 49 }
2、Message:就是消息对象,一般使用都只是用来传递数据(从网络获取的)等,常用属性有
①what :int类型,用于标识不同的消息,在handler中使用
②arg1,arg2 :int类型,用于传递int型的数据
③obj :Object类型,用于传递对象
④data :Bundle类型,
创建Message有一些需要注意的点:
①使用Message.obtain()或者Handler.obtainMessage()进行创建而不是new,可以利用公共池中对象避免重新分配空间。
②一个Message是和一个handler关联的,表现为Message中的target属性,但是通常这个属性是由系统自动赋值的,就是那个发送该消Message到MessageQueue的handler。
3、Handler:主要作用有以下三点
①关联所在线程的Looper对象和其所管理的MessageQueue对象,这是在构造函数中体现的,最终都会调用以下两个构造函数

1 public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) { 2 if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) { 3 final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass(); 4 if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) && 5 (klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) { 6 Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " + 7 klass.getCanonicalName()); 8 } 9 } 10 11 mLooper = Looper.myLooper(); 12 if (mLooper == null) { 13 throw new RuntimeException( 14 "Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()"); 15 } 16 mQueue = mLooper.mQueue; 17 mCallback = callback; 18 mAsynchronous = async; 19 } 20 21 22 public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback, boolean async) { 23 mLooper = looper; 24 mQueue = looper.mQueue; 25 mCallback = callback; 26 mAsynchronous = async; 27 }
!!!注意:在构造函数中,必须有一个Looper对象与其绑定,因为handler要将Message发送到MessageQueue中,而MessageQueue是由Looper创建的。
②发送消息到上面关联的消息队列,可以使用post和sendMessage两种类型方法。可以看到他们内部的调用过程是一样的。最终都是调用MessageQueue中的方法将消息绑定到一个链表上。

1 public final boolean post(Runnable r) 2 { 3 return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0); 4 } 5 6 public final boolean postDelayed(Runnable r, long delayMillis) 7 { 8 return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), delayMillis); 9 } 10 //这是上面用到的将Runnable封装到Message中的方法 11 private static Message getPostMessage(Runnable r) { 12 Message m = Message.obtain(); 13 m.callback = r; 14 return m; 15 } 16 17 18 public final boolean sendMessage(Message msg) 19 { 20 return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0); 21 }

1 public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis) 2 { 3 if (delayMillis < 0) { 4 delayMillis = 0; 5 } 6 return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis); 7 } 8 9 10 public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { 11 MessageQueue queue = mQueue; 12 if (queue == null) { 13 RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( 14 this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue"); 15 Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e); 16 return false; 17 } 18 return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis); 19 } 20 21 22 private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { 23 msg.target = this; 24 if (mAsynchronous) { 25 msg.setAsynchronous(true); 26 } 27 return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis); 28 }
③在Looper.loop()的循环读取过程中,读取的Message将通过msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);交由Handler中的dispatchMessage()进行处理。

1 public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) { 2 if (msg.callback != null) { 3 handleCallback(msg); 4 } else { 5 if (mCallback != null) { 6 if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) { 7 return; 8 } 9 } 10 handleMessage(msg); 11 } 12 }
这里就说明了Handler处理消息有三种方式,需要说明的是:
a、msg.callback就是通过post/postDelayed或者构造函数传入的Runnable对象
b、mCallback就是通过构造函数传入的实现其内部接口的对象,该方法返回true则退出,否则向下执行
四、扩展:
0、HandlerThread:在上面的基本使用中,是创建一个子线程,然后在子线程中通过主线程中的handler实例向主线程的MessageQueue中发送消息。而该类的实现是在子线程中开启一个Looper,然后在使用时将handler与该子线程中的Looper/MessageQueue进行绑定,即可通过handler将消息发送到子线程中进行处理,避免了主线程的阻塞。通过上述的描述,该类的使用只需简单的两步即可:
①实例化一个线程对象并开启该线程:HandlerThread downThread=new HandlerThread("ThreadName");downThread.start();
②将Handler与该线程的Looper绑定:Handler handler=new Handler(downThread.getLooper());
1、在子线程中使用Handler(这里指的是在子线程中创建Handler实例来接受和Message)。通过上面的说明我们知道,Handler创建之前必须有一个该线程的Looper对象被创建。在主线程中直接使用是因为已经由系统进行创建了,此时在创建则会出错。下面是android中给出的标准使用方法:

1 class LooperThread extends Thread { 2 public Handler mHandler; 3 4 public void run() { 5 Looper.prepare(); 6 7 mHandler = new Handler() { 8 public void handleMessage(Message msg) { 9 // process incoming messages here 10 } 11 }; 12 13 Looper.loop(); 14 } 15 }
2、上面说主线程不能再创建Looper,这是因为主线程被初始化是就是一个Looper线程,各种消息都是通过Handler机制处理的。
3、AsyncTask:异步消息处理机制,在内部封装了Handler处理流程。
①首先是android推荐的标准使用方式:创建一个子类,然后调用execute()即可

1 private class DownloadFilesTask extends AsyncTask<URL, Integer, Long> { 2 protected Long doInBackground(URL... urls) { 3 int count = urls.length; 4 long totalSize = 0; 5 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 6 totalSize += Downloader.downloadFile(urls[i]); 7 publishProgress((int) ((i / (float) count) * 100)); 8 // Escape early if cancel() is called 9 if (isCancelled()) break; 10 } 11 return totalSize; 12 } 13 14 protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... progress) { 15 setProgressPercent(progress[0]); 16 } 17 18 protected void onPostExecute(Long result) { 19 showDialog("Downloaded " + result + " bytes"); 20 } 21 }
这里简要说明三个泛型参数的作用:
a、Params:就是后台执行需要的参数,例如下载时需要url
b、Progress:就是任务执行的进度,在onProgressUpdate(Progress...)中会被使用,
c、Result:就是任务完成返回的结果,在onPostExecute(Result)中进行处理。
②源码解析:首先说明,Handler机制就是在子线程中处理任务,通过Handler将需要处理的消息传递到与其绑定的Looper的消息队列中,再由Looper取出交由Handler处理。
a、任务在子线程中处理,这里就是通过线程池处理,而任务就是doInBackground()中的部分,该函数被放在线程池的工作任务之中

1 public AsyncTask() { 2 mWorker = new WorkerRunnable<Params, Result>() { 3 public Result call() throws Exception { 4 mTaskInvoked.set(true); 5 6 Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND); 7 //noinspection unchecked 8 //!!!重点:doInBackground()在这里被封装 9 Result result = doInBackground(mParams); 10 Binder.flushPendingCommands(); 11 return postResult(result); 12 } 13 }; 14 15 mFuture = new FutureTask<Result>(mWorker) { 16 @Override 17 protected void done() { 18 try { 19 postResultIfNotInvoked(get()); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e); 22 } catch (ExecutionException e) { 23 throw new RuntimeException("An error occurred while executing doInBackground()", 24 e.getCause()); 25 } catch (CancellationException e) { 26 postResultIfNotInvoked(null); 27 } 28 } 29 }; 30 }
调用execute()就是用默认线程池来进行处理任务

1 @MainThread 2 public final AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> execute(Params... params) { 3 return executeOnExecutor(sDefaultExecutor, params); 4 } 5 6 7 public final AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> executeOnExecutor(Executor exec, 8 Params... params) { 9 if (mStatus != Status.PENDING) { 10 switch (mStatus) { 11 case RUNNING: 12 throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:" 13 + " the task is already running."); 14 case FINISHED: 15 throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:" 16 + " the task has already been executed " 17 + "(a task can be executed only once)"); 18 } 19 } 20 21 mStatus = Status.RUNNING; 22 23 onPreExecute(); 24 25 mWorker.mParams = params; 26 exec.execute(mFuture); 27 28 return this; 29 }
下面是这个线程池的本身部分,但是要注意:这是默认的情况,即调用execute()时的默认处理,默认处理是指:1、通过执行器模仿单一线程池的效果,即多个任务(一个AsyncTask实例的一次execute()创建一个任务)时只能有一个在线程中执行,2、而且线程中只能有128个任务(这是由阻塞队列的大小限制的)。
其实这是升级之后的效果,我们可以通过执行executeOnExecutor(Executor exec, Params... params)而不是execute()传入定制的线程池来解决上面问题。

1 //这是一个执行器,负责添加任务到一个ArrayDeque队列中,并且将第一个任务分配给线程池处理。注意下面的execute是synchronized的,说明一次只能有一个线程在处理一个任务。 2 private static volatile Executor sDefaultExecutor = SERIAL_EXECUTOR; 3 public static final Executor SERIAL_EXECUTOR = new SerialExecutor(); 4 private static class SerialExecutor implements Executor { 5 final ArrayDeque<Runnable> mTasks = new ArrayDeque<Runnable>(); 6 Runnable mActive; 7 8 public synchronized void execute(final Runnable r) { 9 mTasks.offer(new Runnable() { 10 public void run() { 11 try { 12 r.run(); 13 } finally { 14 scheduleNext(); 15 } 16 } 17 }); 18 if (mActive == null) { 19 scheduleNext(); 20 } 21 } 22 23 protected synchronized void scheduleNext() { 24 if ((mActive = mTasks.poll()) != null) { 25 THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR.execute(mActive); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 30 //这是上面用到的线程池的设置 31 private static final int CPU_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); 32 private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = CPU_COUNT + 1; 33 private static final int MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE = CPU_COUNT * 2 + 1; 34 private static final int KEEP_ALIVE = 1; 35 36 private static final ThreadFactory sThreadFactory = new ThreadFactory() { 37 private final AtomicInteger mCount = new AtomicInteger(1); 38 39 public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { 40 return new Thread(r, "AsyncTask #" + mCount.getAndIncrement()); 41 } 42 }; 43 44 private static final BlockingQueue<Runnable> sPoolWorkQueue = 45 new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(128); 46 47 public static final Executor THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR 48 = new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE, 49 TimeUnit.SECONDS, sPoolWorkQueue, sThreadFactory);
可以看到构造函数的任务对象中的最后一句是postResult(result),而该方法就是向AsyncTask内部的Handler发送消息。
b、下面就到了Handler的部分,

1 //获取内部Handler 2 private static Handler getHandler() { 3 synchronized (AsyncTask.class) { 4 if (sHandler == null) { 5 sHandler = new InternalHandler(); 6 } 7 return sHandler; 8 } 9 } 10 11 private static class InternalHandler extends Handler { 12 public InternalHandler() { 13 super(Looper.getMainLooper()); 14 } 15 16 @SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "RawUseOfParameterizedType"}) 17 @Override 18 public void handleMessage(Message msg) { 19 AsyncTaskResult<?> result = (AsyncTaskResult<?>) msg.obj; 20 switch (msg.what) { 21 case MESSAGE_POST_RESULT: 22 // There is only one result 23 result.mTask.finish(result.mData[0]); 24 break; 25 case MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS: 26 result.mTask.onProgressUpdate(result.mData); 27 break; 28 } 29 } 30 }
可以看到,这个handler处理两种类型的消息,一种是MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS,由publishProgress发送,触发;一种是MESSAGE_POST_RESULT,由postResult发送。

1 //发送MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS消息,触发onProgressUpdate() 2 protected final void publishProgress(Progress... values) { 3 if (!isCancelled()) { 4 getHandler().obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS, 5 new AsyncTaskResult<Progress>(this, values)).sendToTarget(); 6 } 7 } 8 //所以重写这个方法可以在主UI中更新界面 9 protected void onProgressUpdate(Progress... values) { 10 } 11 12 13 //发送MESSAGE_POST_RESULT消息,触发finish() 14 private Result postResult(Result result) { 15 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 16 Message message = getHandler().obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_RESULT, 17 new AsyncTaskResult<Result>(this, result)); 18 message.sendToTarget(); 19 return result; 20 } 21 //!!!这里的结束有两种情况,一种是被取消,一种是执行完成。 22 private void finish(Result result) { 23 if (isCancelled()) { 24 onCancelled(result); 25 } else { 26 onPostExecute(result); 27 } 28 mStatus = Status.FINISHED; 29 }
有关AsyncTask的使用还有一个问题就是如果在执行耗时任务时用户退出Activity,此时该任务线程可能没有执行完所以不会退出,这是可能造成内存泄露,需要在onPause中进行判断。还有其他问题参见http://droidyue.com/blog/2014/11/08/bad-smell-of-asynctask-in-android/index.html
参考:
