Volley是android官方开发的一个HTTP框架,简化了利用java中原生的HTTP操作API-HttpURLConnection和HttpClient的操作。
一、首先是Volley的简单使用示例:

1 package com.dqxst.first; 2 3 import android.graphics.Bitmap; 4 import android.graphics.BitmapFactory; 5 import android.os.Bundle; 6 import android.os.Handler; 7 import android.os.Message; 8 import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; 9 import android.util.LruCache; 10 import android.widget.ImageView; 11 import android.widget.Toast; 12 13 import com.android.volley.RequestQueue; 14 import com.android.volley.Response; 15 import com.android.volley.VolleyError; 16 import com.android.volley.toolbox.ImageLoader; 17 import com.android.volley.toolbox.ImageRequest; 18 import com.android.volley.toolbox.NetworkImageView; 19 import com.android.volley.toolbox.Volley; 20 import com.dqxst.first.adapter.Images; 21 22 import java.io.IOException; 23 import java.net.HttpURLConnection; 24 import java.net.MalformedURLException; 25 import java.net.URL; 26 27 public class HttpActivity extends AppCompatActivity { 28 private final static int LOAD_FAIL = 0; 29 private final static int LOAD_SUCCESS = 1; 30 31 private final Handler handler = new Handler() { 32 // private Context that=context; 33 @Override 34 public void handleMessage(Message msg) { 35 Bitmap photo = (Bitmap) msg.obj; 36 switch (msg.what) { 37 case LOAD_FAIL: 38 // Toast.makeText(that,"加载失败",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); 39 break; 40 case LOAD_SUCCESS: 41 iv.setImageBitmap(photo); 42 } 43 } 44 }; 45 46 private static ImageView iv; 47 private NetworkImageView niv; 48 49 @Override 50 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 51 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 52 setContentView(R.layout.activity_http); 53 init(); 54 // httpURLConnection(); 55 // volley(); 56 volley2(); 57 volley3(); 58 } 59 60 private void volley3() { 61 //这是第三种加载图片的方式,其实内部还是第二种凡是进行实现,但是通过一种自定义控件的形式表现 62 RequestQueue queue=Volley.newRequestQueue(this); 63 ImageLoader loader=new ImageLoader(queue,new BitmapCache()); 64 65 niv.setDefaultImageResId(R.drawable.loading); 66 niv.setErrorImageResId(R.drawable.load_error); 67 niv.setImageUrl(Images.imageThumbUrls[3],loader); 68 } 69 70 private void volley2() { 71 //这是Volley中一种加载图片的方式,和最基本的Request方式不同, 72 //优点是在loader中可以传入一个用于缓存的参数,可以利用LruCache来进行缓存管理 73 RequestQueue queue = Volley.newRequestQueue(HttpActivity.this); 74 ImageLoader loader = new ImageLoader(queue, new BitmapCache()); 75 ImageLoader.ImageListener listener = ImageLoader.getImageListener(iv,R.drawable.loading,R.drawable.load_error); 76 loader.get(Images.imageThumbUrls[2],listener); 77 } 78 79 public class BitmapCache implements ImageLoader.ImageCache{ 80 private int maxMemory=10*1024*1024; 81 private LruCache<String,Bitmap> cache=new LruCache<String,Bitmap>(maxMemory){ 82 @Override 83 protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap value) { 84 return value.getByteCount(); 85 } 86 }; 87 @Override 88 public Bitmap getBitmap(String s) { 89 return cache.get(s); 90 } 91 92 @Override 93 public void putBitmap(String s, Bitmap bitmap) { 94 cache.put(s,bitmap); 95 } 96 } 97 98 private void volley() { 99 //Volley基本使用分3步 100 //1、创建RequestQueue请求队列, 101 RequestQueue queue = Volley.newRequestQueue(HttpActivity.this); 102 //2、创建一个请求对象,这里是加载图片的请求对象 103 ImageRequest request = new ImageRequest(Images.imageThumbUrls[1], new Response.Listener<Bitmap>() { 104 @Override 105 public void onResponse(Bitmap bitmap) { 106 iv.setImageBitmap(bitmap); 107 } 108 }, 500, 500, null, new Response.ErrorListener() { 109 @Override 110 public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError volleyError) { 111 Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "加载出错", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); 112 } 113 }); 114 //3、最后,需要将请求对象添加到请求队列中进行工作。 115 queue.add(request); 116 } 117 118 private void httpURLConnection() { 119 new Thread(new Runnable() { 120 @Override 121 public void run() { 122 try { 123 Bitmap bitmap; 124 URL url = new URL(Images.imageThumbUrls[0]); 125 HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); 126 con.setConnectTimeout(5 * 1000); 127 con.setReadTimeout(10 * 1000); 128 bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(con.getInputStream()); 129 Message msg = new Message(); 130 if (bitmap != null) { 131 msg.what = LOAD_SUCCESS; 132 msg.obj = bitmap; 133 } else { 134 msg.what = LOAD_FAIL; 135 } 136 handler.sendMessage(msg); 137 } catch (MalformedURLException e) { 138 e.printStackTrace(); 139 } catch (IOException e) { 140 e.printStackTrace(); 141 } 142 } 143 }).start(); 144 } 145 146 private void init() { 147 iv = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.http_imageView); 148 niv= (NetworkImageView) findViewById(R.id.volley_NetworkImageView); 149 } 150 }

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 4 android:layout_width="match_parent" 5 android:layout_height="match_parent" 6 android:orientation="vertical" 7 android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" 8 android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" 9 android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" 10 android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" 11 tools:context="com.dqxst.first.HttpActivity"> 12 13 <ImageView 14 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 15 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 16 android:id="@+id/http_imageView" 17 android:src="@drawable/loading" 18 android:contentDescription="test"/> 19 20 <com.android.volley.toolbox.NetworkImageView 21 android:id="@+id/volley_NetworkImageView" 22 android:layout_width="200dp" 23 android:layout_height="200dp" /> 24 </LinearLayout>
通过以上的基本使用代码,可以看到一些Volley的基本情况
1、由于android的UI线程的限制,所以需要在新建线程中进行网络操作,所以网络操作需要涉及线程之间的通信,而一般使用的HTTP框架都需要对其进行自动处理进行简化,Volley框架也是如此,关于具体实现见下文的源码分析部分
2、可以看到,Volley中最基本的使用就是第一种方式,就是通过继承Request对象来实现的请求方式。Volley本身就有StringRequest等一系列具体的实现。详细的说明见二。
二、继承Request实现的HTTP请求。
首先先看Volley中的StringRequest的实现,

1 package com.android.volley.toolbox; 2 3 import com.android.volley.NetworkResponse; 4 import com.android.volley.Request; 5 import com.android.volley.Response; 6 import com.android.volley.Response.ErrorListener; 7 import com.android.volley.Response.Listener; 8 import com.android.volley.toolbox.HttpHeaderParser; 9 import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; 10 11 public class StringRequest extends Request<String> { 12 private final Listener<String> mListener; 13 14 //构造函数,主要作用有2, 15 //1、调用父类来进行初始化 16 //2、初始化监听类属性,用于监听Response服务器返回的结果 17 public StringRequest(int method, String url, Listener<String> listener, ErrorListener errorListener) { 18 super(method, url, errorListener); 19 this.mListener = listener; 20 } 21 22 public StringRequest(String url, Listener<String> listener, ErrorListener errorListener) { 23 this(0, url, listener, errorListener); 24 } 25 26 //该方法是响应的处理,调用监听器中的相应方法 27 protected void deliverResponse(String response) { 28 this.mListener.onResponse(response); 29 } 30 31 //处理响应数据的方法, 32 //参数NetworkResponse是对响应结果的一种封装,包括了响应头和响应体data 33 protected Response<String> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) { 34 String parsed; 35 try { 36 parsed = new String(response.data, HttpHeaderParser.parseCharset(response.headers)); 37 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException var4) { 38 parsed = new String(response.data); 39 } 40 41 return Response.success(parsed, HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response)); 42 } 43 } 44
通过学习上面的实现过程,可以对Volley进行扩展实现,满足个性化的使用。例如,
1、对响应结果为XML的数据进行解析(就是将parseNetworkResponse中的数据通过xml的方式进行解析即可),
2、使用Gson/fastjson对JSON数据进行解析,因为Volley中使用的是Android中自带的json解析方式,并且分为JsonArrayRequest和JsonObjectRequest两个具体实现。
三、源码解析:
1、在使用Volley时,第一步是创建一个RequestQueue对象,通常是由Volley对象的方法创建而不是直接new一个,源码见下

1 RequestQueue queue = Volley.newRequestQueue(HttpActivity.this); 2 3 public static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context) { 4 return newRequestQueue(context, (HttpStack)null); 5 } 6 7 public static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context, HttpStack stack) { 8 File cacheDir = new File(context.getCacheDir(), "volley"); 9 String userAgent = "volley/0"; 10 11 try { 12 String network = context.getPackageName(); 13 PackageInfo queue = context.getPackageManager().getPackageInfo(network, 0); 14 userAgent = network + "/" + queue.versionCode; 15 } catch (NameNotFoundException var6) { 16 ; 17 } 18 19 //1、创建http连接操作对象,其内部使用的是HttpURLConnection(sdk>=9)和HttpClient(sdk<9) 20 if(stack == null) { 21 if(VERSION.SDK_INT >= 9) { 22 stack = new HurlStack(); 23 } else { 24 stack = new HttpClientStack(AndroidHttpClient.newInstance(userAgent)); 25 } 26 } 27 28 //2、创建一个Network对象,这里使用的是Volley中的实现BasicNetwork, 29 //!!!该对象主要是调用上面的http连接进行连接,并对响应结果进行处理, 30 BasicNetwork network1 = new BasicNetwork((HttpStack)stack); 31 32 //3、创建RequestQueue对象,并调用start(),这一部分解释见2 33 RequestQueue queue1 = new RequestQueue(new DiskBasedCache(cacheDir), network1); 34 queue1.start(); 35 return queue1; 36 }
2、RequestQueue对象是整个Volley中最重要的一个对象,它的一部分功能类似于一个线程池(可以生成和管理线程)

1 public void start() { 2 this.stop(); 3 4 //1、 创建一个mCacheDispatcher并调用其start(),其实就是创建一个缓存线程 5 this.mCacheDispatcher = new CacheDispatcher(this.mCacheQueue, this.mNetworkQueue, this.mCache, this.mDelivery); 6 this.mCacheDispatcher.start(); 7 8 //2、这里默认循环4次,创建4个NetworkDispatcher对象并调用start(),其实是创建四个工作线程 9 for(int i = 0; i < this.mDispatchers.length; ++i) { 10 NetworkDispatcher networkDispatcher = new NetworkDispatcher(this.mNetworkQueue, this.mNetwork, this.mCache, this.mDelivery); 11 this.mDispatchers[i] = networkDispatcher; 12 networkDispatcher.start(); 13 } 14 15 }
3、使用Volley的最后一步就是使用RequestQueue的add()将实现的Request加入到队列中,如queue.add(request);

1 public <T> Request<T> add(Request<T> request) { 2 request.setRequestQueue(this); 3 Set var2 = this.mCurrentRequests; 4 synchronized(this.mCurrentRequests) { 5 this.mCurrentRequests.add(request); 6 } 7 8 request.setSequence(this.getSequenceNumber()); 9 request.addMarker("add-to-queue"); 10 //这里判断的是请求是否可以缓存,使用的是mShouldCache属性,默认值为true,即可以缓存 11 if(!request.shouldCache()) { 12 this.mNetworkQueue.add(request); 13 return request; 14 } else { 15 Map var8 = this.mWaitingRequests; 16 synchronized(this.mWaitingRequests) { 17 String cacheKey = request.getCacheKey(); 18 if(this.mWaitingRequests.containsKey(cacheKey)) { 19 Object stagedRequests = (Queue)this.mWaitingRequests.get(cacheKey); 20 if(stagedRequests == null) { 21 stagedRequests = new LinkedList(); 22 } 23 24 ((Queue)stagedRequests).add(request); 25 this.mWaitingRequests.put(cacheKey, stagedRequests); 26 if(VolleyLog.DEBUG) { 27 VolleyLog.v("Request for cacheKey=%s is in flight, putting on hold.", new Object[]{cacheKey}); 28 } 29 } else { 30 this.mWaitingRequests.put(cacheKey, (Object)null); 31 //在这里将Request对象加入到缓存队列中进行操作 32 this.mCacheQueue.add(request); 33 } 34 35 return request; 36 } 37 } 38 }
4、通过上面的源码可以看到,最终的操作是落在

1 public class CacheDispatcher extends Thread { 2 3 @Override 4 public void run() { 5 if (DEBUG) VolleyLog.v("start new dispatcher"); 6 Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND); 7 // Make a blocking call to initialize the cache. 8 mCache.initialize(); 9 //这里表明该线程一直在运行 10 while (true) { 11 try { 12 // Get a request from the cache triage queue, blocking until 13 // at least one is available. 14 final Request<?> request = mCacheQueue.take(); 15 request.addMarker("cache-queue-take"); 16 // 检测请求是否被取消,是则退出 17 if (request.isCanceled()) { 18 request.finish("cache-discard-canceled"); 19 continue; 20 } 21 // 检测是否有缓存的结果,没有则调用NetworkQueue重新进行请求 22 Cache.Entry entry = mCache.get(request.getCacheKey()); 23 if (entry == null) { 24 request.addMarker("cache-miss"); 25 // Cache miss; send off to the network dispatcher. 26 mNetworkQueue.put(request); 27 continue; 28 } 29 // 检测缓存是否过期,是则重新请求 30 if (entry.isExpired()) { 31 request.addMarker("cache-hit-expired"); 32 request.setCacheEntry(entry); 33 mNetworkQueue.put(request); 34 continue; 35 } 36 // We have a cache hit; parse its data for delivery back to the request. 37 request.addMarker("cache-hit"); 38 Response<?> response = request.parseNetworkResponse( 39 new NetworkResponse(entry.data, entry.responseHeaders)); 40 request.addMarker("cache-hit-parsed"); 41 if (!entry.refreshNeeded()) { 42 // Completely unexpired cache hit. Just deliver the response. 43 mDelivery.postResponse(request, response); 44 } else { 45 // Soft-expired cache hit. We can deliver the cached response, 46 // but we need to also send the request to the network for 47 // refreshing. 48 request.addMarker("cache-hit-refresh-needed"); 49 request.setCacheEntry(entry); 50 // Mark the response as intermediate. 51 response.intermediate = true; 52 // Post the intermediate response back to the user and have 53 // the delivery then forward the request along to the network. 54 mDelivery.postResponse(request, response, new Runnable() { 55 @Override 56 public void run() { 57 try { 58 mNetworkQueue.put(request); 59 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 60 // Not much we can do about this. 61 } 62 } 63 }); 64 } 65 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 66 // We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit. 67 if (mQuit) { 68 return; 69 } 70 continue; 71 } 72 } 73 } 74 }

1 public void run() { 2 Process.setThreadPriority(10); 3 4 //外层循环,保证工作线程持续工作 5 while(true) { 6 Request request; 7 //内层循环,循环访问工作队列,从其中取出需要处理的任务, 8 //注意这里使用了take(),是一种阻塞的实现,详见线程深入学习二 9 while(true) { 10 try { 11 request = (Request)this.mQueue.take(); 12 break; 13 } catch (InterruptedException var4) { 14 if(this.mQuit) { 15 return; 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 20 try { 21 request.addMarker("network-queue-take"); 22 if(request.isCanceled()) { 23 request.finish("network-discard-cancelled"); 24 } else { 25 this.addTrafficStatsTag(request); 26 //这里说明真正执行http的是mNetwork对象, 27 //Volley中默认就是HttpURLConnection(API9之后)或HttpClient 28 //这在1中源码部分可见, 29 //最终将HTTP相应封装成NetworkResponse 30 NetworkResponse e = this.mNetwork.performRequest(request); 31 request.addMarker("network-http-complete"); 32 //这里是检测的notModified属性其实是检测返回的状态码是否为304 33 //第二个是判断响应是否已经提交过 34 if(e.notModified && request.hasHadResponseDelivered()) { 35 request.finish("not-modified"); 36 } else { 37 Response response = request.parseNetworkResponse(e); 38 request.addMarker("network-parse-complete"); 39 //!!!在这里将获取的数据进行缓存 40 if(request.shouldCache() && response.cacheEntry != null) { 41 this.mCache.put(request.getCacheKey(), response.cacheEntry); 42 request.addMarker("network-cache-written"); 43 } 44 45 request.markDelivered(); 46 this.mDelivery.postResponse(request, response); 47 } 48 } 49 } catch (VolleyError var5) { 50 this.parseAndDeliverNetworkError(request, var5); 51 } catch (Exception var6) { 52 VolleyLog.e(var6, "Unhandled exception %s", new Object[]{var6.toString()}); 53 this.mDelivery.postError(request, new VolleyError(var6)); 54 } 55 } 56 }
看完了源码的简要分析,就可以搞明白Volley官方对其进行解释的一幅图了,如下:
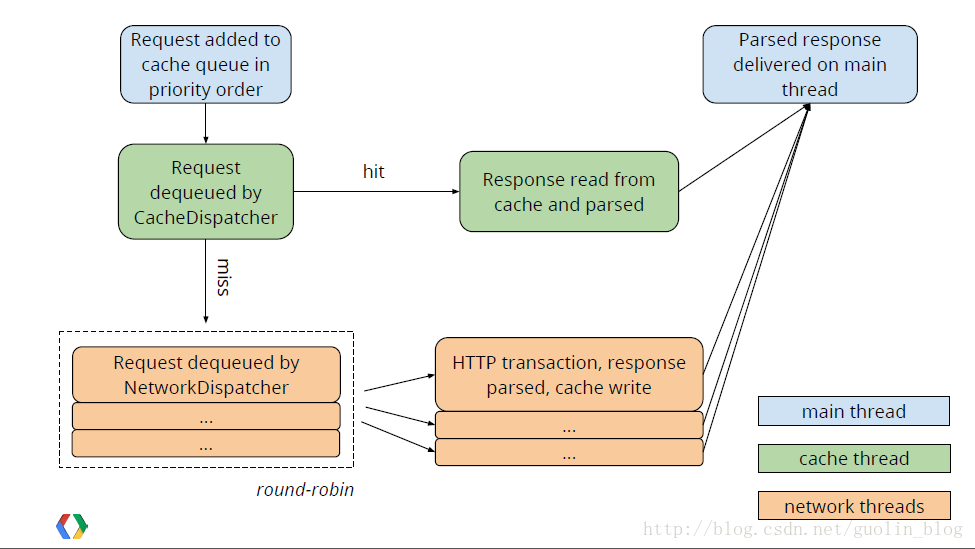
四、其他问题:
1、Volley发送POST请求
通过上面的源码分析,可以知道最终的HTTP操作会在

1 public HttpResponse performRequest(Request<?> request, Map<String, String> additionalHeaders) throws IOException, AuthFailureError { 2 String url = request.getUrl(); 3 HashMap map = new HashMap(); 4 map.putAll(request.getHeaders()); 5 map.putAll(additionalHeaders); 6 if(this.mUrlRewriter != null) { 7 String parsedUrl = this.mUrlRewriter.rewriteUrl(url); 8 if(parsedUrl == null) { 9 throw new IOException("URL blocked by rewriter: " + url); 10 } 11 12 url = parsedUrl; 13 } 14 15 URL parsedUrl1 = new URL(url); 16 //创建HttpURLConnection对象用于连接,下面的方法就是对连接进行基本设置 17 HttpURLConnection connection = this.openConnection(parsedUrl1, request); 18 Iterator protocolVersion = map.keySet().iterator(); 19 20 while(protocolVersion.hasNext()) { 21 String responseCode = (String)protocolVersion.next(); 22 connection.addRequestProperty(responseCode, (String)map.get(responseCode)); 23 } 24 25 //这个方法是根据请求方式对请求进行一些设置,主要就是对一些请求如POST的参数进行传递 26 setConnectionParametersForRequest(connection, request); 27 ProtocolVersion protocolVersion1 = new ProtocolVersion("HTTP", 1, 1); 28 int responseCode1 = connection.getResponseCode(); 29 if(responseCode1 == -1) { 30 throw new IOException("Could not retrieve response code from HttpUrlConnection."); 31 } else { 32 BasicStatusLine responseStatus = new BasicStatusLine(protocolVersion1, connection.getResponseCode(), connection.getResponseMessage()); 33 BasicHttpResponse response = new BasicHttpResponse(responseStatus); 34 response.setEntity(entityFromConnection(connection)); 35 Iterator i$ = connection.getHeaderFields().entrySet().iterator(); 36 37 while(i$.hasNext()) { 38 Entry header = (Entry)i$.next(); 39 if(header.getKey() != null) { 40 BasicHeader h = new BasicHeader((String)header.getKey(), (String)((List)header.getValue()).get(0)); 41 response.addHeader(h); 42 } 43 } 44 45 return response; 46 } 47 } 48 49 //对请求进行一些基本设置 50 private HttpURLConnection openConnection(URL url, Request<?> request) throws IOException { 51 HttpURLConnection connection = this.createConnection(url); 52 int timeoutMs = request.getTimeoutMs(); 53 connection.setConnectTimeout(timeoutMs); 54 connection.setReadTimeout(timeoutMs); 55 connection.setUseCaches(false); 56 connection.setDoInput(true); 57 if("https".equals(url.getProtocol()) && this.mSslSocketFactory != null) { 58 ((HttpsURLConnection)connection).setSSLSocketFactory(this.mSslSocketFactory); 59 } 60 61 return connection; 62 } 63 64 //根据请求方式进行设置,主要是对POST等请求传递参数 65 static void setConnectionParametersForRequest(HttpURLConnection connection, Request<?> request) throws IOException, AuthFailureError { 66 switch(request.getMethod()) { 67 case -1: 68 //!!!这里调用请求对象来获取POST传递的参数 69 byte[] postBody = request.getPostBody(); 70 if(postBody != null) { 71 connection.setDoOutput(true); 72 connection.setRequestMethod("POST"); 73 connection.addRequestProperty("Content-Type", request.getPostBodyContentType()); 74 DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(connection.getOutputStream()); 75 out.write(postBody); 76 out.close(); 77 } 78 break; 79 case 0: 80 connection.setRequestMethod("GET"); 81 break; 82 case 1: 83 connection.setRequestMethod("POST"); 84 addBodyIfExists(connection, request); 85 break; 86 case 2: 87 connection.setRequestMethod("PUT"); 88 addBodyIfExists(connection, request); 89 break; 90 case 3: 91 connection.setRequestMethod("DELETE"); 92 break; 93 case 4: 94 connection.setRequestMethod("HEAD"); 95 break; 96 case 5: 97 connection.setRequestMethod("OPTIONS"); 98 break; 99 case 6: 100 connection.setRequestMethod("TRACE"); 101 break; 102 case 7: 103 addBodyIfExists(connection, request); 104 connection.setRequestMethod("PATCH"); 105 break; 106 default: 107 throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown method type."); 108 } 109 110 } 111 112 private static void addBodyIfExists(HttpURLConnection connection, Request<?> request) throws IOException, AuthFailureError { 113 byte[] body = request.getBody(); 114 if(body != null) { 115 connection.setDoOutput(true); 116 connection.addRequestProperty("Content-Type", request.getBodyContentType()); 117 DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(connection.getOutputStream()); 118 out.write(body); 119 out.close(); 120 } 121 122 }
从上面可以看到最终调用Request去获取POST传递的参数,而最终调用的方法就是getParams()。

1 protected Map<String, String> getParams() throws AuthFailureError { 2 return null; 3 }
结论:要实现POST请求,需要重写Request中的getParams()方法传递参数,并将method设置为1或-1(为-1时是判断是否有请求参数,即getParams()是否为null)。
注意:上面是将参数以普通的形式即键值对的形式进行发送,但有时需要以json串的形式进行发送,此时就需要使用JsonObjectRequest/JsonArrayRequest,并需要重写getHeaders()添加json处理的头信息

1 2 @Override 3 public Map<String, String> getHeaders() { 4 HashMap<String, String> headers = new HashMap<String, String>(); 5 headers.put("Accept", "application/json"); 6 headers.put("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=UTF-8"); 7 8 return headers; 9 }
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/17482095
http://blog.csdn.net/gaolu/article/details/38439375
2、加载图片:在一中的基本使用部分代码里,有两种专门针对图片的操作方式,一个是使用ImageLoader,一个是使用自定义图片控件NetworkImageView。从本质上来说两者使用的都是ImageLoader进行实现的。两者的区别在于:
①如果要是针对普通的图片展示形式(因为NetworkImageView仅仅是增加了通过URL来添加图片的功能,基本显示还是ImageView)可以使用该自定义控件,更简便一些;
②如果有特殊的展示需求,例如需要圆形图片而使用自定义控件(circularimageview)时可以使用ImageLoader方式。
其实通过源码可以发现,ImageLoader就是对Request方式进行封装,可以将图片直接显示在指定的ImageView控件上而已,方便了用户的操作。但是最主要的一个区别是:使用这种方式没有使用默认的磁盘缓存DiskBaseedCache方案,而是需要用户指定缓存的方式。
3、Volley的缓存:在上面对缓存介绍的比较少,其实缓存是Volley中比较重要的部分。有了缓存可以降低HTTP请求的次数,提升用户的体验。从上图中可以看到Volley首先是从缓存中进行查询,如果缓存没有才对服务器进行请求。具体见如下分析。
①首先是在创建RequestQueue对象时需要传入一个实现了Cache接口的对象,通过Volley类创建的时候默认使用的就是DiskBasedCache,从名字可以看到这是一个机遇硬盘的缓存方案,缓存路径就是应用的cache目录(可以从上面的3.1部分源码看到)。

1 public RequestQueue(Cache cache, Network network, int threadPoolSize, ResponseDelivery delivery) { 2 this.mSequenceGenerator = new AtomicInteger(); 3 this.mWaitingRequests = new HashMap(); 4 this.mCurrentRequests = new HashSet(); 5 this.mCacheQueue = new PriorityBlockingQueue(); 6 this.mNetworkQueue = new PriorityBlockingQueue(); 7 this.mCache = cache; 8 this.mNetwork = network; 9 this.mDispatchers = new NetworkDispatcher[threadPoolSize]; 10 this.mDelivery = delivery; 11 } 12 13 public RequestQueue(Cache cache, Network network, int threadPoolSize) { 14 this(cache, network, threadPoolSize, new ExecutorDelivery(new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()))); 15 } 16 17 public RequestQueue(Cache cache, Network network) { 18 this(cache, network, 4); 19 }
②对于DiskBaseedCache对象,会在Volley创建RequestQueue时传入,并在其start()用于创建CacheDispatcher对象,作用域缓存。最后会在其run()中被初始化。

1 //Volley.newRequestQueue() 2 RequestQueue queue1 = new RequestQueue(new DiskBasedCache(cacheDir), network1); 3 4 //RequestQueue。start() 5 this.mCacheDispatcher = new CacheDispatcher(this.mCacheQueue, this.mNetworkQueue, this.mCache, this.mDelivery); 6 this.mCacheDispatcher.start(); 7 8 //CacheDispatcher.run() 9 this.mCache.initialize();
③缓存操作:默认的存储路径是data/data/<package>/Volley下。有了DiskBaseedCache缓存对象之后就可以实现保存(在NetworkDispatcher中)和取出缓存(在CacheDispatcher中)的操作,通过调用其put()/get()实现,还可以通过调用其remove()方法删除缓存。
当网络断开的情况下,Volley同样首先从缓存中获取数据,会先判断其是否过期,根据缓存中的ttl,就是缓存头的MaxAge。
4、多线程间通信的实现:其内部使用了handler机制。解析如下:
①在通过网络线程或者缓存线程获取到响应之后,都会调用一个方法来提交响应

1 //CacheDispatcher的run()中部分 2 this.mDelivery.postResponse(e, response); 3 4 this.mDelivery.postResponse(e, response, new Runnable() { 5 public void run() { 6 try { 7 CacheDispatcher.this.mNetworkQueue.put(e); 8 } catch (InterruptedException var2) { 9 ; 10 } 11 12 } 13 }); 14 15 //NetWorkDispatcher的run()中部分 16 this.mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
②默认使用的是ExecutorDelivery来进行提交响应结果

1 //RequestQueue构造函数,传入ExecutorDelivery对象执行提交响应 2 //并且将绑定主UI线程的Handler对象传入 3 public RequestQueue(Cache cache, Network network, int threadPoolSize) { 4 this(cache, network, threadPoolSize, new ExecutorDelivery(new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()))); 5 } 6 7 8 //ExecutorDelivery部分 9 public ExecutorDelivery(final Handler handler) { 10 this.mResponsePoster = new Executor() { 11 public void execute(Runnable command) { 12 handler.post(command); 13 } 14 }; 15 } 16 //执行提交的部分 17 public void postResponse(Request<?> request, Response<?> response) { 18 this.postResponse(request, response, (Runnable)null); 19 } 20 public void postResponse(Request<?> request, Response<?> response, Runnable runnable) { 21 request.markDelivered(); 22 request.addMarker("post-response"); 23 this.mResponsePoster.execute(new ExecutorDelivery.ResponseDeliveryRunnable(request, response, runnable)); 24 }
③经过上述处理,最终实际提交的是其内部的ResponseDeliveryRunnable。由Handler机制可知,最后处理消息就是该Runnable的run().在向下就可以看到最后使用了我们提供的监听器中的方法进行处理,实现了线程间通信。

1 public void run() { 2 if(this.mRequest.isCanceled()) { 3 this.mRequest.finish("canceled-at-delivery"); 4 } else { 5 if(this.mResponse.isSuccess()) { 6 this.mRequest.deliverResponse(this.mResponse.result); 7 } else { 8 this.mRequest.deliverError(this.mResponse.error); 9 } 10 11 if(this.mResponse.intermediate) { 12 this.mRequest.addMarker("intermediate-response"); 13 } else { 14 this.mRequest.finish("done"); 15 } 16 17 if(this.mRunnable != null) { 18 this.mRunnable.run(); 19 } 20 21 } 22 }
五、源码分析续之HTTP处理
上面的源码分析中没有分析Volley中是如何具体处理HTTP协议的,在这里进行分析。从上面知道,Volley的网络请求最终是由BasicNetwork这个类进行调度处理的(真正的处理时HttpURLConnection类),当然也可以自定义一个处理类,只要实现Network接口,完成其中的网络操作的方法即可。
1 public interface Network { 2 NetworkResponse performRequest(Request<?> var1) throws VolleyError; 3 }
1、下面是BasicNetwork中的performRequest(),就是通过这个方法对HTTP请求过程进行调度的。但是实际的请求并不在这里执行,见下面分析:
1 public NetworkResponse performRequest(Request<?> request) throws VolleyError { 2 long requestStart = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime(); 3 4 while(true) { 5 HttpResponse httpResponse = null; 6 Object responseContents = null; 7 HashMap responseHeaders = new HashMap(); 8 9 try { 10 HashMap e = new HashMap(); 11 this.addCacheHeaders(e, request.getCacheEntry()); 12 httpResponse = this.mHttpStack.performRequest(request, e); 13 StatusLine statusCode2 = httpResponse.getStatusLine(); 14 int networkResponse1 = statusCode2.getStatusCode(); 15 Map responseHeaders1 = convertHeaders(httpResponse.getAllHeaders()); 16 if(networkResponse1 != 304) { 17 byte[] responseContents1; 18 if(httpResponse.getEntity() != null) { 19 responseContents1 = this.entityToBytes(httpResponse.getEntity()); 20 } else { 21 responseContents1 = new byte[0]; 22 } 23 24 long requestLifetime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart; 25 this.logSlowRequests(requestLifetime, request, responseContents1, statusCode2); 26 if(networkResponse1 >= 200 && networkResponse1 <= 299) { 27 return new NetworkResponse(networkResponse1, responseContents1, responseHeaders1, false); 28 } 29 30 throw new IOException(); 31 } 32 33 return new NetworkResponse(304, request.getCacheEntry() == null?null:request.getCacheEntry().data, responseHeaders1, true); 34 } catch (SocketTimeoutException var12) { 35 attemptRetryOnException("socket", request, new TimeoutError()); 36 } catch (ConnectTimeoutException var13) { 37 attemptRetryOnException("connection", request, new TimeoutError()); 38 } catch (MalformedURLException var14) { 39 throw new RuntimeException("Bad URL " + request.getUrl(), var14); 40 } catch (IOException var15) { 41 boolean statusCode = false; 42 NetworkResponse networkResponse = null; 43 if(httpResponse == null) { 44 throw new NoConnectionError(var15); 45 } 46 47 int statusCode1 = httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); 48 VolleyLog.e("Unexpected response code %d for %s", new Object[]{Integer.valueOf(statusCode1), request.getUrl()}); 49 if(responseContents == null) { 50 throw new NetworkError(networkResponse); 51 } 52 53 networkResponse = new NetworkResponse(statusCode1, (byte[])responseContents, responseHeaders, false); 54 if(statusCode1 != 401 && statusCode1 != 403) { 55 throw new ServerError(networkResponse); 56 } 57 58 attemptRetryOnException("auth", request, new AuthFailureError(networkResponse)); 59 } 60 } 61 }
①请求时间记录:在2,24,25行可以看到有记录整个请求时间的数据并且进行打印
②执行HTTP请求,使用的是mHttpStack进行操作,现在主要使用的就是HurlStack进行的,其内部使用HttpURLConnection(在下面进行说明)。
③对部分状态码的结果进行处理(16-31行):注意,这里处理的状态码只有200-299和304,其余的状态码都抛出IOException,在异常处理中尝试处理。
a、304状态:说明请求的文档的缓存仍然有效,则直接将缓存数据直接封装在最终的响应中以供使用。
b、2xx状态:对于非304的状态,进行的处理是将其中的content信息从流中读取出来存放到responseContents1属性中,还有之前就已经读取的头信息集合放在responseHeaders1属性中。如果状态在200-299之间,则将这些数据进行封装最终返回,其他状态则抛出异常。
④异常处理:从③可知,这里的异常可能不是真正的异常,处理过程如下,
a、超时(连接超时和读取超时):针对两种不同的连接方式(HttpURLConnection/HttpClient)的不同异常进行处理,就是执行重试策略。默认的重试策略就是超时时间增加一倍然后重试1次。超时时间增加是由乘积因子决定的。
b、URL格式错误:直接报错
c、IOException:该异常可能有两种情况引起:
1、确实是IOException即读取过程的异常:这部分就是对响应结果进行检测,如果响应的结果为null则报错。(在42-51行)
2、由于上面没有处理的状态码报错:如果是401或403状态,直接报错,其他状态进行重试。
2、执行HTTP请求的就是HurlStack中的方法,下面对其过程进行说明:
1 public HttpResponse performRequest(Request<?> request, Map<String, String> additionalHeaders) throws IOException, AuthFailureError { 2 String url = request.getUrl(); 3 HashMap map = new HashMap(); 4 map.putAll(request.getHeaders()); 5 map.putAll(additionalHeaders); 6 if(this.mUrlRewriter != null) { 7 String parsedUrl = this.mUrlRewriter.rewriteUrl(url); 8 if(parsedUrl == null) { 9 throw new IOException("URL blocked by rewriter: " + url); 10 } 11 12 url = parsedUrl; 13 } 14 15 URL parsedUrl1 = new URL(url); 16 HttpURLConnection connection = this.openConnection(parsedUrl1, request); 17 Iterator protocolVersion = map.keySet().iterator(); 18 19 while(protocolVersion.hasNext()) { 20 String responseCode = (String)protocolVersion.next(); 21 connection.addRequestProperty(responseCode, (String)map.get(responseCode)); 22 } 23 24 setConnectionParametersForRequest(connection, request); 25 ProtocolVersion protocolVersion1 = new ProtocolVersion("HTTP", 1, 1); 26 int responseCode1 = connection.getResponseCode(); 27 if(responseCode1 == -1) { 28 throw new IOException("Could not retrieve response code from HttpUrlConnection."); 29 } else { 30 BasicStatusLine responseStatus = new BasicStatusLine(protocolVersion1, connection.getResponseCode(), connection.getResponseMessage()); 31 BasicHttpResponse response = new BasicHttpResponse(responseStatus); 32 response.setEntity(entityFromConnection(connection)); 33 Iterator i$ = connection.getHeaderFields().entrySet().iterator(); 34 35 while(i$.hasNext()) { 36 Entry header = (Entry)i$.next(); 37 if(header.getKey() != null) { 38 BasicHeader h = new BasicHeader((String)header.getKey(), (String)((List)header.getValue()).get(0)); 39 response.addHeader(h); 40 } 41 } 42 43 return response; 44 } 45 }
