目录
1. 数组操作符重载
数组操作符重载
通过重载数组操作符,可以使类的对象支持数组的下标访问
- 数组操作符只能重载为类的成员函数
- 重载函数能且仅能使用一个参数,也就是数组下标
- 可以定义不同参数的多个重载函数
在重载数组操作符时,要记得数组操作符的原生语义——数组访问和指针运算。
a[n] <--> *(a + n) <--> *(n + a) <--> n[a]
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int a[3];
public:
int &operator [] (int i)
{
return a[i];
}
int &operator [] (const string &s)
{
if( s == "1st" )
{
return a[0];
}
else if( s == "2nd" )
{
return a[1];
}
else if( s == "3rd" )
{
return a[2];
}
return a[0];
}
};
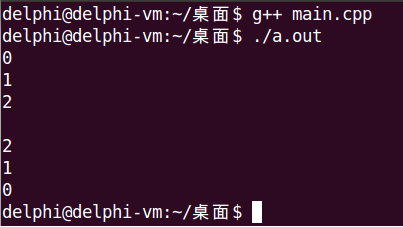
int main()
{
Test t;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
t[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cout << t[i] << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << t["3rd"] << endl;
cout << t["2nd"] << endl;
cout << t["1st"] << endl;
return 0;
}
数组类IntArray改进
IntArray.h
class IntArray
{
public:
int &operator [] (int index); //Add
IntArray &self(); //Add
};
IntArray.cpp
int &IntArray::operator [] (int index)
{
return m_pointer[index];
}
IntArray &IntArray::self()
{
return *this;
}
2. 函数操作符重载(函数对象)
- 函数操作符只能通过类的成员函数重载
- 可以定义不同参数的多个重载函数
- 函数操作符重载的本质是使用具体的类对象取代函数,也就是函数对象,函数对象具备函数调用的行为
- 函数对象用于在工程中取代函数指针
/*
* 本示例代码实现以下需求:
* - 编写一个函数,可以获得斐波那契数列每项的值
* - 每调用一次返回一个值
* - 函数可根据需要重复使用
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Fib
{
int a0;
int a1;
public:
Fib()
{
a0 = 0;
a1 = 1;
}
Fib(int n)
{
a0 = 0;
a1 = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
int t = a1;
a1 = a0 + a1;
a0 = t;
}
}
int operator () ()
{
int ret = a1;
a1 = a0 + a1;
a0 = ret;
return ret;
}
};
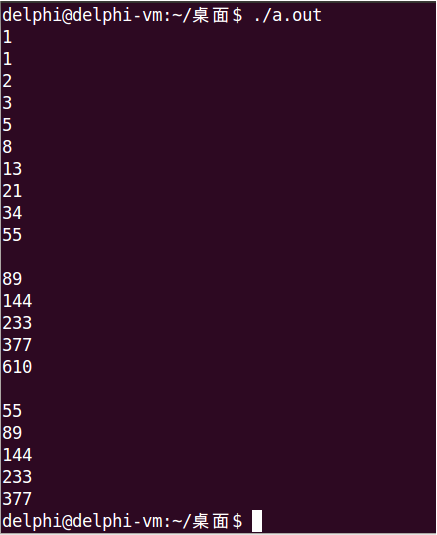
int main()
{
Fib fib;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << fib() << endl;
}
cout << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cout << fib() << endl;
}
cout << endl;
Fib fib2(10);
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cout << fib2() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3. 指针操作符重载与智能指针
指针操作符重载
指针操作符指的是->和*
- 指针操作符只能通过类的成员函数重载
- 重载函数不能使用参数,也就是说,只能定义一个重载函数
智能指针
- 利用指针操作符重载,可以实现智能指针
- 智能指针只能用来指向堆空间中的对象或者变量!!!
- 智能指针在生命周期结束时会自动释放堆空间
- 智能指针的意义在于减少开发人员的内存管理工作,最大程度上避免内存问题。
/*
* 实现智能指针类Pointer,要求如下:
* - 一片堆空间最多只能由一个指针标识
* - 禁止指针运算和指针比较
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int i;
public:
Test(int i)
{
cout << "Test(int i)" << endl;
this->i = i;
}
int value()
{
return i;
}
~Test()
{
cout << "~Test()" << endl;
}
};
class Pointer
{
private:
Test *mp;
public:
Pointer(Test *p = NULL)
{
mp = p;
}
Pointer(const Pointer &obj)
{
mp = obj.mp;
const_cast<Pointer &>(obj).mp = NULL;
}
Pointer &operator = (const Pointer &obj)
{
if (this != &obj)
{
delete mp;
mp = obj.mp;
const_cast<Pointer &>(obj).mp = NULL;
}
return *this;
}
Test *operator -> ()
{
return mp;
}
Test &operator * ()
{
return *mp;
}
bool isNull()
{
return (mp == NULL);
}
~Pointer()
{
delete mp;
}
};
int main()
{
Pointer p1 = new Test(0);
Pointer p2 = p1;
cout << p1.isNull() << endl;
cout << p2->value() << endl;
Pointer p3;
p3 = p2;
cout << p2.isNull() << endl;
cout << p3->value() << endl;
return 0;
}

4. 前置、后置操作符重载
重载实现
前置、后置操作符指的是++和--,我们以++为例进行讲解,--和++是一样的
- 全局函数和成员函数均可进行重载
- 重载前置++操作符不需要参数
- 重载后置++操作符需要一个int类型的占位参数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
Test(int i)
{
mValue = i;
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
Test &operator ++ ()
{
++mValue;
return *this;
}
Test operator ++ (int)
{
Test ret(mValue);
mValue++;
return ret;
}
};
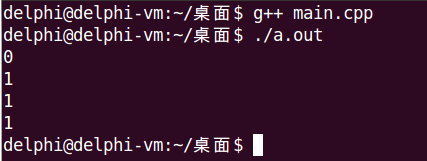
int main()
{
Test t1(0);
Test t2(0);
Test t = t1++;
cout << t.value() << endl;
cout << t1.value() << endl;
t = ++t2;
cout << t.value() << endl;
cout << t2.value() << endl;
return 0;
}
前置、后置重载的区别
- 对于基础类型的变量,前置++和后置++的效率基本相同,没有什么区别
- 对于类类型的对象,前置++的效率高于后置++,因为后置++重载会调用构造与析构函数
- 在工程中尽量使用前置++重载以提高程序效率