1、动手实验

源码
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
}
{
public Parent()
{
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
{
public Child()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
}
Parent Created
Child Created

2、思索
为什么子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须采用父类的构造方法?能不能反过来?为什么?
构造方法是用来初始化变量的,子类继承了父类的变量,如果不调用父类构造方法,则有些变量未初始化。
若先调用子类构造方法,父类里并没有子类的变量,会导致出错
3、
class A{
}
public class part1{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(new A());
}
}
运行结果为:
exercise.A@15db9742
初始化时调用了object类中的构造方法,返回输出该对象的哈希值,并用16进制表示。
4、

class Father
{
public void show()
{
System.out.println("父类");
}
}
class Son extends Father
{
public void show()
{
super.show();
System.out.println("子类");
}
}
public class test2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Son s=new Son();
s.show();
}
}
结果:
父类
子类
5、
public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
}
}
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
1. 左边的程序运行结果是什么?
2. 你如何解释会得到这样的输出?
3. 计算机是不会出错的,之所以得到这样的运行结果也是有原因的,那么从这些运行结果中,你能总结出Java的哪些语法特性?
结果
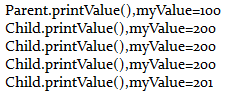
当把子类对象赋给父类对象后,父类对象调用的方法全是子类中的方法,此时parent.myValue++所改变的数值只是父类中myValue的值,所以结果仍是子类中myValue的数值200,而((Child)parent).myValue++改变的则是子类中myValue的值,所以输出201。