用户自定义函数 和存储过程是类似的,
是一组 有序的t-sql语句,udf被 预先优化和编译,并且可以作为一个单元来进行调用.
使用存储过程 时 可传入参数,传出参数.可以返回值,不过该值用于指示成功或者失败,而非返回数据.也可以返回结果集,
但是在没有将结果集插入到某种表(通常是临时表)中以供后面使用的情况下,不能在 查询中真正使用它们. 即使使用
表值 输出参数,在查询中使用结果之前,也要额外的一个步骤.
那么 UDF可以传入参数,但是不可传出参数. 但是可以返回值,和系统函数一样,可以返回标量值,这个值的好处是 不像存储过程那样只限于
整型数据类型,而是可以返回大多数sqlserver的数据类型.
下面具体介绍两种 UDF
- 返回标量的UDF
- 返回表 的UDF
返回标量的UDF
select name, (select avg(sec) from stu) as average, sec-(select avg(sec) from stu) as [Difference] from stu where SID=2
这是简单的sql语句,下面 有两个UDF代替其中的两个列
create function averages() returns int as begin return (select avg(sec) from stu); end go create function sdifference(@arg int) returns int as begin return @arg - dbo.averages(); end go select name, dbo.averages() as average, dbo.sdifference(sec) as [Difference] from stu where SID=2
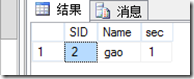
那么会在数据中看到:
执行结果和之前的sql语句是一样的.
返回表的UDF
既然UDF可以传入参数,又可以返回表,那是不是 就相当于参数化的视图……是不是听起来很让人兴奋呢.
下面创建一个简单函数:
create function getPeopleByname(@name nvarchar(30)) returns table as return (select * from stu where name = @name)
下面调用这个函数:
select * from getPeopleByname('gao')
结果如下:
下面 UDF结合 递归, 查询所有树的 节点
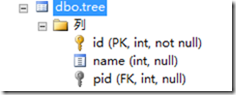
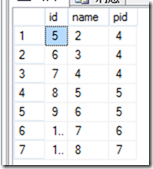
表:
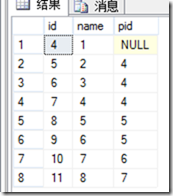
数据:
下面定义函数:
create function sss(@id as int) returns @t table ( id int not null, name int not null, pid int null ) as begin declare @lay as int; insert into @t select * from tree where pid =@id; select @lay = min(id) from tree where pid =@id; --第一次 @lay=5 while @lay is not null begin insert into @t select * from sss(@lay); select @lay=min(id) from tree where id>@lay and pid=@id end return; end go
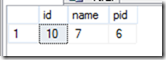
执行函数,参数 是 任意父节点 id
select * from sss(6)
执行:
select * from sss(4)
将查出 所有的子节点来.
.net调用函数:http://www.cnblogs.com/Mr-Joe/archive/2012/05/10/2494093.html