业务过程中碰到多个join引起慢SQL问题,数据量不大,但查询很慢,搜到一片BLog,参考解决。
业务过程不记录,以blog内容重现:
原SQL:
select distinct abc.pro_col1, abc.col3 from t0 p INNER JOIN t1 abc on p.id=abc.par_col2 inner join t2 s on s.col3=abc.col3 inner join t3 po on po.id=s.col4 where p.state=2 and po.state=3 order by abc.pro_col1, abc.col3;
以上SQL同:
select select distinct abc.pro_col1, abc.col3 from t0 p, t1 abc, t2 s, t3 po where p.id=abc.par_col2 and s.col3=abc.col3 and po.id=s.col4 and p.state=2 and po.state=3 order by abc.pro_col1, abc.col3;
分析优化:
从语义来看,这条SQL是在经过几个JOIN后取其中一个表的两个字段的唯一值。
但是每一次关联,都可能产生冗余的值,所以导致了结果集越来越庞大。
修改建议,每一次JOIN都输出唯一值,减少冗余。即多次JOIN导致查询结果集越来越大(笛卡儿积),可以把过滤条件放在前面。
select distinct pro_col1, col3 from ( select distinct t1.pro_col1, t1.col3, s.col4 from ( select distinct abc.pro_col1, abc.col3 from t1 abc INNER JOIN t0 p on (p.id = abc.par_col2 and p.state=2) ) t1 inner join t2 s on (s.col3 = t1.col3) ) t2 inner join t3 po on (po.id = t2.col4 and po.state=3) order by t2.pro_col1, t2.col3 ;
以下实例:
postgres=# create table rt1(id int, info text); CREATE TABLE postgres=# create table rt2(id int, info text); CREATE TABLE postgres=# create table rt3(id int, info text); CREATE TABLE postgres=# create table rt4(id int, info text); CREATE TABLE postgres=# insert into rt1 select generate_series(1,1000),'test'; INSERT 0 1000 postgres=# insert into rt2 select 1,'test' from generate_series(1,1000); INSERT 0 1000 postgres=# insert into rt3 select 1,'test' from generate_series(1,1000); INSERT 0 1000 postgres=# insert into rt4 select 1,'test' from generate_series(1,1000); INSERT 0 1000
对比:
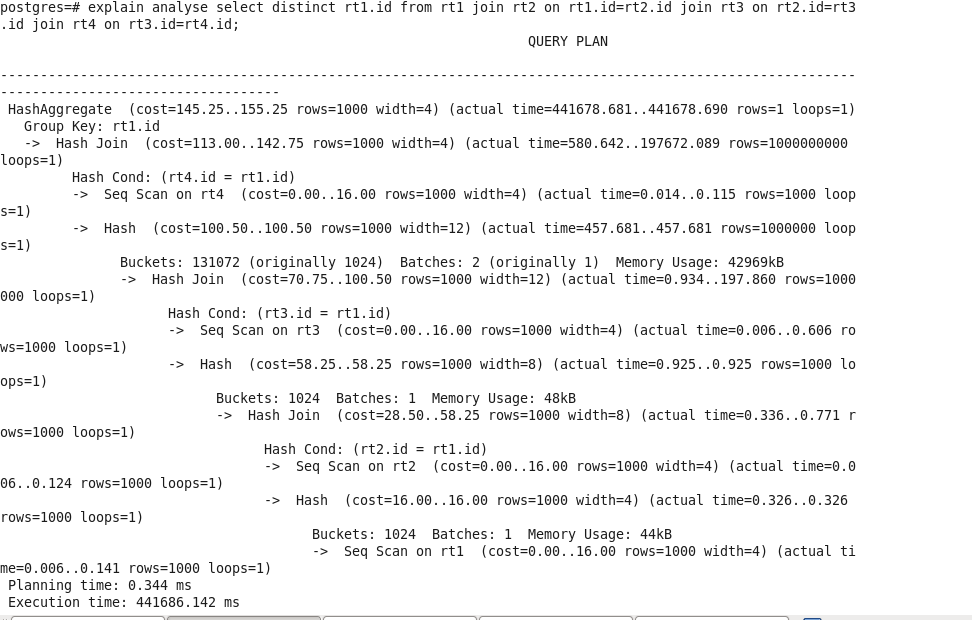
优化后查询:
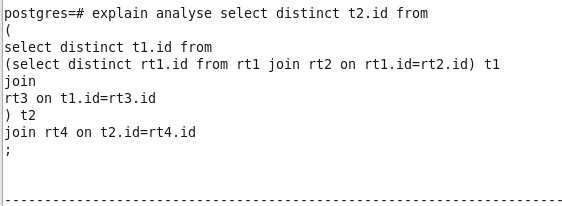

从执行时间可以看到,优化后的速度何止是快。