pandas官方文档:https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/?v=20190307135750
pandas基于Numpy,可以看成是处理文本或者表格数据。
pandas中有两个主要的数据结构,其中Series数据结构类似于Numpy中的一维数组,DataFrame类似于多维表格数据结构。
pandas是python数据分析的核心模块。它主要提供了五大功能:
- 支持文件存取操作,支持数据库(sql)、html、json、pickle、csv(txt、excel)、sas、stata、hdf等。
- 支持增删改查、切片、高阶函数、分组聚合等单表操作,以及和dict、list的互相转换。
- 支持多表拼接合并操作。
- 支持简单的绘图操作。
- 支持简单的统计分析操作。
一、Series数据结构
Series是一种类似于一维数组的对象,由一组数据和一组与之相关的数据标签(索引)组成。
Series比较像列表(数组)和字典的结合体
import numpy as np import pandas as pd df = pd.Series(0, index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']) print(df) # a 0 # b 0 # c 0 # d 0 # dtype: int64 print(df.values) # 值 # [0 0 0 0] print(df.index) # 索引 # Index(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], dtype='object')
1、Series的创建
import numpy as np import pandas as pd df = pd.Series(np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, np.nan]), index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']) # 1、从ndarray创建Series print(df) # a 1.0 # b 2.0 # c 3.0 # d 4.0 # e NaN # dtype: float64 df = pd.Series({'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 4, 'e': np.nan}) # 2、也可以从字典创建Series dates = pd.date_range('20190101', periods=6, freq='M') print(type(dates)) # <class 'pandas.core.indexes.datetimes.DatetimeIndex'>
print(dates) # DatetimeIndex(['2019-01-31', '2019-02-28', '2019-03-31', '2019-04-30', # '2019-05-31', '2019-06-30'], # dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='M') df=pd.Series(0,index=dates) # 3、时间序列索引 print(df) # 2019-01-31 0 # 2019-02-28 0 # 2019-03-31 0 # 2019-04-30 0 # 2019-05-31 0 # 2019-06-30 0 # Freq: M, dtype: int64
产生时间对象数组:date_range参数详解:
- start:开始时间
- end:结束时间
- periods:时间长度
- freq:时间频率,默认为'D',可选H(our),W(eek),B(usiness),S(emi-)M(onth),(min)T(es), S(econd), A(year),…
2、Series属性
print(df ** 2) # 3、与标量运算 # a 1.0 # b 4.0 # c 9.0 # d 16.0 # e NaN # dtype: float64 print(df + df) # 4、两个Series运算
# a 2.0 # b 4.0 # c 6.0 # d 8.0 # e NaN # dtype: float64 print(df[0] ) # 5、数字索引; 1.0
print(df[[0, 1, 2]]) # 行索引 # a 1.0 # b 2.0 # c 3.0 # dtype: float64
print(df['a'] ) # 6、键索引(行标签) ;1.0
print(df[['b','c']])
print('a' in df) # 7、in运算;True print(df[0:2] ) # 8、切片 # a 1.0 # b 2.0 # dtype: float64 print(np.sin(df)) # 9、通用函数 # a 0.841471 # b 0.909297 # c 0.141120 # d -0.756802 # e NaN # dtype: float64 print(df[df > 1] ) # 10、布尔值过滤 # b 2.0 # c 3.0 # d 4.0 # dtype: float64
2、Series缺失数据处理
df = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, np.nan], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']) print(df) # a 1.0 # b 2.0 # c 3.0 # d 4.0 # e NaN # dtype: float64 print(df.dropna() ) # 1、过滤掉值为NaN的行 # a 1.0 # b 2.0 # c 3.0 # d 4.0 # dtype: float64 print(df.fillna(5) ) # 2、用指定值填充缺失数据 # a 1.0 # b 2.0 # c 3.0 # d 4.0 # e 5.0 # dtype: float64 print(df.isnull() ) # 3、返回布尔数组,缺失值对应为True # a False # b False # c False # d False # e True # dtype: bool print(df.notnull() ) # 4、返回布尔数组,缺失值对应为False # a True # b True # c True # d True # e False # dtype: bool
二、DataFrame数据结构
DataFrame是一个表格型的数据结构,含有一组有序的列。
DataFrame可以被看做是由Series组成的字典,并且共用一个索引。
1、DataFrame的创建
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((3, 4))) # 创建一个三行四列的DataFrame print(df1) # 0 1 2 3 # 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 # 1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 # 2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
dates = pd.date_range('20190101', periods=6, freq='M') np.random.seed(1) arr = 10 * np.random.randn(6, 4) print(arr) # [[ 16.24345364 -6.11756414 -5.28171752 -10.72968622] # [ 8.65407629 -23.01538697 17.44811764 -7.61206901] # [ 3.19039096 -2.49370375 14.62107937 -20.60140709] # [ -3.22417204 -3.84054355 11.33769442 -10.99891267] # [ -1.72428208 -8.77858418 0.42213747 5.82815214] # [-11.00619177 11.4472371 9.01590721 5.02494339]] df = pd.DataFrame(arr, index=dates, columns=['c1', 'c2', 'c3', 'c4']) # 自定义index和column print(df)
# c1 c2 c3 c4
# 2019-01-31 16.243454 -6.117564 -5.281718 -10.729686
# 2019-02-28 8.654076 -23.015387 17.448118 -7.612069
# 2019-03-31 3.190391 -2.493704 14.621079 -20.601407
# 2019-04-30 -3.224172 -3.840544 11.337694 -10.998913
# 2019-05-31 -1.724282 -8.778584 0.422137 5.828152
# 2019-06-30 -11.006192 11.447237 9.015907 5.024943
2、DataFrame属性
print(df.dtypes) # 1、查看数据类型 # 0 float64 # 1 float64 # 2 float64 # 3 float64 # dtype: object print(df.index) # 2、查看行索引 # DatetimeIndex(['2019-01-31', '2019-02-28', '2019-03-31', '2019-04-30', # '2019-05-31', '2019-06-30'], # dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='M') print(df.columns) # 3、查看各列的标签 # Index(['c1', 'c2', 'c3', 'c4'], dtype='object') print(df.values) # 4、查看数据框内的数据,也即不含行标签和列头的数据 # [[ 16.24345364 -6.11756414 -5.28171752 -10.72968622] # [ 8.65407629 -23.01538697 17.44811764 -7.61206901] # [ 3.19039096 -2.49370375 14.62107937 -20.60140709] # [ -3.22417204 -3.84054355 11.33769442 -10.99891267] # [ -1.72428208 -8.77858418 0.42213747 5.82815214] # [-11.00619177 11.4472371 9.01590721 5.02494339]] print(df.describe()) # 5、查看数据每一列的极值,均值,中位数,只可用于数值型数据 # c1 c2 c3 c4 # count 6.000000 6.000000 6.000000 6.000000 # mean 2.022213 -5.466424 7.927203 -6.514830 # std 9.580084 11.107772 8.707171 10.227641 # min -11.006192 -23.015387 -5.281718 -20.601407 # 25% -2.849200 -8.113329 2.570580 -10.931606 # 50% 0.733054 -4.979054 10.176801 -9.170878 # 75% 7.288155 -2.830414 13.800233 1.865690 # max 16.243454 11.447237 17.448118 5.828152 print(df.T) # 6、transpose转置,也可用T来操作 # 2019-01-31 2019-02-28 2019-03-31 2019-04-30 2019-05-31 2019-06-30 # c1 16.243454 8.654076 3.190391 -3.224172 -1.724282 -11.006192 # c2 -6.117564 -23.015387 -2.493704 -3.840544 -8.778584 11.447237 # c3 -5.281718 17.448118 14.621079 11.337694 0.422137 9.015907 # c4 -10.729686 -7.612069 -20.601407 -10.998913 5.828152 5.024943 print(df.sort_index(axis=0)) # 7、排序,axis=0 可按行标签排序输出; 按行标签][2019-01-01, 2019-01-02...]从大到小排序 # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 2019-01-31 16.243454 -6.117564 -5.281718 -10.729686 # 2019-02-28 8.654076 -23.015387 17.448118 -7.612069 # 2019-03-31 3.190391 -2.493704 14.621079 -20.601407 # 2019-04-30 -3.224172 -3.840544 11.337694 -10.998913 # 2019-05-31 -1.724282 -8.778584 0.422137 5.828152 # 2019-06-30 -11.006192 11.447237 9.015907 5.024943 print(df.sort_index(axis=1)) # 7、排序,axis=1 可按列头标签排序输出;按列标签[c1, c2, c3, c4从大到小排序 # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 2019-01-31 16.243454 -6.117564 -5.281718 -10.729686 # 2019-02-28 8.654076 -23.015387 17.448118 -7.612069 # 2019-03-31 3.190391 -2.493704 14.621079 -20.601407 # 2019-04-30 -3.224172 -3.840544 11.337694 -10.998913 # 2019-05-31 -1.724282 -8.778584 0.422137 5.828152 # 2019-06-30 -11.006192 11.447237 9.015907 5.024943 print(df.sort_values(by='c2')) # 8、按数据值来排序 ;按c2列的值从大到小排序 # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 2019-02-28 8.654076 -23.015387 17.448118 -7.612069 # 2019-05-31 -1.724282 -8.778584 0.422137 5.828152 # 2019-01-31 16.243454 -6.117564 -5.281718 -10.729686 # 2019-04-30 -3.224172 -3.840544 11.337694 -10.998913 # 2019-03-31 3.190391 -2.493704 14.621079 -20.601407 # 2019-06-30 -11.006192 11.447237 9.015907 5.024943
3、DataFrame取值
print(df['c2']) # 1、 通过columns标签取值 # 2019-01-31 -6.117564 # 2019-02-28 -23.015387 # 2019-03-31 -2.493704 # 2019-04-30 -3.840544 # 2019-05-31 -8.778584 # 2019-06-30 11.447237 # Freq: M, Name: c2, dtype: float64 print(df[['c2', 'c3']]) # c2 c3 # 2019-01-31 -6.117564 -5.281718 # 2019-02-28 -23.015387 17.448118 # 2019-03-31 -2.493704 14.621079 # 2019-04-30 -3.840544 11.337694 # 2019-05-31 -8.778584 0.422137 # 2019-06-30 11.447237 9.015907 print(df[0:3]) # 2、 通过columns索引取值 # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 2019-01-31 16.243454 -6.117564 -5.281718 -10.729686 # 2019-02-28 8.654076 -23.015387 17.448118 -7.612069 # 2019-03-31 3.190391 -2.493704 14.621079 -20.601407 print(df.loc['20200228':'20200430']) # 3、loc 通过行标签取值: # c1 c2 c3 c3 # 2020-02-29 8.654076 -23.015387 17.448118 -7.612069 # 2020-03-31 3.190391 -2.493704 14.621079 -20.601407 # 2020-04-30 -3.224172 -3.840544 11.337694 -10.998913 print(df.iloc[1:3]) # 4、iloc 通过行索引选择数据,取第二行到三行。 # c1 c2 c3 c3 # 2020-02-29 8.654076 -23.015387 17.448118 -7.612069 # 2020-03-31 3.190391 -2.493704 14.621079 -20.601407 print(df.iloc[2, 1]) # 第三行第二列值:-2.493703754774101 print(df.iloc[1:4, 1:4]) # 第 2-4行与第2-4列: # c2 c3 c4 # 2019-02-28 -23.015387 17.448118 -7.612069 # 2019-03-31 -2.493704 14.621079 -20.601407 # 2019-04-30 -3.840544 11.337694 -10.998913
print(df['c3'] > 10) # 5、 使用逻辑判断取值
# 2020-01-31 False
# 2020-02-29 True
# 2020-03-31 True
# 2020-04-30 True
# 2020-05-31 False
# 2020-06-30 False
# Freq: M, Name: c3, dtype: boolprint(df[df['c3'] > 10]) # 5、 使用逻辑判断取值# c1 c2 c3 c4
# 2020-02-29 8.654076 -23.015387 17.448118 -7.612069
# 2020-03-31 3.190391 -2.493704 14.621079 -20.601407
# 2020-04-30 -3.224172 -3.840544 11.337694 -10.998913
print(df[(df['c1'] > 0) & (df['c2'] > -8)]) # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 2019-01-31 16.243454 -6.117564 -5.281718 -10.729686 # 2019-03-31 3.190391 -2.493704 14.621079 -20.601407
5、DataFrame值替换
df.iloc[1:3]=5 # 将2-3行的值设为5 print(df) # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 2020-01-31 16.243454 -6.117564 -5.281718 -10.729686 # 2020-02-29 5.000000 5.000000 5.000000 5.000000 # 2020-03-31 5.000000 5.000000 5.000000 5.000000 # 2020-04-30 -3.224172 -3.840544 11.337694 -10.998913 # 2020-05-31 -1.724282 -8.778584 0.422137 5.828152 df.iloc[0:3, 0:2] = 0 # 将1-3行1-2列的值设为0 print(df) # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 2019-01-31 0.000000 0.000000 -5.281718 -10.729686 # 2019-02-28 0.000000 0.000000 17.448118 -7.612069 # 2019-03-31 0.000000 0.000000 14.621079 -20.601407 # 2019-04-30 -3.224172 -3.840544 11.337694 -10.998913 # 2019-05-31 -1.724282 -8.778584 0.422137 5.828152 # 2019-06-30 -11.006192 11.447237 9.015907 5.024943 # 针对行做处理 df[df['c3'] > 10] = 100 # 将C3列的大于10的行数值设为0 print(df) # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 2019-01-31 0.000000 0.000000 -5.281718 -10.729686 # 2019-02-28 100.000000 100.000000 100.000000 100.000000 # 2019-03-31 100.000000 100.000000 100.000000 100.000000 # 2019-04-30 100.000000 100.000000 100.000000 100.000000 # 2019-05-31 -1.724282 -8.778584 0.422137 5.828152 # 2019-06-30 -11.006192 11.447237 9.015907 5.024943 # 针对行做处理 df = df.astype(np.int32) df[df['c3'].isin([100])] = 1000 # 将C3列的等于100的行数值设为1000 print(df) # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 2019-01-31 0 0 -5 -10 # 2019-02-28 1000 1000 1000 1000 # 2019-03-31 1000 1000 1000 1000 # 2019-04-30 1000 1000 1000 1000 # 2019-05-31 -1 -8 0 5 # 2019-06-30 -11 11 9 5
6、处理丢失数据
print(df.isnull()) # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 0 False True False False # 1 False False False False # 2 False False True False # 3 False False False False # 4 False False False False # 5 False False False True # 6 True True True True print(df.isnull().sum()) # 1、通过在isnull()方法后使用sum()方法即可获得该数据集某个特征含有多少个缺失值 # c1 1 # c2 2 # c3 2 # c4 2 # dtype: int64 print(df.dropna(axis=0)) # 2、axis=0删除有NaN值的行 # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 # 3 7.0 3.2 4.7 1.4 # 4 6.4 3.2 4.5 1.5 print(df.dropna(axis=1)) # 3、axis=1删除有NaN值的列 # Empty DataFrame # Columns: [] # Index: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] print(df.dropna(how='all')) # 4、删除全为NaN值得行或列 # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 0 5.1 NaN 1.4 0.2 # 1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 # 2 4.7 3.2 NaN 0.2 # 3 7.0 3.2 4.7 1.4 # 4 6.4 3.2 4.5 1.5 # 5 6.9 3.1 4.9 NaN print(df.dropna(thresh=4)) #5、 保留至少有4个非NaN数据的行,删除行不为4个值的, # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 # 3 7.0 3.2 4.7 1.4 # 4 6.4 3.2 4.5 1.5 print(df.dropna(subset=['c2'])) # 6、删除c2中有NaN值的行 # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 # 2 4.7 3.2 NaN 0.2 # 3 7.0 3.2 4.7 1.4 # 4 6.4 3.2 4.5 1.5 # 5 6.9 3.1 4.9 NaN print(df.fillna(value=10)) # 7、用指定值填充nan值 # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 0 5.1 10.0 1.4 0.2 # 1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 # 2 4.7 3.2 10.0 0.2 # 3 7.0 3.2 4.7 1.4 # 4 6.4 3.2 4.5 1.5 # 5 6.9 3.1 4.9 10.0 # 6 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0
7、合并数据
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((3, 4))) print(df1) # 0 1 2 3 # 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 # 1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 # 2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3, 4))) print(df2) # 0 1 2 3 # 0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 # 1 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 # 2 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 print(pd.concat((df1, df2), axis=0)) # 1、axis=0合并行 # 0 1 2 3 # 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 # 1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 # 2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 # 0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 # 1 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 # 2 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 print(pd.concat((df1, df2), axis=1)) # 2、axis=1合并列 # 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 # 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 # 1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 # 2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 print(df1.append(df2)) # append只能合并行
# 0 1 2 3 # 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 # 1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 # 2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 # 0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 # 1 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 # 2 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
二、读取CSV文件
import pandas as pd from io import StringIO
test_data = ''' 5.1,,1.4,0.2 4.9,3.0,1.4,0.2 4.7,3.2,,0.2 7.0,3.2,4.7,1.4 6.4,3.2,4.5,1.5 6.9,3.1,4.9, ,,, ''' test_data = StringIO(test_data) df = pd.read_csv(test_data, header=None) df.columns = ['c1', 'c2', 'c3', 'c4'] print(df) # c1 c2 c3 c4 # 0 5.1 NaN 1.4 0.2 # 1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 # 2 4.7 3.2 NaN 0.2 # 3 7.0 3.2 4.7 1.4 # 4 6.4 3.2 4.5 1.5 # 5 6.9 3.1 4.9 NaN # 6 NaN NaN NaN NaN
三、导入导出数据
pandas的读写Excel需要依赖xlrd模块,所以我们需要去安装一下, 命令:pip install xlrd
使用df = pd.read_excel(filename)读取文件,使用df.to_excel(filename)保存文件。
1、读取文件导入数据
df = pd.read_excel(filename)
读取文件导入数据函数主要参数:
- sep :指定分隔符,可用正则表达式如's+'
- header=None :指定文件无行名
- name :指定列名
- index_col :指定某列作为索引
- skip_row :指定跳过某些行
- na_values :指定某些字符串表示缺失值
- parse_dates :指定某些列是否被解析为日期,布尔值或列表
2、写入文件导出数据
df.to_excel(filename)
写入文件函数的主要参数:
- sep 分隔符
- na_rep 指定缺失值转换的字符串,默认为空字符串
- header=False 不保存列名
- index=False 不保存行索引
- cols 指定输出的列,传入列表
3、实例
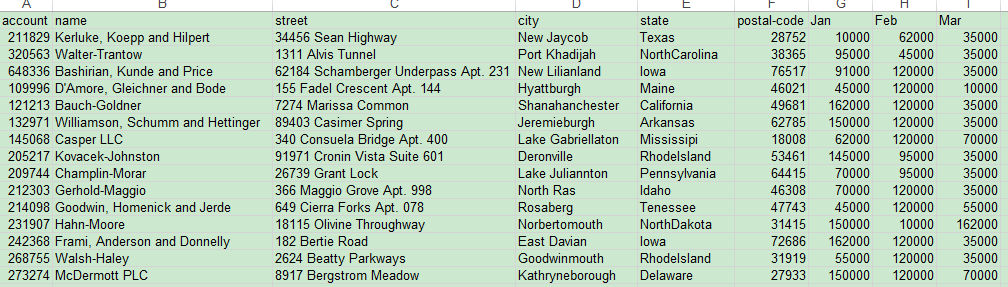
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.read_excel("http://pbpython.com/extras/excel-comp-data.xlsx") print(df.head()) print(len(df.index)) # 行数 (不包含表头,且一下均如此) print(df.index.values) # 行索引 print(len(df.columns)) # 列数 print(df.columns.values) # 列索引
data = df.loc[0].values # 表示第0行数据 data = df.loc[[1, 2]].values # 读取多行数据(这里是第1行和第2行) data = df.iloc[:, 1].values # 读第1列数据 data = df.iloc[:, [1, 2]].values # 读取多列数据(这里是第1列和第2列) data = df.iloc[1, 2] # 读取指定单元格数据(这里是第1行第一列数据) data = df.iloc[[1, 2], [1, 2]].values # 读取多行多列数据(第1,2行1,2列的数据) # 任务:输出满足成绩大于等于90的数据 temp = [] for i in range(len(df.index.values)): if df.iloc[i, 3] >= 90: temp.append(df.iloc[i].values) df2 = pd.DataFrame(data=temp, columns=df.columns.values)
writer = pd.ExcelWriter('out_test.xlsx')# 不写index会输出索引
df2.to_excel(writer, 'Sheet', index=False)
writer.save()实例:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/e664b9a3bf70
https://www.jianshu.com/p/66d2e68b726f
https://www.cnblogs.com/xhuangtao/p/11963279.html
四、pandas读取json文件
import pandas as pd strtext = '[{"ttery":"min","issue":"20130801-3391","code":"8,4,5,2,9","code1":"297734529","code2":null,"time":1013395466000}, {"ttery":"min","issue":"20130801-3390","code":"7,8,2,1,2","code1":"298058212","code2":null,"time":1013395406000}, {"ttery":"min","issue":"20130801-3389","code":"5,9,1,2,9","code1":"298329129","code2":null,"time":1013395346000}, {"ttery":"min","issue":"20130801-3388","code":"3,8,7,3,3","code1":"298588733","code2":null,"time":1013395286000}, {"ttery":"min","issue":"20130801-3387","code":"0,8,5,2,7","code1":"298818527","code2":null,"time":1013395226000}]' df = pd.read_json(strtext, orient='records') print(df) # ttery issue code code1 code2 time # 0 min 20130801-3391 8,4,5,2,9 297734529 NaN 1013395466000 # 1 min 20130801-3390 7,8,2,1,2 298058212 NaN 1013395406000 # 2 min 20130801-3389 5,9,1,2,9 298329129 NaN 1013395346000 # 3 min 20130801-3388 3,8,7,3,3 298588733 NaN 1013395286000 # 4 min 20130801-3387 0,8,5,2,7 298818527 NaN 1013395226000
df = pd.read_json(strtext, orient='records') df.to_excel('pandas处理json.xlsx', index=False, columns=["ttery", "issue", "code", "code1", "code2", "time"])
orient参数的五种形式
orient是表明预期的json字符串格式。orient的设置有以下五个值:
1.'split' : dict like {index -> [index], columns -> [columns], data -> [values]}
这种就是有索引,有列字段,和数据矩阵构成的json格式。key名称只能是index,columns和data。
s = '{"index":[1,2,3],"columns":["a","b"],"data":[[1,3],[2,8],[3,9]]}' df = pd.read_json(s, orient='split') print(df) # a b # 1 1 3 # 2 2 8 # 3 3 9
2.'records' : list like [{column -> value}, ... , {column -> value}]
这种就是成员为字典的列表。如我今天要处理的json数据示例所见。构成是列字段为键,值为键值,每一个字典成员就构成了dataframe的一行数据。
strtext = '[{"ttery":"min","issue":"20130801-3391","code":"8,4,5,2,9","code1":"297734529","code2":null,"time":1013395466000}, {"ttery":"min","issue":"20130801-3390","code":"7,8,2,1,2","code1":"298058212","code2":null,"time":1013395406000}]' df = pd.read_json(strtext, orient='records') print(df) # ttery issue code code1 code2 time # # 0 min 20130801-3391 8,4,5,2,9 297734529 NaN 1013395466000 # # 1 min 20130801-3390 7,8,2,1,2 298058212 NaN 1013395406000
3.'index' : dict like {index -> {column -> value}}
以索引为key,以列字段构成的字典为键值。如:
s = '{"0":{"a":1,"b":2},"1":{"a":9,"b":11}}' df = pd.read_json(s, orient='index') print(df) # a b # 0 1 2 # 1 9 11
4.'columns' : dict like {column -> {index -> value}}
这种处理的就是以列为键,对应一个值字典的对象。这个字典对象以索引为键,以值为键值构成的json字符串。如下图所示:
s = '{"a":{"0":1,"1":9},"b":{"0":2,"1":11}}' df = pd.read_json(s, orient='columns') print(df) # a b # 0 1 2 # 1 9 11
5.'values' : just the values array。
values这种我们就很常见了。就是一个嵌套的列表。里面的成员也是列表,2层的。
s = '[["a",1],["b",2]]' df = pd.read_json(s, orient='values') print(df) # 0 1 # 0 a 1 # 1 b 2
五、pandas读取sql语句
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import pymysql def conn(sql): # 连接到mysql数据库 conn = pymysql.connect( host="localhost", port=3306, user="root", passwd="123", db="db1", ) try: data = pd.read_sql(sql, con=conn) return data except Exception as e: print("SQL is not correct!") finally: conn.close() sql = "select * from test1 limit 0, 10" # sql语句 data = conn(sql) print(data.columns.tolist()) # 查看字段 print(data) # 查看数据